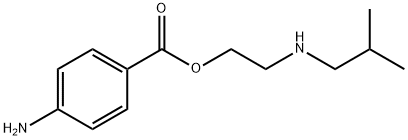
Butethamine
- CAS No.
- 2090-89-3
- Chemical Name:
- Butethamine
- Synonyms
- Butethamine;2-(2-methylpropylamino)ethyl 4-aminobenzoate;2-(2-methylpropylamino)ethyl 4-azanylbenzoate;p-Aminobenzoic acid 2-(isobutylamino)ethyl ester;4-aminobenzoic acid 2-(isobutylamino)ethyl ester;Ethanol, 2-[(2-methylpropyl)amino]-, 1-(4-aminobenzoate)
- CBNumber:
- CB51178187
- Molecular Formula:
- C13H20N2O2
- Molecular Weight:
- 236.31
- MDL Number:
- MOL File:
- 2090-89-3.mol
| Boiling point | 378.78°C (rough estimate) |
|---|---|
| Density | 1.0604 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5430 (estimate) |
| FDA UNII | F8E12S0YYS |
Butethamine Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Originator
Monoceine,Novocol,US,1941
Definition
ChEBI: Butethamine is a benzoate ester.
Manufacturing Process
The preparation of the normal butyl analog is as follows:
10 g of isobutylaminoethanol, 16 g of p-nitrobenzoyl chloride and 5 g of
sodium hydroxide in 175 cc of water were allowed to react. The temperature
was maintained between 30°-40°C during reaction. The reaction mixture was
extracted with ether, the ether evaporated, and the resultant oil washed with
water to remove any unreacted secondary amino alcohol and then dried. The
yield was 21 g or 91% of theory. The compound responded positively when
tested for the presence of the amine configuration and also the nitro group.
The yellow viscous oil which was formed was isobutylaminoethyl p-nitrobenzoate. 20 g of this latter material was directly reduced with 15 g of tin
and 50 cc of concentrated hydrochloric acid. The temperature of the reduction
was controlled by addition from time to time of small quantities of cold water
to maintain the temperature at or near 70°C. When the reaction was
completed 150 cc of sodium hydroxide was added and the solution then
cooled to 15°C. The oil which gradually formed combined with undissolved tin
to form a pasty mass which soon settled. The supernatant liquid was decanted
and the residue washed two or three times with water to remove all traces of
alkali. The oily mass, freed from most of its water, was then extracted with
ether and filtered. The filtrate was evaporated to dryness and the yield of the
base obtained was 13 g or 73.5% of theory. In order to get the melting point
of the base, the monohydrochloride was first formed and purified, then the
hydrochloride was dissolved in water and just neutralized with ammonia water.
The colorless oil formed soon crystallized into a white solid, which after
filtration and air drying, had a melting point of 74°-74.5°C. The hydrochloride
was made when the oily base was dissolved in propyl alcohol and the
calculated quantity of aqueous hydrochloric acid added to form the
monohydrochloride of this compound. After repeated recrystallizations, a white
needle crystal was formed which had a melting point at 146°C.
Therapeutic Function
Local anesthetic
Butethamine Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of2
Preparation Products
Butethamine Suppliers
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shaanxi Didu New Materials Co. Ltd | +86-89586680 +86-13289823923 | 1026@dideu.com | China | 8739 | 58 |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Shaanxi Didu New Materials Co. Ltd | 58 |