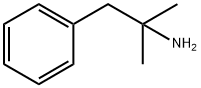
PHENTERMINE
- CAS No.
- 122-09-8
- Chemical Name:
- PHENTERMINE
- Synonyms
- Wilpo;Linyl;Inoamin;Ionamin;Lonamin;mg18570;Omnibex;Duromine;Lipopill;MG 18370
- CBNumber:
- CB8309334
- Molecular Formula:
- C10H15N
- Molecular Weight:
- 149.24
- MDL Number:
- MFCD00059195
- MOL File:
- 122-09-8.mol
| Melting point | 143°C (estimate) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | bp750 205°; bp21 100° |
| Density | 0,93 g/cm3 |
| vapor pressure | 32.4Pa at 25℃ |
| refractive index | 1.5090 (estimate) |
| Flash point | 100 °C |
| storage temp. | Store at 0-5°C |
| solubility | Methanol: 50 mg/ml |
| form | Oil |
| pka | pKa 10.11 (Uncertain) |
| color | Colourless to Pale Yellow |
| Water Solubility | 18.6g/L at 25℃ |
| LogP | 1.9 at 25℃ |
| EWG's Food Scores | 1 |
| FDA UNII | C045TQL4WP |
| ATC code | A08AA01 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | .alpha.,.alpha.-Dimethylphenethylamine (122-09-8) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS02,GHS06,GHS08 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H225-H301+H311+H331-H370 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P210-P260-P280-P301+P310-P311 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xn,T,F | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 20/21/22-36/37/38-40-39/23/24/25-23/24/25-11-67 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 26-36/37/39-36/37-24/25-23-45-16 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | 1851 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 1 | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 6.1(b) | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| Hazardous Substances Data | 122-09-8(Hazardous Substances Data) | |||||||||
| Toxicity | man,TDLo,oral,1429ug/kg (1.429mg/kg),AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM: SYMPATHOMIMETIC,Therapie. Vol. 34, Pg. 205, 1979. | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
PHENTERMINE Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Originator
Wilpo ,Dorsey, US,1961
Uses
Appetite suppressant (systemic).
Definition
ChEBI: Phentermine is a primary amine. It has a role as a dopaminergic agent, an adrenergic agent, a sympathomimetic agent, an appetite depressant, a central nervous system stimulant and a central nervous system drug. It is a conjugate base of a phentermine(1+).
Manufacturing Process
Preparation of isobutyrophenone: In a 12 liter, 3-necked flask, 1,280 grams of aluminum chloride was covered with 2,000 cc of dry thiophene-free benzene and a solution of 919 grams of isobutyryl chloride, (BP 92°-94°C) in 1 liter of benzene was added slowly with stirring. After heating for 3 hours at reflux, the solution was cooled and poured over a mixture of 1 liter of concentrated hydrochloric acid and 5 kg of ice. The benzene layer was separated, the aqueous layer extracted with benzene, and the combined benzene solutions were washed, dried and concentrated in vacuo. The residue was distilled rapidly to give 1,051 grams of isobutyrophenone, boiling at 81°-89°C at 1 mm, yield 83.4%.
Preparation of 1,3-Diphenyl-2,2-Dimethylpropanone-1: Sodamide was prepared from 12.5 grams of sodium added in small portions to 600 cc of liquid ammonia with 1 gram of hydrous ferric chloride as catalyst. The ammonia was replaced by 200 cc of dry toluene and without delay a solution of 74 grams of isobutyrophenone and 76.5 grams of benzyl bromide in 200 cc of benzene was slowly added with stirring. The reaction mixture was heated on a boiling water bath for 48 hours. Water was then added, the organic layer separated and the product isolated by distillation. The 1,3-diphenyl-2,2
Phentermine dimethylpropanone-1 boiled from 142°-143°C at a pressure of 3 mm, nD201.5652.
Preparation of α,α-Dimethyl-β-Phenylpropionamide: Sodamide was prepared from 7.6 grams of sodium in 350 cc of liquid ammonia with 0.9 gram of hydrous ferric chloride. The ammonia was replaced by 250 cc of toluene, the mixture was heated to 60°C and 71.4 grams of 1,3-diphenyl-2,2-dimethyl propanone-1 dissolved in 150 cc of toluene was added. The mixture was stirred and heated on a steam bath for 5 hours. A clear red color appeared in 15 minutes and disappeared after about an hour. After cooling, water was added, the organic layer was washed, dried, and concentrated to give 36.5 grams of α,α-dimethyl-β-phenyl propionamide which crystallized slowly after the addition of an equal volume of petroleum ether. The product melted at 62°C after crystallization from benzene-petroleum ether.
Preparation of Di-(β-Phenyl-α,α-Dimethylethyl)Urea: 3.5 grams of α,αdimethyl-β-phenylpropionamide in 420 cc of water was added to a solution of 87.5 grams of potassium hydroxide and 35 grams of bromine in 350 cc of water. After 2 hours at 60°C, the product was obtained on crystallization from ethanol, melting at 184°C.
Preparation of ω-Phenyl-tert-Butylamine: 24 grams of the urea derivative obtained as indicated above, were well mixed with 96 grams of calcium hydroxide in a flask immersed in an air bath and provided with a dropping funnel the stem of which reached the bottom of the flask. The mixture was heated to 240°-260°C (inside temperature) for 7 hours during which time 86 cc of water was slowly added. The vapors were collected in a receiver cooled with ice. After extraction with ether and distillation, the product was obtained as a colorless liquid boiling from 80°-84°C at 9 mm according to US Patent 2,590,079.
The ether solution may be dried and saturated with hydrogen chloride and the precipitated hydrochloride recrystallized from a mixture of 50 parts alcohol and 100 parts of acetone.
The pure hydrochloride is thus obtained as a white crystalline substance having a MP of 195°-196°C, according to US Patent 2,408,345.
brand name
Ionamin (Fisons);Adipex nouveau;Adipex-p;Aneroxina;Bellapront;Dapex;Ex-adipos;Fastin;Inonamin;Ionakraft;Ionamine;Levum;Minobese forte;Mirapront;Netto-longcaps;Obestin 30;Oby-trim;Ona-mast;Panbesy;Panshape;Parmine;Phentermyl;Pronidin;Raucherstop 5 ht;Reducyl;Regulin;Span r/d;Teramine.
Therapeutic Function
Antiobesity
World Health Organization (WHO)
Phentermine, a sympathomimetic amine, was introduced in 1959 for use as an anorexic agent. It retains a place in the treatment of obesity. However,since it has been subject to abuse and because dependence can occur, phentermine is controlled under Schedule IV of the 1971 Convention on Psychotropic Substances. (Reference: (UNCPS4) United Nations Convention on Psychotropic Substances (IV), , , 1971)
Synthesis Reference(s)
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 70, p. 4048, 1948 DOI: 10.1021/ja01192a023
General Description
Oily liquid. Insoluble in water.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
PHENTERMINE neutralizes acids in exothermic reactions to form salts plus water. May be incompatible with isocyanates, halogenated organics, peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides. May generate hydrogen, a flammable gas, in combination with strong reducing agents such as hydrides.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, intravenous, and intraperitoneal routes. Human systemic effects by ingestion: sympathomimetic. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx
Synthesis
Phentermine is prepared by converting the
condensation product of benzaldehyde and
nitropropane to the corresponding aminoalcohol
followed by transformation to the chloroamine
and then catalytic hydrogenation
.
PHENTERMINE Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of4
Preparation Products
122-09-8(PHENTERMINE)Related Search:
1of4