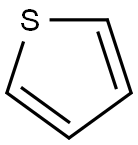
Thiophene
- CAS No.
- 110-02-1
- Chemical Name:
- Thiophene
- Synonyms
- Thiophen;CYP3A;THIOFURAN;HLP;cp34;thiophenone;Thiacyclopentadiene;THIOPHENE FOR SYNTHESIS 5 ML;Thiophene, benzene free, extra pure, 99.5%;CP33
- CBNumber:
- CB5852798
- Molecular Formula:
- C4H4S
- Molecular Weight:
- 84.14
- MDL Number:
- MFCD00005413
- MOL File:
- 110-02-1.mol
| Melting point | -38 °C (lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 84 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1.051 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor density | 2.9 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 40 mm Hg ( 12.5 °C) |
| refractive index |
n |
| Flash point | -9 °C |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | Miscible with carbon tetrachloride, heptane, pyrimidine, dioxane, toluene, and many organic solvents (quoted, Keith and Walters, 1992) |
| form | powder |
| color | Clear |
| Specific Gravity | 1.06 |
| Odor | at 0.10 % in propylene glycol. alliaceous garlic |
| Odor Type | sulfurous |
| Odor Threshold | 0.00056ppm |
| explosive limit | 1.5-12.5%(V) |
| Water Solubility | INSOLUBLE |
| Merck | 14,9353 |
| BRN | 103222 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 2.33 and 2.70 in distilled water and seawater, respectively (Przyjazny et al., 1983) |
| Dielectric constant | 9.3(20℃) |
| Stability | Stable. Highly flammable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, nitrates. |
| LogP | 1.81-1.86 at pH10 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 110-02-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EWG's Food Scores | 1 |
| FDA UNII | SMB37IQ40B |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Thiophene(110-02-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Thiophene (110-02-1) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS02,GHS07,GHS08 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H225-H302-H319-H340-H350-H412 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P202-P210-P273-P301+P312-P305+P351+P338-P308+P313 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | F,Xn,Xi,T | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 45-46-11-20/21/22-41-52/53-36-20/22-37/38-22-48/20/21/22 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 53-26-39-45-61-36/37/39-16-36 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 2414 3/PG 2 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | XM7350000 | |||||||||
| Autoignition Temperature | 743 °F | |||||||||
| Hazard Note | Irritant/Highly Flammable | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 3 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | II | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29349990 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in Rabbit: 1400 mg/kg | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Thiophene price More Price(25)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich | 8.08157 | Thiophene for synthesis | 110-02-1 | 5ml | $31.4 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich | 8.08157 | Thiophene for synthesis | 110-02-1 | 250ML | $72.4 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich | SAB5300118 | Monoclonal Anti-CYP3A4 antibody produced in mouse clone 3H8, purified immunoglobulin, buffered aqueous solution | 110-02-1 | 100μG | $524 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich | 8.08157 | Thiophene for synthesis | 110-02-1 | 1L | $212 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich | 06914 | Thiophene analytical standard | 110-02-1 | 1mL | $20.6 | 2022-05-15 | Buy |
Thiophene Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Heterocyclic compound
Thiophene is five-member heterocyclic compounds containing a sulfur atom and is presented at coal tar crude benzene at small amounts. It is a kind of colorless liquid having similar order as benzene aromatic with the boiling point being 84 °C. It is insoluble in water, and can be mixed with ethanol, ethyl ether, acetone, benzene, carbon tetrachloride, heptane, pyridine, and 1,4-dioxane. It is flammable, and has a high heat resistance without being decomposed when being heated to 850 °C. It is not polymerized under acidic conditions, nor does it be decomposed and be susceptible to oxidation. It also has moderate toxicity. The 5 atoms in thiophene ring belong to sp2 hybrid and located in the same plane. The occupied p-orbital of a pair of non-sharing electrons in the sulfur atom is parallel and overlapped with that of occupies the 4 carbon atoms which form 5 atoms/6 electrons closing conjugated system and thus having aromaticity. Thiophene is more prone to have electrophilic substitution reaction than benzene with electrophilic substitution mainly occurring in α-position (2-position or 5-position). An important derivative of thiophene is biotin which can have sulfonation reaction with concentrated sulfuric acid at room temperature with producing 2-thiophene acid which can be dissolved in sulfuric acid. Thereby, people often use this method to remove the thiophene in the crude benzene.
Thiophene can be used in the production of various kinds of dyes, perfumes, thermal shock resistant plastic, highly active solvent, stimulating hormone, insecticide, brightening agents, cosmetics and bio-activating substances and vitamins, anesthetics and antibiotics. It can also be used as the raw materials of preparing a broad spectrum anthelmintic pyrantel as well as antibacterial drugs cephalosporin I and II. Moreover, it can be used for further preparation of solvents such as sulfolane. Using chemical or electrochemical method can enable the synthesis of polythiophene, and having a conductivity of 2~10.6 × 103S/m after doping, and thus is a kind of conductive polymer materials of potential application.
Benzol Refining Products
Although thiophene is able to be chemically synthesized, the cost is too high. Thiophene is presented inside both shale oil and coal tar. The waste acid of crude benzol fraction resulted from the coal tar washed by concentrated sulfuric acid can be used as raw materials. It first undergoes hydrolysis in 110~150 °C, and then separated and purified to obtain thiophene. Thiophene is mainly presented in light benzene purified from the pre-rectification of crude benzene. When the light benzene was refined by adding hydrogen, thiophene is destroyed. When using light benzene acid for refining it, most of thiophene is polymerized with unsaturated compounds into tar-like substance with only a small amount of thiophene taking reaction with sulfuric acid for generating thiophene sulfonic acid which is easily extracted, thus greatly reducing the yield of thiophene.
When using light benzene acid for refining, thiophene is reacted together with sulfuric acid to generate thiophene-sulfonic acid which is dissolved in wasting sulfuric acid, clarify the sulfuric acid, remove the tarry substance, followed by hydrolysis distillation. The distilled condensed stuff was cooled and separated to obtain the thiophene-containing and benzenoid hydrocarbons-containing distilled crude oil. The crude distilled oil was neutralized by adding alkaline to be neutral or slightly basic with a distillation column (with theoretical plate number of 30 to 40) for distillation to obtain thiophene product (with thiophene content higher than 90%). During the rectification process, separate out the middle distilled fraction and reflux it back into the crude oil distillate. After distilling all the amount of thiophene, people can also distill out product of inter-xylene product (with content being higher than 95%) from the waste residue.
For this method of extraction of thiophene from waste sulfuric acid, thiophene extraction efficiency from crude benzene is low and demanding using hydrolysis distillation equipment with corrosion resistant materials. In order to increase the extraction efficiency of thiophene, many countries are studying new ways of thiophene extraction method from crude benzene, from which the relative successful method is extraction & rectification extraction method for thiophene (ER method). The approach is adding a suitable extraction agent to thiophene containing benzene in order to increase the relative volatility between benzene and thiophene in order to separate out the thiophene from rectification. In many kinds of extracting agents, α-pyrrolidone and N-methylpyrrolidone (NMP) have a strong dissolving ability to although this extraction agent is only with moderate selectivity. However, it has good chemical property and thermal stability, and is easy for recycling. The price is relatively cheap. All the above points make it be an appropriate extraction agent.
The above information is edited by the Chemicalbook of Dai Xiongfeng.
Maximal allowed amount and maximal allowed residue

Chemical Properties
It is colorless, transparent liquid with an aromatic odor similar to benzene. It is soluble in alcohol, ether and other organic solvents but insoluble in water.
Uses
1. It is used not only for the synthesis of cephalosporin drugs, but also for the production of dyes, synthetic resins, solvents, etc.
2. It is used for making drugs and plasticizers; thiophene is an important organic chemical raw material which has broad range of applications. It is mainly used for dyes, medicines and resins. It can be used for synthesis of new broad-spectrum cephalosporin antibiotic, and is an important pharmaceutical and chemical additive. It can also be applied for the manufacture of color films and trick photography and synthesizing a complicated reagent used for the extraction and separation of uranium and other metals.
3. It is used as the raw material and a plasticizer of medicine, dyes, and plastics.
4. It is mainly used as the intermediates of pharmaceutical industry used for preparing thiophene acetic pyridine, and pyrantel. It can also been used as a raw material for synthesizing resin and dye industry. It is also be used as an organic solvent. As a chemical reagent, it is used as a standard reagent for chromatography analysis.
5. It is used as a solvent, standard reference agent for chromatography analysis, and also for organic synthesis.
6. Thiophene can be used for the manufacture of dyes, pharmaceuticals and resin; used for the synthesis of new broad-spectrum cephalosporin antibiotics; used for the manufacture of color films and trick photography; used for the synthesis of some complex reagent; it is an important intermediate in the synthesis of Bakelite and resins. Thiophene itself is a good dewaxing solvents and paint cleaners. The derivatives of thiophene have a variety of pharmacological activities. There are a variety of thiophene-azo dyes with excellent performance. The sulfonylurea derivatives of thiophene are new herbicides of ultra-efficient as well as low toxicity. Other derivatives can also be used as insecticides, fungicides, and animal and plant growth-promoting agent. In addition, some derivatives of thiophene are also the component of organic semiconductors. In short, thiophene and its derivatives have a very important position in the pharmaceutical industry, dye industry, pesticide industry, resin industry, and chemical industry.
Production methods
Thiophene is presented in the shale oil and coal tar. First use the waste acid of crude benzene washing as the raw material for hydrolysis at 110-150 °C. The gas coming from hydrolysis is put into the overhead condenser through hydrolysis distillation column. The condensed product has content of 15%-25% thiophene, 50%-60% xylene, and also benzene, toluene, methyl thiophene and some unknown substances. Per ton of waste acid can be extracted out for about 10 kg distillation product. After dehydration with solid sodium hydroxide and further refined purification by distillation, you can get thiophene product of 90%-95%. Chemical synthesis of thiophene can use butane and sulfur as raw materials; butane first undergoes dehydrogenation and then form a ring with sulfur to form thiophene. Laboratory prepare thiophene through the reaction between 1,4-dicarbonyl compound and phosphorus trisulfide.
Chemical Properties
Thiophene is a colourless to pale yellow liquid that has an odor similar to benzene. It is a heterocyclic compound with a five-membered ring containing four carbon atoms and one sulfur atom. The ring system is also known as a thienyl ring. It occurs as an impurity in commercial benzene and is used as a solvent and in organic syntheses.
Physical properties
Clear, colorless liquid with an aromatic odor resembling benzene. An odor threshold concentration of 0.056 ppbv was reported by Nagata and Takeuchi (1990).
Uses
Thiophene is an important building block in dyes, agrochemicals and pharmaceuticals synthesis. It is involved in the chloroalkylation reactions in 2,5-positions. It is also used to prepare butane by reduction with raney nickel, 2-vinylthiophene, dithienyl, and 2-halo thiophenes by reacting with halogens.
Uses
Solvent similar to benzene, but suitable for lower and higher temps; manufacture of resins from thiophene-phenol mixtures and formaldehyde; manufacture of dyes and pharmaceuticals.
Uses
Thiophene is used as a building block of various organic molecules and pharmaceuticals providing functional properties.
Production Methods
Thiophene is present in coal tar and is recovered in the benzene distillation fraction (up to about 0.5% of the benzene present). Its removal from benzene is accomplished by mixing with concentrated sulfuric acid, soluble thiophene sulfonic acid being formed. Thiophene gives a characteristic blue coloration with isatin in concentrated sulfuric acid. The basic nomenclature of the thiophene ring system and its derivatives is indicated by the following: the sulfur atom is number 1, positions 2 and 5 are equivalent in the parent ring, as are the 3 and 4 positions.
Definition
ChEBI: Thiophene is a monocyclic heteroarene that is furan in which the oxygen atom is replaced by a sulfur. It has a role as a non-polar solvent. It is a mancude organic heteromonocyclic parent, a member of thiophenes, a monocyclic heteroarene and a volatile organic compound.
General Description
Thiophene appears as a colorless liquid with an unpleasant odor. Insoluble in water and slightly denser than water. Flash point 30 °F. Vapors heavier than air. Irritates the skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Used to make pharmaceuticals and dyes.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Thiophene reacts violently with strong oxidizing agents and concentrated nitric acid causing fire and explosion hazards [Handling Chemicals Safely 1980. p. 899]. A mixture of Thiophene and N-nitrosoacetanilide exploded at 0°C [Ber., 1887, 30, 367].
Hazard
Flammable, dangerous fire risk.
Health Hazard
May cause toxic effects if inhaled or absorbed through skin. Inhalation or contact with material may irritate or burn skin and eyes. Fire will produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Vapors may cause dizziness or suffocation. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
HIGHLY FLAMMABLE: Will be easily ignited by heat, sparks or flames. Vapors may form explosive mixtures with air. Vapors may travel to source of ignition and flash back. Most vapors are heavier than air. They will spread along ground and collect in low or confined areas (sewers, basements, tanks). Vapor explosion hazard indoors, outdoors or in sewers. Runoff to sewer may create fire or explosion hazard. Containers may explode when heated. Many liquids are lighter than water.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Mildly toxic by inhalation and subcutaneous routes. A very dangerous fire hazard when exposed to heat or flame. Explosive reaction with N-nitrosoacetanilide. Violent or explosive reaction with nitric acid. Incompatible with oxidizing materials. To fight fire, use foam, CO2, dry chemical. When heated to decomposition it emits highly toxic fumes of SOx.
Environmental Fate
Photolytic. A rate constant 9.70 x 10-12 cm3/molecule?sec was reported for the reaction of thiophene and OH radicals in the atmosphere at room temperature (Atkinson, 1985). Thiophene also reacts with NO3 radicals in the atmosphere at rate constants ranging from 3.2 x 10-14 (Atkinson et al., 1985) to 3.93 x 10-14 cm3/molecule?sec (Atkinson, 1991).
Purification Methods
The simplest purification procedure is to dry thiophen with solid KOH, or reflux it with sodium, and fractionally distil it through a glass-helices-packed column. More extensive treatments include an initial wash with aqueous HCl, then water, drying with CaSO4 or KOH, and passage through columns of activated silica gel or alumina. Fawcett and Rasmussen [J Am Chem Soc 67 1705 1945] washed thiophene successively with 7M HCl, 4M NaOH, and distilled water, dried with CaCl2 and fractionally distilled it. *Benzene was removed by fractional crystallisation by partial freezing, and the thiophene was degassed and sealed in Pyrex flasks. [Also a method is described for recovering the thiophene from the *benzene-enriched portion.] [Beilstein 17 H 29, 17 I 17, 17 II 35, 17 III/IV 234, 17/1 V 297.]
Thiophene Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of2
Preparation Products
1of5
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIMAGCHEM CORP | +86-13806087780 | sale@simagchem.com | China | 17365 | 58 |
| Shandong Zhishang New Material Co., Ltd. | +8617653113209 | sales002@sdzschem.com | China | 3049 | 58 |
| Jiangsu Guotai Guomian Trading Co. Ltd. | +86-512-58916079 +86-13601562190 | pharmachem@gtgmt.com | China | 148 | 58 |
| Hebei Chuanghai Biotechnology Co,.LTD | +86-13131129325 | sales1@chuanghaibio.com | China | 5893 | 58 |
| Henan Fengda Chemical Co., Ltd | +86-371-86557731 +86-13613820652 | info@fdachem.com | China | 20287 | 58 |
| Capot Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-(0)57185586718 +86-13336195806 | sales@capot.com | China | 29791 | 60 |
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 | info@tianfuchem.com | China | 21634 | 55 |
| Nanjing Finetech Chemical Co., Ltd. | 025-85710122 17714198479 | sales@fine-chemtech.com | CHINA | 885 | 55 |
| ATK CHEMICAL COMPANY LIMITED | +undefined-21-51877795 | ivan@atkchemical.com | China | 32957 | 60 |
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co.,Ltd. | +86-0551-65418679 +8618949832763 | info@tnjchem.com | China | 2986 | 55 |
Related articles
- Why thiophene is commonly used in drugs?
- In medicinal chemistry, thiophene derivatives are extremely significant heterocycles exhibiting remarkable applications in dif....
- Nov 9,2022
- Unique properties of thiophene
- Thiophene, systematic name 1-thia-2,4-cyclopentadiene, CAS number 110-02-1. From the structural point of view, thiophene is a ....
- May 5,2022
- Synthesis of Thiophene
- Thiophene is a five-membered, fully unsaturated, coplanar, sulfur heterocycle comprised of four carbon atoms and one sulfur at....
- Jan 26,2022
View Lastest Price from Thiophene manufacturers
| Image | Update time | Product | Price | Min. Order | Purity | Supply Ability | Manufacturer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
2024-11-05 | Thiophene
110-02-1
|
US $0.00-0.00 / KG | 1g | 99% | 2000tons | Shaanxi Dideu Medichem Co. Ltd | |
 |
2024-10-25 | Thiophene
110-02-1
|
US $9.00 / Kg/Drum | 16T | 99% | 1000tons/month | Hebei Yanxi Chemical Co., Ltd. | |
 |
2024-10-11 | Thiophene
110-02-1
|
US $10.70 / KG | 10KG | 99% | 10000kg | Hebei Chuanghai Biotechnology Co,.LTD |