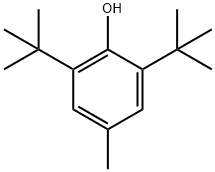
Butylated Hydroxytoluene
- CAS No.
- 128-37-0
- Chemical Name:
- Butylated Hydroxytoluene
- Synonyms
- BHT;2,6-DI-TERT-BUTYL-4-METHYLPHENOL;BUTYLHYDROXYTOLUENE;BHT264;p21;2,6-DI-TERT-BUTYL-P-CRESOL;DBPC;Topanol;IONOL;BHT (BAGS)
- CBNumber:
- CB8355755
- Molecular Formula:
- C15H24O
- Molecular Weight:
- 220.35
- MDL Number:
- MFCD00011644
- MOL File:
- 128-37-0.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
| Melting point | 69-73 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 265 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.048 |
| vapor density | 7.6 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | <0.01 mm Hg ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.4859 |
| FEMA | 2184 | BUTYLATED HYDROXYTOLUENE |
| Flash point | 127 °C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | methanol: 0.1 g/mL, clear, colorless |
| form | Crystals |
| pka | pKa 14(H2O t = 25 c = 0.002 to 0.01) (Uncertain) |
| color | white |
| Odor | faint characteristic odor |
| Odor Type | phenolic |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
| Merck | 14,1548 |
| BRN | 1911640 |
| Exposure limits |
ACGIH: TWA 2 mg/m3 NIOSH: TWA 10 mg/m3 |
| Stability | Stable, but light-sensitive. Incompatible with acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, brass, copper, copper alloys, steel, bases, oxidizing agents. Combustible. |
| InChIKey | NLZUEZXRPGMBCV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| LogP | 5.2 |
| FDA 21 CFR | 172.115; 182.3173; 582.3173; 172.615; 175.105; 175.300; 177.1010; 181.24 |
| Substances Added to Food (formerly EAFUS) | BUTYLATED HYDROXYTOLUENE |
| SCOGS (Select Committee on GRAS Substances) | Butylated Hydroxytoluene (BHT) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 128-37-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EWG's Food Scores | 4 |
| FDA UNII | 1P9D0Z171K |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 40, Sup 7) 1987 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Butylated hydroxytoluene(128-37-0) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 2,6-Di-tert-butyl-p-cresol (128-37-0) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS09 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Warning | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H410 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P273-P391-P501 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | Xn,N | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 22-36/37/38-36/38-50/53 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 26-36-37/39-61-60 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | 3077 | |||||||||
| OEB | B | |||||||||
| OEL | TWA: 10 mg/m3 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 1 | |||||||||
| RTECS | GO7875000 | |||||||||
| F | 8-10-23 | |||||||||
| Autoignition Temperature | 878 °F | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 9 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| HS Code | 29071900 | |||||||||
| Toxicity | LD50 orally in mice: 1040 mg/kg (McOmie) | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Butylated Hydroxytoluene price More Price(65)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich | W218405 | Butylated hydroxytoluene ≥99%, FCC, FG | 128-37-0 | 1kg | $76.5 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich | W218405 | Butylated hydroxytoluene ≥99%, FCC, FG | 128-37-0 | 10Kg | $395 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich | W218405 | Butylated hydroxytoluene ≥99%, FCC, FG | 128-37-0 | 20kg | $533 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich | 8.22021 | 2,6-Di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol for synthesis | 128-37-0 | 100g | $33.5 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich | 8.22021 | 2,6-Di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol for synthesis | 128-37-0 | 500g | $60.7 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
Butylated Hydroxytoluene Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
description
Butylated hydroxytoluene is a synthetic phenolic compound mainly used as an antioxidant and preservative in the food industry. It is used to prevent the lipid oxidation in oils and fat-containing foods.Butylated Hydroxytoluene toxicity is generally considered as being low.Since Butylated Hydroxytoluene is used in many near consumer products population wide exposure is expected.
Chemical Properties
Butylated hydroxytoluene is white or light yellow crystal. Butylated Hydroxytoluene has a melting point of 71°C, a boiling point of 265°C, a relative density of 1.048 (20/4°C), and a refractive index of 1.4859 (75°C). Solubility of Butylated Hydroxytoluene at normal temperature: methanol 25, ethanol 25-26, isopropanol 30, mineral oil 30, acetone 40, petroleum ether 50, benzene 40, lard (40-50°C ) 40-50, corn oil and soybean oil 40-50. Butylated Hydroxytoluene is insoluble in water, 10NaOH solution, glycerol, and propylene glycol. Butylated Hydroxytoluene is odorless, odorless with good thermal stability.
Application from Literature
The applications of butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT) have been reported as following [1-9]:
• Butylated hydroxytoluene metabolites causing DNA strand breaks in cultured cells and DNA breaks between nucleosomes (a typical feature of apoptosis), which result in relieving inflammation.
• Inhibiting secretion, aggregation, and protein phosphorylation caused by protein kinase C activators at the process of the pre-incubation of aspirin-treated platelets.
• Inhibiting liver cancer formation induced by aflatoxin B1.
• As Michael receptor, butylated hydroxytoluene can react with uninucleophiles and proteins.
• Reaction of 2, 6-di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol with fluorine (II) - benzophenone dianion complex.
• Food additive 2, 6-di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol can promote acute lung toxicity and tumor growth in mice.
• Butylated hydroxytoluene can be used to prepare organoaluminum compound methylaluminum bis (2, 6-di-tert-butyl-4-alkylphenol oxide).
Uses
Butylated hydroxytoluene has wide application, such as flavors, fragrances, biochemical reagents-other chemical reagents, chemical raw materials, organic chemical raw materials, biochemical, inorganic salts, antioxidants, food additives, feed additives, feed storage additives, aromatic hydrocarbons, bulk drugs and so on. As a phenolic antioxidant, butylated hydroxytoluene can inhibit lipid peroxidation and exhibit electrophilic quinone methyl ether toxicity mediated by oxidative metabolism. The BHT metabolites, 6-tert-butyl-2- [2 ′-(2′-hydroxymethyl) -propyl] -4-methylphenol, may cause lung damage in mice and promote tumor growth.
Mammalian physiology
Butylated Hydroxytoluene is a phenolic antioxidant. Butylated Hydroxytoluene can inhibit lipid peroxidation and cause lung injury in mice and promote tumor growth, which may be due to the metabolites of Butylated Hydroxytoluene, 6-tert-butyl-2-[2′-(2′-hydroxymethyl)-propyl]-4-Methylphenol. Butylated Hydroxytoluene metabolites have also been reported to cause DNA strand breaks in cultured cells and DNA breaks between nucleosomes (a typical feature of apoptosis). A single intraperitoneal injection of Butylated Hydroxytoluene (60mg/kg body weight) into rats caused a significant increase in nuclear DNA methyltransferase activity in the liver, kidney, heart, spleen, brain, and lung.
Description
The antioxidant butylated hydroxytoluene is contained in food, adhesive glues, industrial oils and greases, including cutting fluids. Sensitization seems very rare.
Description
Butylated Hydroxytoluene is a synthetic antioxidant. It scavenges peroxide, 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH; ), superoxide, and ABTS radicals in cell-free assays, as well as inhibits lipid peroxidation of linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 90150.1 | 21909) in vitro when used at a concentration of 45 μg/ml. Butylated Hydroxytoluene (0.025-3.2 mM) reduces freeze-thaw-induced malondialdehyde (MDA) production and increases sperm viability in boar spermatozoa preparations. Formulations containing BHT have been used as antioxidant cosmetic and food additives.
Chemical Properties
BHA and BHT (butylated hydroxytoluene) are monohydric phenolic antioxidants that, prior to their introduction and acceptance in the food industry, were used to protect petroleum against oxidative degumming. Butylated Hydroxytoluene has a very faint, musty, occasional cresylictype odor. BHA and Butylated Hydroxytoluene are extensively used in foods as antioxidants. Most fats, oils and fat-containing foods are naturally susceptible to rapid rancification and other oxidative reactions that produce compounds having objectionable taste and odor, making foods containing them unpalatable. Lipid oxidation is autocatalytic and proceeds as a complex of chain reactions, the nature and speed of which vary with the substrate, temperature, light, availability of oxygen and presence or absence of oxidation catalysts. Antioxidants like BHT act as “chain breaks” in the autooxidation processes under the usual conditions of processing, storage and use of fat-containing foods (Burdock, 1997).
Chemical Properties
Butylated Hydroxytoluene is a white to pale yellow crystalline solid or powder.
Chemical Properties
white crystalline solid
Chemical Properties
Butylated hydroxytoluene occurs as a white or pale yellow crystalline solid or powder with a faint characteristic phenolic odor.
Occurrence
Not reported found naturally.
Uses
Because they prevent rancidity, antioxidants are of great interest to the food industry. For example, butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT), butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA), and EDTA are frequently used to preserve various foods, such as cheese or fried products. Butylated hydroxytoluene is a powerful inhibitor of lipid peroxidation, yet large doses of it can induce oxidative DNA damage and cancer development in the rat forestomach.
Uses
Antioxidant 264 as general antioxidants is used widely in polymer materials, petroleum products and food processing industries. Antioxidant 264 is commonly used rubber antioxidant, heat, oxygen aging have some protective effect, but also can inhibit copper harm. This product does not change color, not pollution. Antioxidants 264 high solubility in oil, no precipitation, less volatile, non-toxic and non-corrosive.
Uses
Butylated Hydroxytoluene (BHT) is an antioxidant that functions similarly to butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA) but is less stable at high temperatures. It is also termed 2,6-di-tert-butyl-para-cresol. See Butylated Hydroxyanisole.
Uses
Antioxidant for food, animal feed, petroleum products, synthetic rubbers, plastics, animal and vegetable oils, soaps. Antiskinning agent in paints and inks.
Uses
Butylated Hydroxytoluene is also known as butylated hydroxy toluene. It is an anti-oxidant that also has preservative and masking capabilities.
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of phenols that is 4-methylphenol substituted by tert-butyl groups at positions 2 and 6.
Preparation
Butylated Hydroxytoluene is produced commercially by the alkylation of para-cresol with isobutylene. Butylated Hydroxytoluene is also produced by several western European manufacturers, production/processing plants in Germany, France, the Netherlands, United Kingdom and Spain.
Production Methods
Prepared by the reaction of p-cresol with isobutene.
General Description
White crystalline solid.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Phenols, such as 2,6-Di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol, do not behave as organic alcohols, as one might guess from the presence of a hydroxyl (-OH) group in their structure. Instead, they react as weak organic acids. Phenols and cresols are much weaker as acids than common carboxylic acids (phenol has Ka = 1.3 x 10^[-10]). These materials are incompatible with strong reducing substances such as hydrides, nitrides, alkali metals, and sulfides. Flammable gas (H2) is often generated, and the heat of the reaction may ignite the gas. Heat is also generated by the acid-base reaction between phenols and bases. Such heating may initiate polymerization of the organic compound. Phenols are sulfonated very readily (for example, by concentrated sulfuric acid at room temperature). The reactions generate heat. Phenols are also nitrated very rapidly, even by dilute nitric acid. Nitrated phenols often explode when heated. Many of them form metal salts that tend toward detonation by rather mild shock. May react with oxidizing materials.
Health Hazard
2,6-Di-tert-butyl-p-cresol or Butylated Hydroxytoluene is of relatively low acute toxicity in animals, and there is no evidence of either acute or chronic effects among exposed workers.
Fire Hazard
2,6-Di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol is combustible.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Pharmaceutical Applications
Butylated hydroxytoluene is used as an antioxidant in
cosmetics, foods, and pharmaceuticals. It is mainly used to
delay or prevent the oxidative rancidity of fats and oils and to
prevent loss of activity of oil-soluble vitamins.
Butylated hydroxytoluene is also used at 0.5–1.0% w/w
concentration in natural or synthetic rubber to provide enhanced
color stability.
Butylated hydroxytoluene has some antiviral activity and has
been used therapeutically to treat herpes simplex labialis.
Contact allergens
This antioxidant is contained in food, adhesive glues, industrial oils, and greases, including cutting fluids. Sensitization seems very rare.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Butylated hydroxytoluene is a phenolic antioxidant. It has been shown to inhibit lipid peroxidation. It causes lung injury and promotes tumors in mice, but this may be due to a metabolite of Butylated Hydroxytoluene, 6-tert-butyl-2-[2′-(2′-hydroxymethyl)-propyl]-4-methylphenol. Metabolites of Butylated Hydroxytoluene have also been reported to induce DNA strand breaks and internucleosomal DNA fragmentation (a characteristic of apoptosis) in cultured cells. In rats, a single intraperitoneal injection of Butylated Hydroxytoluene (60 mg/kg body mass) results in a significant increase in nuclear DNA methyl transferase activity in the liver, kidneys, heart, spleen, brain and lungs. Incubation of alveolar macrophages with Butylated Hydroxytoluene significantly reduced the level of TNF-α which may explain the mechanism by which this antioxidant reduces inflammation. Preincubation of aspirin-treated platelets with Butylated Hydroxytoluene inhibits the secretion, aggregation, and protein phosphorylation induced by protein kinase C activators. Butylated Hydroxytoluene was also found to inhibit the initiation of hepatocarcinogenesis by aflatoxin B1.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
Carcinogenicity
The IARC has determined that there is limited evidence for the carcinogenicity of Butylated Hydroxytoluene in experimental animals.Butylated Hydroxytoluene has given primarily negative results in a large number of in vivo and in vitro genotoxic assays.No significant reproductive effects were observed in three-generation toxicity studies in mice administered up to 0.4% in the diet.6 The 2003 ACGIH threshold limit valuetime- weighted average (TLV-TWA) for 2,6-ditert- butyl-p-cresol is 2mg/m3.
Environmental Fate
The metabolites of Butylated Hydroxytoluene can bind to cellular macromolecules, such as proteins and DNA, and cause toxicity.
Potential Exposure
DBPC is used as a food and feed additive, flavor, and packaging material; as an antioxidant in human foods and animal feeds. It is also used as an antioxidant to sta- bilize petroleum fuels, rubber and vinyl plastics.
Safety Profile
Poison by intraperitoneal andintravenous routes. Moderately toxic by ingestion. Anexperimental teratogen. Other experimental reproductiveeffects. A human skin irritant. A skin and eye irritant.Questionable carcinogen with experimental carcinogenicand.
Safety
Butylated hydroxytoluene is readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is metabolized and excreted in the urine mainly as glucuronide conjugates of oxidation products. Although there have been some isolated reports of adverse skin reactions, butylated hydroxytoluene is generally regarded as nonirritant and nonsensitizing at the levels employed as an antioxidant.
The WHO has set a temporary estimated acceptable daily intake for butylated hydroxytoluene at up to 125 μg/kg body-weight.
Ingestion of 4 g of butylated hydroxytoluene, although causing severe nausea and vomiting, has been reported to be nonfatal.
LD50 (guinea pig, oral): 10.7 g/kg
LD50 (mouse, IP): 0.14 g/kg
LD50 (mouse, IV): 0.18 g/kg
LD50 (mouse, oral): 0.65 g/kg
LD50 (rat, oral): 0.89 g/kg
storage
Exposure to light, moisture, and heat causes discoloration and a loss of activity. Butylated hydroxytoluene should be stored in a wellclosed container, protected from light, in a cool, dry place.
Shipping
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Purification Methods
Dissolve Butylated Hydroxytoluene in n-hexane at room temperature, then cool with rapid stirring, to -60o. The precipitate is separated, redissolved in hexane, and the process is repeated until the mother liquor is no longer coloured. The final product is stored under N2 at 0o [Blanchard J Am Chem Soc 82 2014 1960]. It has also been recrystallised from EtOH, MeOH, *benzene, n-hexane, methylcyclohexane or pet ether (b 60-80o), and is dried in a vacuum. [Beilstein 6 IV 3511.]
Toxicity evaluation
Butylated Hydroxytoluene is a white crystalline solid. It is insoluble in water and alkalies; but soluble in most common organic solvents such as alcohol and ether. Its melting point is 70°C, boiling point is 265°C, flash point is 127°C, and specific gravity is 1.048 at 20°C.
Incompatibilities
Contact with oxidizers may cause fire and explosion hazard.
Incompatibilities
Butylated hydroxytoluene is phenolic and undergoes reactions characteristic of phenols. It is incompatible with strong oxidizing agents such as peroxides and permanganates. Contact with oxidizing agents may cause spontaneous combustion. Iron salts cause discoloration with loss of activity. Heating with catalytic amounts of acids causes rapid decomposition with the release of the flammable gas isobutene.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Accepted as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (IM and IV injections, nasal sprays, oral capsules and tablets, rectal, topical, and vaginal preparations). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Butylated Hydroxytoluene Preparation Products And Raw materials
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tianjin Zhongxin Chemtech Co., Ltd. | +86-022-66880623 +8618622897568 | sales@tjzxchem.com | China | 563 | 58 |
| Ningxia Jinhua Chemical Co.,Ltd | 025-52279164 | info@nxjhchem.com | China | 79 | 58 |
| Henan Fengda Chemical Co., Ltd | +86-371-86557731 +86-13613820652 | info@fdachem.com | China | 20287 | 58 |
| Hebei Andu Technology Com.,Ltd | +86-86-17798073498 +8617798073498 | admin@hbandu.com | China | 299 | 58 |
| HebeiShuoshengImportandExportco.,Ltd | +86-18532138899 +86-18532138899 | L18532138899@163.com | China | 939 | 58 |
| Hebei Weibang Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +8615531157085 | abby@weibangbio.com | China | 8812 | 58 |
| Shaanxi Dideu Medichem Co. Ltd | +86-29-81148696 +86-15536356810 | 1022@dideu.com | China | 3882 | 58 |
| Hebei Mojin Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +86 13288715578 +8613288715578 | sales@hbmojin.com | China | 12840 | 58 |
| Hebei Yanxi Chemical Co., Ltd. | +8617531190177 | peter@yan-xi.com | China | 5857 | 58 |
| Wuhan Fortuna Chemical Co., Ltd | +86-027-59207850 | info@fortunachem.com | China | 5978 | 58 |
Related articles
- Butylated Hydroxytoluene: uses and side effects
- Butylated hydroxytoluene, a cresol derivative, is an additive used as an antioxidant in foods such as packet cake mixes, potat....
- Apr 22,2024
- The Antioxidant of Butylated Hydroxytoluene
- The passage introduces the antioxidant of Butylated Hydroxytoluene.
- Nov 17,2022
- Butylated Hydroxytoluene - Properties and Application
- Butylated hydroxytoluene are also be named as 2, 6-di-tert-butyl-4-methylphenol, 2, 6-di-tert-butyl-p-cresol, Antioxidant 264,....
- Mar 30,2020
Related Qustion
- Q:Is it safe to use Butylated Hydroxytoluene in skincare?
- A:Butylated hydroxytoluene, aka BHT, is a preservative and antioxidant found commonly in food and skincare products alike.
- Aug 20,2024
View Lastest Price from Butylated Hydroxytoluene manufacturers
| Image | Update time | Product | Price | Min. Order | Purity | Supply Ability | Manufacturer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
2024-11-22 | Butylated Hydroxytoluene
128-37-0
|
US $6.00 / kg | 1kg | 99% | 2000KG/Month | HebeiShuoshengImportandExportco.,Ltd | |
 |
2024-11-22 | BHT / Butylated Hydroxytoluene
128-37-0
|
US $120.00 / kg | 1kg | 99% | 20ton | Hebei Zhuanglai Chemical Trading Co.,Ltd | |
 |
2024-11-22 | Antioxidant
128-37-0
|
US $35.00 / kg | 1kg | ≥98% | 3000tons/month | Hebei Andu Technology Com.,Ltd |
-

- Butylated Hydroxytoluene
128-37-0
- US $6.00 / kg
- 99%
- HebeiShuoshengImportandExportco.,Ltd
-

- BHT / Butylated Hydroxytoluene
128-37-0
- US $120.00 / kg
- 99%
- Hebei Zhuanglai Chemical Trading Co.,Ltd
-

- Antioxidant
128-37-0
- US $35.00 / kg
- ≥98%
- Hebei Andu Technology Com.,Ltd
Butylated Hydroxytoluene Spectrum
128-37-0(Butylated Hydroxytoluene)Related Search:
1of4