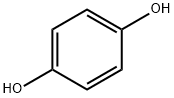
Hydroquinone
- CAS No.
- 123-31-9
- Chemical Name:
- Hydroquinone
- Synonyms
- HQ;QUINOL;Dihydroquinone;1,4-DIHYDROXYBENZENE;HYDROQUINON;Hidroquinone;p-Hydroquinone;HYDROXYQUINOL;1,4-HYDROQUINONE;Hydrochinon
- CBNumber:
- CB6717931
- Molecular Formula:
- C6H6O2
- Molecular Weight:
- 110.11
- MDL Number:
- MFCD00002339
- MOL File:
- 123-31-9.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
| Melting point | 172-175 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 285 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.32 |
| bulk density | 600kg/m3 |
| vapor density | 3.81 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 1 mm Hg ( 132 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.6320 |
| Flash point | 165 °C |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: 50 mg/mL, clear |
| pka | 10.35(at 20℃) |
| form | Needle-Like Crystals or Crystalline Powder |
| color | White to off-white |
| Odor | odorless |
| biological source | synthetic |
| Water Solubility | 70 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Air & Light Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,4808 |
| BRN | 605970 |
| Henry's Law Constant | (x 10-9 atm?m3/mol): <2.07 at 20 °C (approximate - calculated from water solubility and vapor pressure) |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH REL: 15-min ceiling 2, IDLH 50; OSHA PEL: TWA 2; ACGIH TLV: TWA 2 (adopted). |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong bases, oxygen, ferric salts. Light and air-sensitive. Discolours in air. |
| InChIKey | QIGBRXMKCJKVMJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | 0.59 at 20℃ |
| Indirect Additives used in Food Contact Substances | HYDROQUINONE |
| FDA 21 CFR | 175.105 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 123-31-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EWG's Food Scores | 6-9 |
| FDA UNII | XV74C1N1AE |
| ATC code | D11AX11 |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 15, Sup 7, 71) 1999 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Hydroquinone(123-31-9) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Hydroquinone (123-31-9) |
| UNSPSC Code | 41116107 |
| NACRES | NA.77 |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |     GHS05,GHS07,GHS08,GHS09 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H302-H318-H341-H351-H410 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P202-P273-P280-P301+P312-P305+P351+P338-P308+P313 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xn,N | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 22-40-41-43-50-68-R68-R50-R43-R41-R40-R22 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 26-36/37/39-61-S61-S36/37/39-S26 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | 2662 | |||||||||
| OEL | Ceiling: 2 mg/m3 [15-minute] | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | MX3500000 | |||||||||
| Autoignition Temperature | 930 °F | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 9 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29072210 | |||||||||
| Hazardous Substances Data | 123-31-9(Hazardous Substances Data) | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in rats: 320 mg/kg (Woodard) | |||||||||
| IDLA | 50 mg/m3 | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Hydroquinone price More Price(36)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich | PHL80712 | Hydroquinone phyproof? Reference Substance | 123-31-9 | 100MG | $262 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich | 8.22333 | Hydroquinone for synthesis | 123-31-9 | 250g | $40.2 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich | 8.22333 | Hydroquinone for synthesis | 123-31-9 | 1kg | $104 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich | 8.22333 | Hydroquinone for synthesis | 123-31-9 | 2.5kg | $209 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich | 8.22333 | Hydroquinone for synthesis | 123-31-9 | 25kg | $1090 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
Hydroquinone Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Hydroquinone (HQ) is produced by the oxidation of aniline or phenol, by the reduction of quinone, or from a reaction of acetylene and carbon monoxide. Hydroquinone occurs naturally as a glucose ether, also known as arbutin, in the leaves of many plants and in fruits, as well as one of the agents used in the defense mechanism of the bombardier beetle, family Carabidae.
Chemical Properties
white needle-like crystals or crystalline powder
Chemical Properties
Hydroquinone, a colorless, hexagonal prism, has been reported to be a good antimitotic and tumor-inhibiting agent. It is a reducing agent used in a photographic developer, which polymerizes in the presence of oxidizing agents. In the manufacturing industry it may occur include bacteriostatic agent, drug, fur processing, motor fuel, paint, organic chemicals, plastics, stone coating, and styrene monomers.
Physical properties
Colorless to pale brown, odorless, hexagonal crystals
Originator
Quinnone,Dermohr,US,1980
Uses
Use as photographic reducer and developer; as reagent in the determination of small quantities of phosphate; as antioxidant. Depigmentor
Uses
K channel agonist, antihypertensive
Uses
Photographic reducer and developer; antioxidant; stabilizing agent for some polymers; intermediate in the manufacturing of some dyes and pigments; in cosmetic formulations.
Uses
hydroquinone is a pigment-lightening agent used in bleaching creams. Hydroquinone combines with oxygen very rapidly and becomes brown when exposed to air. Although it occurs naturally, the synthetic version is the one commonly used in cosmetics. Application to the skin may cause allergic reaction and increase skin sun sensitivity. Hydroquinone is potentially carcinogenic and is associated with causing ochronosis, a discoloration of the skin. The u.S. FDA has banned hydroquinone from oTC cosmetic formulations, but allows 4 percent in prescription products. Its use in cosmetics is prohibited in some european countries and in Australia.
Uses
reducing agent prevents polymerization of resin monomers lightens darkened skin, light sensitive
Definition
ChEBI: A benzenediol comprising benzene core carrying two hydroxy substituents para to each other.
Indications
Hydroquinone interferes with the production of the pigment melanin by epidermal melanocytes through at least two mechanisms: it competitively inhibits tyrosinase, one of the principal enzymes responsible for converting tyrosine to melanin, and it selectively damages melanocytes and melanosomes (the organelles within which melanin is stored).
Production Methods
There are three current manufacturing processes for HQ:
oxidative cleavage of diisopropylbenzene, oxidation of aniline,
and hydroxylation of phenol.
Diisopropylbenzene is air oxidized to the intermediate
diisopropylbenzene bishydroperoxide. This hydroperoxide
is purified by extraction and reacted further to form
hydroquinone. The purified product is isolated by filtration
and packaged. The process can be almost entirely closed,
continuous, computer-controlled, and monitored.
HQcan also be prepared by oxidizing aniline to quinone in
the presence of manganese dioxide and sulfuric acid.
p-Benzoquinone is then reduced to HQ using iron oxide.
The resulting hydroquinone is crystallized and dried.
The process occurs in a closed system.
HQis also manufactured by hydroxylation of phenol using
hydrogen peroxide as a hydroxylation agent. The reaction is
catalyzed by strong mineral acids or ferrous or cobalt salts.
Manufacturing Process
Into a pressure reactor there was charged 100 ml of methanol and 1 g of
diruthenium nonacarbonyl. The reactor was closed, cooled in solid carbon
dioxide/acetone, and evacuated. Acetylene, to the extent of 1 mol (26 g), was
metered into the cold reactor. Carbon monoxide was then pressured into this
vessel at 835-980 atmospheres, during a period of 16.5 hours; while the
reactor was maintained at 100°C to 150°C. The reactor was then cooled to
room temperature and opened.
The reaction mixture was removed from the vessel and distilled at a pressure of 30-60 mm, and a bath temperature of 30°C to 50°C until the methanol had
all been removed. The extremely viscous tarry residue remaining in the still
pot was given a very crude distillation, the distillate boiling at 82°C to
132°C/2 mm. In an attempt to purify this distillate by a more careful
distillation, 5.3 g of a liquid distilling from 53°C to 150°C/5 mm was collected.
At this point, much solid sublimate was noted not only in this distillate but in
the condenser of the still. 7 g of the solid sublimate was scraped out of the
condenser of the still. Recrystallization of the sublimate from ethyl acetate
containing a small amount of petroleum ether gave beautiful crystals melting
at 175°C to 177°C (5 g). Infrared analysis confirmed that this compound was
hydroquinone (9% conversion).
brand name
Aida;Ambi- skin tone;Black and white;Creme des 3 fleur d'orient;Eldopaque forte;Eldoquin forte 4% cream;Epocler;Esoterica facial;Esoterica regular;Esoterica sensitive skin;Esoterica sunscreen;Melanex topical sollution;Melpaque hp;Melqui hp;Neostrata aha gel;Neostrata hq;Nuquin hp;Pigmanorm;Porcelana;Sinquin;Solaquin forte sun bleaching;Superfade age spot;Ultraquin plaine.
Therapeutic Function
Depigmentor
World Health Organization (WHO)
Hydroquinone was introduced in 1965 as a topical depigmenting agent for hyperpigmentation. At high concentrations hydroquinone is corrosive and in most countries has been restricted to the level of approximately 2% and limited to the period of less than 2 months. Additional consideration for restrictive action is that animal experiments have also demonstrated carcinogenic and mutagenic potential of hydroquinone.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Chemistry Letters, 14, p. 731, 1985
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 50, p. 1722, 1985
Tetrahedron Letters, 22, p. 2337, 1981 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(01)82900-2
General Description
Light colored crystals or solutions. May irritate the skin, eyes and mucous membranes. Mildly toxic by ingestion or skin absorption.
Air & Water Reactions
Darkens on exposure to air and light. Miscible in water. Solutions become brown in air due to oxidation. Oxidation is very rapid in the presence of alkali.
Reactivity Profile
Hydroquinone is a slight explosion hazard when exposed to heat. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. Also incompatible with bases. Hydroquinone reacts with oxygen and sodium hydroxide. Reacts with ferric salts . Hot and/or concentrated NaOH can cause Hydroquinone to decompose exothermically at elevated temperature. (NFPA Pub. 491M, 1975, 385)
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion and inhalation, irritant. Questionable carcinogen.
Health Hazard
Hydroquinone is very toxic; the probable oral lethal dose for humans is 50-500 mg/kg, or between 1 teaspoon and 1 ounce for a 150 lb. person. It is irritating but not corrosive. Fatal human doses have ranged from 5-12 grams, but 300-500 mg have been ingested daily for 3-5 months without ill effects. Death is apparently initiated by respiratory failure or anoxia.
Health Hazard
Exposures to hydroquinone in large quantities by accidental oral ingestion produce toxicity and poisoning. The symptoms of poisoning include, but are not limited to, blurred speech, tinnitus, tremors, sense of suffocation, vomiting, muscular twitching, headache, convul- sions, dyspnea and cyanosis from methemoglobinemia, coma, and collapse from respira- tory failure. Occupational workers should be allowed to work with protective clothing and dust masks with full-face or goggles to protect the eyes, and under proper management.
Fire Hazard
Dust cloud may explode if ignited in an enclosed area. Hydroquinone can react with oxidizing materials and is rapidly oxidized in the presence of alkaline materials. Oxidizes in air.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
reaction suitability
reagent type: reductant
Contact allergens
Hydroquinone is used in photography developers (black and white, X-ray, and microfilms), in plastics, in hair dyes as an antioxidant and hair colorant. Hydroquinone is found in many skin bleaching creams.
Clinical Use
Hydroquinone is applied topically to treat disorders characterized by excessive melanin in the epidermis, such as melasma. In the United States, nonprescription skin-lightening products contain hydroquinone at concentrations of 2% or less; higher concentrations are available by prescription.
Side effects
The incidence of adverse effects with hydroquinone increases in proportion to its concentration. A relatively common side effect is local irritation, which may actually exacerbate the discoloration of the skin being treated. Allergic contact dermatitis occurs less commonly. A rare but more serious complication is exogenous ochronosis, in which a yellow-brown pigment deposited in the dermis results in blue-black pigmentation of the skin that may be permanent.
Potential Exposure
Tumorigen,Mutagen; Reproductive Effector; Human Data; PrimaryImritant. Hydroquinone is a reducing agent and is used as anindustrial chemical, chemical intermediate, pharmaceutical,and veterinary drug; as a photographic developer; and as anantioxidant or stabilizer for certain materials, which polymer-ize in the presence of oxidizing agents. Many of its derivativesare used as bacteriostatic agents, and others, particularly 2,5- bis(ethyleneimino) hydroquinone, have been reported to begood antibiotic and tumor-inhibiting agents.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek med-ical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from ex posure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, includ-ing resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medi-cal attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
Carcinogenicity
No case reports of cancer associated with HQ exposure have been published.
Source
Hydroquinone occurs naturally in strawberry tree leaves, pears, blackberries, Chinese alpenrose, bilberries, blackberries, hyacinth flowers, anise, cowberries, and lingonberries (Duke, 1992).
Environmental Fate
Biological. In activated sludge, 7.5% mineralized to carbon dioxide after 5 d (Freitag et al.,
1985). Under methanogenic conditions, inocula from a municipal sewage treatment plant digester
degraded hydroquinone to phenol prior to being mineralized to carbon dioxide and methane
(Young and Rivera, 1985). In various pure cultures, hydroquinone degraded to the following
intermediates: benzoquinone, 2-hydroxy-1,4-benzoquinone, and β-ketoadipic acid. Hydroquinone
also degraded in activated sludge but no products were identified (Harbison and Belly, 1982).
Heukelekian and Rand (1955) reported a 5-d BOD value of 0.74 g/g which is 39.2% of the
ThOD value of 1.89 g/g. In activated sludge inoculum, following a 20-d adaptation period, 90.0%
COD removal was achieved. The average rate of biodegradation was 54.2 mg COD/g?h (Pitter,
1976).
Photolytic. A carbon dioxide yield of 53.7% was achieved when hydroquinone adsorbed on
silica gel was irradiated with light (λ >290 nm) for 17 h (Freitag et al., 1985).
Chemical/Physical. Ozonolysis products reported are p-quinone and dibasic acids (Verschueren,
1983). Moussavi (1979) studied the autoxidation of hydroquinone in slightly alkaline (pH 7 to 9)
aqueous solutions at room temperature. The oxidation of hydroquinone by oxygen followed
first-order kinetics that yielded hydrogen peroxide and p-quinone as products. At pH values of 7.0,
8.0, and 9.0, the calculated half-lives of this reaction were 111, 41, and 0.84 h, respectively
(Moussavi, 1979).
Chlorine dioxide reacted with hydroquinone in an aqueous solution forming p-benzoquinone (Wajon et al., 1982). Kanno et al. (1982) studied the aqueous reaction of hydroquinone and other substituted aromatic hydrocarbons (aniline, toluidine, 1- and 2-naphthylamine, phenol, cresol,
pyrocatechol, resorcinol, and 1-naphthol) with hypochlorous acid in the presence of ammonium
ion. They reported that the aromatic ring was not chlorinated as expected but was cleaved by
chloramine forming cyanogen chloride. As the pH was lowered, the amount of cyanogen chloride
formed increased (Kanno et al., 1982).
At influent concentrations of 1.0, 0.1, 0.01, and 0.001 mg/L, the GAC adsorption capacities
were 160, 90, 51, and 29 mg/g, respectively (Dobbs and Cohen, 1980).
storage
(1) Color Code-- Yellow Stripe (strong reducingagent): Reactivity Hazard; Store separately inan area iso-lated from flammables, combustibles, or other yellow-codedmaterials. (2) Color Code- _Blue: Health Hazard/Poison:Store in a secure poison location. Prior to working with thischemical you should be trained on its proper handling andstorage. Hydroquinone must be stored to avoid contact withsodium hydroxide since violent reactions occur. Store intightly closed containers in a cool, well-ventilated areaaway from oxidizing materials. Where possible, automati-cally pump liquid from drums or other storage containers toprocess containers.
Shipping
This compound requires aa shipping label of“POISONOUS/TOXIC MATERIALS.”It falls in HazardClass 6.1 and Packing Group II.
Purification Methods
Crystallise quinol from acetone, *benzene, EtOH, EtOH/*benzene, water or acetonitrile (25g in 30mL), preferably under nitrogen. Dry it under vacuum. [Wolfenden et al. J Am Chem Soc 109 463 1987, Beilstein 6 H 836, 6 IV 5712.]
Toxicity evaluation
Benzene, phenol, and hydroquinone are metabolized in vivo to benzoquinone and excreted as the mercapturate, N-acetyl-S- (2,5-dihydroxyphenyl)-L-cysteine. Hydroquinone is a reducing cosubstrate for peroxidase enzymes, and the resultant semiquinone and p-benzoquinone may bind to DNA.
Incompatibilities
Hydroquinone is a reducing agent. Dustforms an explosive mixture with air. May explode on con-tact with oxygen. Incompatible with strong oxidizers, caus-tics; reacts violently with sodium hydroxide. May beoxidized to quinone at room temperatures in the presence ofmoi sture.
Toxics Screening Level
The initial threshold screening level (ITSL) for hydroquinone (CAS # 123-31-9) is 140 μg/m 3 based on an annual averaging time. The initial risk screening level (IRSL) is 0.058 μg/m 3 with an annual averaging time, and the secondary risk screening level (SRSL) is 0.58 μg/m 3 with an annual averaging time.
Hydroquinone Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of3
Preparation Products
1of8
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hebei Chuanghai Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +86-15531157085 +86-15531157085 | abby@chuanghaibio.com | China | 8808 | 58 |
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co.,Ltd. | +86-0551-65418671 +8618949823763 | sales@tnjchem.com | China | 34563 | 58 |
| Wuhan Biet Co., Ltd. | +8617320528784 | min@biet.com.cn | China | 42 | 58 |
| Hebei Jingbo New Material Technology Co., Ltd | +8619931165850 | hbjbtech@163.com | China | 1000 | 58 |
| Hebei Chuanghai Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +86-15350571055 +86-15350571055 | Sibel@chuanghaibio.com | China | 6087 | 58 |
| Hebei Chuanghai Biotechnology Co,.LTD | +86-13131129325 | sales1@chuanghaibio.com | China | 5872 | 58 |
| Hebei Mujin Biotechnology Co.,Ltd | +8613288715578 | angelia@hbmojin.com | China | 750 | 58 |
| Capot Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-(0)57185586718 +86-13336195806 | sales@capot.com | China | 29730 | 60 |
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 | info@tianfuchem.com | China | 21630 | 55 |
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co.,Ltd. | +86-0551-65418679 +8618949832763 | info@tnjchem.com | China | 2986 | 55 |
Related articles
- Adverse effects of Hydroquinone
- Hydroquinone (HQ) is regarded as the gold standard for the treatment of disorders of hyperpigmentation including melasma. It c....
- Mar 3,2022
- Hydroquinone-Skin lightening and Controversy
- Hydroquinone exists in stems, leaves and juices of many plants in nature, is a chemical substance with a wide range of uses wi....
- Oct 9,2019
Related Qustion
- Q:Why is Hydroquinone prohibited in skincare cosmetic products?
- A:Hydroquinone and mercury are ingredients added to skin-lightening products to limit the skin's production of melanin.
- Jun 27,2024
View Lastest Price from Hydroquinone manufacturers
| Image | Update time | Product | Price | Min. Order | Purity | Supply Ability | Manufacturer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
2025-04-11 | Hydroquinone
123-31-9
|
US $1.00 / KG | 1KG | ≥99% | 2000mt/year | Jinan Finer Chemical Co., Ltd | |
 |
2025-04-10 | Hydroquinone
123-31-9
|
US $20.00 / kg | 1kg | 99.9% | 10000 | Hebei Miaoyin Technology Co.,Ltd | |
|
|
2025-03-31 | Hydroquinone
123-31-9
|
US $100.00 / kg | 1kg | 99%min | 200TON | Hebei Chuanghai Biotechnology Co., Ltd |
-

- Hydroquinone
123-31-9
- US $1.00 / KG
- ≥99%
- Jinan Finer Chemical Co., Ltd
-

- Hydroquinone
123-31-9
- US $20.00 / kg
- 99.9%
- Hebei Miaoyin Technology Co.,Ltd
-
- Hydroquinone
123-31-9
- US $100.00 / kg
- 99%min
- Hebei Chuanghai Biotechnology Co., Ltd
123-31-9(Hydroquinone)Related Search:
1of4