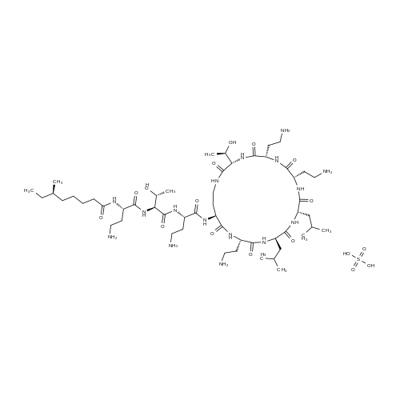
Colistin sulfate
- CAS No.
- 1264-72-8
- Chemical Name:
- Colistin sulfate
- Synonyms
- COLISTIN SULPHATE;POLYMYXIN E;COLISTINE SULFATE;CoL;COLISTIN SULFATE SALT;COLISTINE SULPHATE;belcomycin;Colomyci;istin suL;Belcomycine
- CBNumber:
- CB8359485
- Molecular Formula:
- 2(C52H98N16O13).5(H2SO4)
- Molecular Weight:
- 2801.27
- MDL Number:
- MFCD27976775
- MOL File:
- 1264-72-8.mol
| Melting point | 200-220°C |
|---|---|
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: soluble50mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| color | White to off-white |
| PH | 4.0~6.0(10g/l, 25℃) |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water |
| Merck | 14,2479 |
| InChIKey | VEXVWZFRWNZWJX-NBKAJXASSA-N |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1264-72-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EWG's Food Scores | 1 |
| FDA UNII | WP15DXU577 |
Colistin sulfate price More Price(35)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich | C4461 | Colistin sulfate salt ≥15,000 U/mg | 1264-72-8 | 1g | $254 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich | 1148001 | Colistin sulfate | 1264-72-8 | 200mg | $457 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Alfa Aesar | J67415 | Colistin sulfate, 50 mg/ml in distilled water, sterile-filtered | 1264-72-8 | 5x1ml | $233.65 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Alfa Aesar | J60915 | Colistin sulfate | 1264-72-8 | 1g | $169 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
| Cayman Chemical | 17584 | Colistin (sulfate) | 1264-72-8 | 1g | $33 | 2024-03-01 | Buy |
Colistin sulfate Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
White or almost white, hygroscopic powder.
Uses
Colistin sulfate A Polymyxin potent antibiotic and apoptosis inducer. This compound induces apoptosis through interaction with the cytoplasmic membrane. Colistin is a key microbiological component in Colistin Oxolinic Acid Blood Agar utilized in the cultivation of Aminobacter aminovorans, Bacillus species, Hyphomicrobium species and Methylobacterium species. It is also a critical component is VCN Inhibitor & VCNT Inhibitor growth media used in the isolation of Neisseria species.
Uses
Cyclic polypeptide antibiotic produced by Bacillus polymyxa. Complex mixture of at least 30 components, primarily colistins A and B. [a]D= -65?(c= 1, Water) LOD: 3%
Uses
antibacterial
Uses
neuromuscular blocker
brand name
Coly-Mycin (Monarch).
Antimicrobial activity
All the polymyxins have a similar antibacterial spectrum,
although there are slight quantitative differences in their
activity in vitro. They are inactive against Gram-positive
organisms, but nearly all enterobacteria, except Proteus spp.,
Burkholderia cepacia and Ser. marcescens, are highly susceptible.
The MIC of polymyxin B or colistin sulfate for Esch. coli
and Klebsiella spp. is 0.01–1 mg/L; the corresponding concentration
for Ps. aeruginosa is 0.03–4 mg/L. Bacteroides fragilis is
resistant, but other Bacteroides spp. and fusobacteria are susceptible.
Resistance of V. cholerae eltor to polymyxin B distinguishes
it from the classic vibrio.
The sulfomethyl derivatives are generally 4–8 times less
active than the sulfates, but their activity is difficult to measure
precisely since on incubation they spontaneously decay
to the parent compound, with a corresponding progressive
increase in antibacterial activity.
Binding of polymyxins to the bacterial cell membrane can
increase permeability to hydrophilic compounds, including
sulfonamides and trimethoprim, producing significant synergy.
Synergy with ciprofloxacin is also described. Calcium
ions exert a strong pH-dependent competition for membrane
binding sites, and the presence of calcium and magnesium
ions in certain culture media adversely affects the bactericidal
activity, notably against Ps. aeruginosa.
Acquired resistance
There is complete cross-resistance between the polymyxins, but stable acquired resistance in normally susceptible species is very rare. Adaptive resistance, probably due to changes in cell-wall permeability, is readily achieved by passage of a variety of enterobacteria in the presence of the agents in vitro.
General Description
In 1950, Koyama et al. isolated an antibiotic fromAerobacillus colistinus (B. polymyxa var. colistinus) thatwas given the name colistin (Coly-Mycin S). It was used inJapan and in some European countries for several years beforeit was made available for medicinal use in the UnitedStates. It is recommended especially for the treatment of refractory urinary tract infections caused by Gram-negativeorganisms such as Aerobacter, Bordetella, Escherichia,Klebsiella, Pseudomonas, Salmonella, and Shigella spp.
Chemically, colistin is a polypeptide, reported by Suzukiet al. whose major component is colistin A. They proposedthe structure for colistin A differs from polymyxin B only by the substitution of D-leucine for D-phenylalanine as one of the amino acid fragments inthe cyclic portion of the structure. Wilkinson and Lowehave corroborated the structure and have shown that colistinA is identical with polymyxin E1.
Two forms of colistin have been prepared, the sulfate andmethanesulfonate, and both forms are available for use in theUnited States. The sulfate is used to make an oral pediatricsuspension; the methanesulfonate is used to make an intramuscularinjection. In the dry state, the salts are stable, andtheir aqueous solutions are relatively stable at acid pH from 2to 6. Above pH 6, solutions of the salts are much less stable.
Hazard
A poison by ingestion.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Polymyxin B and colistin (polymyxin E); mixtures of sulfates
of polypeptides produced by strains of B. polymyxa and
B. polymyxa var. colistinus. Colistimethate sodium (colistin sulfomethate
sodium). Molecular weights: polymyxin B 1 1203;
polymyxin B 2 1189; colistimethate sodium 1748.
A group of basic polypeptide antibiotics with a side chain terminated
by characteristic fatty acids. Five polymyxins (A–E)
were originally characterized and others have since been
added. Polymyxin B and colistin (polymyxin E) sulfates have
been commercially developed.
By treatment with formalin and sodium bisulfite, five of
the six diaminobutyric acid groups of the polymyxins can be
modified by sulfomethyl groups to form undefined mixtures
of the mono-, di-, tri-, tetra- and penta-substituted derivatives.
Sulfomethyl polymyxins differ considerably in their properties from the parent antibiotics: they are less active
antibacterially, less painful on injection, more rapidly excreted
by the kidney and less toxic. Only colistimethate sodium is
now commercially available for systemic use, but polymyxin
B and colistin sulfates are found as ingredients of several topical
formulations.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Mode of Action: Binds to lipids on the cell cytoplasmic membrane of Gram-negative bacteria and disrupts the cell wall integrity. Antimicrobial spectrum: Gram-negative bacteria. It is proposed that renal reabsorption of colistin may involve organic cation transporters and peptide transporters and that the process is sensitive to pH .
Pharmacokinetics
Oral absorption: Negligible
Cmax (colistimethate sodium) 2 mega-units: 6–7 mg/L after 2–3 h
(c. 16 mg colistin base) i.m.
Plasma half-life (colistimethate sodium): c.4–6 h
Plasma protein binding: Very low
Absorption
Polymyxins are not absorbed from the alimentary tract or
mucosal surfaces, but can be absorbed from denuded areas
or large burns.
Distribution
After parenteral administration of the sulfates, blood levels are
usually low (1–4 mg/L 2 h after a 500 000 unit intramuscular
dose). Substantially higher plasma levels are obtained from
intramuscular injections of sulfomethyl polymyxins. There
is some accumulation in patients receiving 120 mg every
8 h. In patients treated intravenously with a priming dose of
1.5–2.5 mg/kg followed by continuous infusion of 4.8–6.0 mg/h
for 20–30 h, steady state levels were around 5–10 mg/L.
The volume of distribution is unknown, but polymyxins
diffuse poorly into tissue fluids and penetration to cerebrospinal
fluid is poor. As a result of binding to mammalian cell
membranes (sulfomethates less so), they persist in the tissues,
where they accumulate on repeated dosage, although they disappear
from the serum. Polymyxin crosses the placenta, but
the levels achieved are low. A small amount appears in the
breast milk.
Metabolism and excretion
The sulfates are excreted almost entirely by the kidney, but
after a considerable lag, with very little of the dose appearing
in the first 12 h. The sulfomethyl derivatives are much
more rapidly excreted, accounting for their shorter half-lives.
Around 80% of a parenteral dose of colistimethate sodium
is eventually found in the urine, with concentrations reaching
around 100–300 mg/L at 2 h. The fate of the remainder
is unknown, but no metabolic products have been described
and none is excreted in the bile. Polymyxins accumulate in
renal failure and are not removed by peritoneal dialysis.
Clinical Use
Colistimethate sodium
Infections due to Ps. aeruginosa and other Gram-negative rods resistant to
less toxic agents
Cystic fibrosis (inhalation therapy for pseudomonas infection)
Polymyxin B and colistin sulfate
Component of preparations for local application
Superficial infections with Ps. aeruginosa and to prevent the colonization
of burns
Selective decontamination of the gut and as a paste for control of
upper respiratory tract colonization in patients on prolonged mechanical
ventilation (in combination with other agents)
Side effects
Pain and tissue injury can occur at the site of injection of the
sulfates, but this is less of a problem with the sulfomethyl
derivatives. Neurological symptoms such as paresthesia with
typical numbness and tingling around the mouth, dizziness
and weakness are relatively common, and neuromuscular
blockade, sometimes severe enough to impede respiration,
occurs. Evidence of nephrotoxicity is observed in about 20%
of patients, leading to acute tubular necrosis in about 2%.
Damage is more likely in patients with pre-existing renal disease.
The appearance of any evidence of deterioration of renal
function or of neuromuscular blockade calls for immediate
cessation of treatment. All the toxic manifestations appear to
be reversible, but complete recovery may be slow.
Although less toxic than the sulfate, untoward effects
have been observed in up to one-quarter of those treated with colistimethate sodium. Nephrotoxicity is common, with
an increase in urea and creatinine over the first few days of
treatment. Acute tubular necrosis is heralded by the appearance
of proteinuria, hematuria and casts, sometimes without
prior evidence of functional impairment. Renal damage usually
continues to progress for up to 2 weeks after withdrawal
of therapy. Renal damage is likely to increase with the dose
and with the simultaneous administration of other potentially
nephrotoxic agents.
Manifestations of central and peripheral neurotoxicity
occur particularly in patients with impaired renal function.
Neuromuscular blockade is seen principally in patients also
receiving anesthetics or other agents that impair neuromuscular
transmission. Complete flaccid paralysis with respiratory
arrest and subsequent complete recovery has been seen in a
patient with myasthenia gravis. Allergy is occasionally seen, and
nebulized colistin has caused bronchial hyperreactivity with
tightness in the chest in adults with cystic fibrosis. Application
of colistin or polymyxin B ear drops can lead to ototoxicity.
Safety Profile
A poison by ingestion, intraperitoneal, subcutaneous, and intravenous routes. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic vapors of NOx and SOx.
Colistin sulfate Preparation Products And Raw materials
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jiangsu Guotai Guomian Trading Co. Ltd. | +86-512-58916079 +86-13601562190 | pharmachem@gtgmt.com | China | 148 | 58 |
| Shaanxi Dideu Medichem Co. Ltd | +86-29-81148696 +86-15536356810 | 1022@dideu.com | China | 3882 | 58 |
| Hebei Mojin Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +86 13288715578 +8613288715578 | sales@hbmojin.com | China | 12837 | 58 |
| Hebei Chuanghai Biotechnology Co,.LTD | +86-13131129325 | sales1@chuanghaibio.com | China | 5889 | 58 |
| shandong perfect biotechnology co.ltd | +86-53169958659 +86-13153181156 | sales@sdperfect.com | China | 294 | 58 |
| Henan Bao Enluo International TradeCo.,LTD | +86-17331933971 +86-17331933971 | deasea125996@gmail.com | China | 2472 | 58 |
| Shaanxi Haibo Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +undefined18602966907 | qinhe02@xaltbio.com | China | 997 | 58 |
| Shaanxi TNJONE Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd | +8618092446649 | sarah@tnjone.com | China | 1143 | 58 |
| Hebei Zhuanglai Chemical Trading Co Ltd | +86-16264648883 +86-16264648883 | niki@zlchemi.com | China | 2397 | 58 |
| Capot Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-(0)57185586718 +86-13336195806 | sales@capot.com | China | 29791 | 60 |
Related articles
- An antibiotic-colistin sulfate
- Colistin sulfate is a polypeptide antibiotic which inhibits gram-negative bacteria by binding to lipopolysaccharides and phosp....
- Sep 11,2019
View Lastest Price from Colistin sulfate manufacturers
| Image | Update time | Product | Price | Min. Order | Purity | Supply Ability | Manufacturer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
2024-12-18 | Colisti Sulfate
1264-72-8
|
US $150.00 / kg | 1kg | 99% | 500kg | Hebei Zhuanglai Chemical Trading Co Ltd | |
 |
2024-12-13 | Colistin sulfate
1264-72-8
|
US $1.00 / KG | 1KG | EP10 | 1ton/month | WUHAN FORTUNA CHEMICAL CO., LTD | |
 |
2024-11-19 | Colistin sulfate
1264-72-8
|
US $81.00-48.00 / mg | ≥95% | 10g | TargetMol Chemicals Inc. |
-

- Colisti Sulfate
1264-72-8
- US $150.00 / kg
- 99%
- Hebei Zhuanglai Chemical Trading Co Ltd
-

- Colistin sulfate
1264-72-8
- US $1.00 / KG
- EP10
- WUHAN FORTUNA CHEMICAL CO., LTD
-

- Colistin sulfate
1264-72-8
- US $81.00-48.00 / mg
- ≥95%
- TargetMol Chemicals Inc.
1264-72-8(Colistin sulfate)Related Search:
1of4