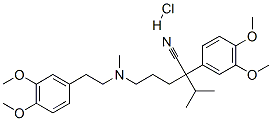
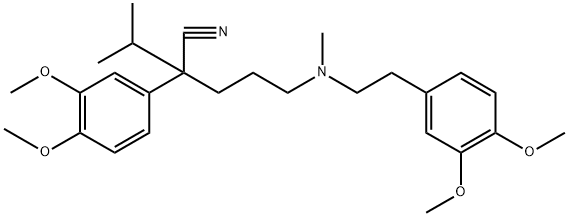
Verapamil hydrochloride
- CAS No.
- 23313-68-0
- Chemical Name:
- Verapamil hydrochloride
- Synonyms
- CALAN;ISOPTIN;Veracim;Veramex;Zolvera;Dignover;Berkatens;Cardibeltin;IPROVERATRIL;VERAPAMIL HCL
- CBNumber:
- CB9460012
- Molecular Formula:
- C27H39ClN2O4
- Molecular Weight:
- 491.06
- MDL Number:
- MFCD00055208
- MOL File:
- 23313-68-0.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
| Melting point | 142 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
|---|---|
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | methanol: 50 mg/mL, clear, colorless |
| form | powder |
| color | white |
| BCS Class | 1,2 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 23313-68-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| FDA UNII | V3888OEY5R |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Hazard Codes | T,Xi |
|---|---|
| Risk Statements | 23/24/25-36/37/38 |
| Safety Statements | 36/37-45-37/39-26 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | YV8320000 |
| F | 8-10 |
Verapamil hydrochloride price
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tocris | 0654 | Verapamil hydrochloride ≥99%(HPLC) | 23313-68-0 | 1G | $103 | 2021-12-16 | Buy |
| Usbiological | 257041 | Verapamil hydrochloride | 23313-68-0 | 1g | $347 | 2021-12-16 | Buy |
| Usbiological | V2121-49L | Verapamil Hydrochloride | 23313-68-0 | 5g | $403 | 2021-12-16 | Buy |
| Usbiological | 291917 | Verapamil hydrochloride | 23313-68-0 | 50g | $425 | 2021-12-16 | Buy |
| Medical Isotopes, Inc. | 14158 | VerapamilHCl | 23313-68-0 | 25g | $1760 | 2021-12-16 | Buy |
Verapamil hydrochloride Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Verapamil hydrochloride (VRP) is a phenylalkylamine calcium ion influx inhibitor (calcium antagonist). Verapamil hydrochloride exerts its pharmacologic effects by modulating the influx of ionic through the slow channels of vascular smooth muscle and cardiac cell membranes. It is widely used for the treatment of hypertension, angina pectoris, supraventricular tachycardia, myocardial infraction, and vascular headaches. Verapamil has also been used in cell biology as an inhibitor of drug efflux pump proteins such as P-glycoprotein, which are often over-expressed in certain tumor cell lines The plasma half-life of verapamil hydrochloride is 2–7 hours, which necessitates multiple dosing. After oral administration of VRP to humans, the drug is rapidly absorbed and widely distributed. It is approximately 90% absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract but is subject to considerable first pass metabolism and its bioavailability is around 20–30%. The low bioavailability is owing to the rapid biotransformation in the liver with a biological half-life of 4.0±1.5 hours.
References
[1] https://dailymed.nlm.nih.gov/dailymed/drugInfo.cfm?setid=3bee2d26-138c-4641-a217-a38d3d657461
[2] V. Kusum Devi, S. Saisivam, G. R. Maria, P. U. Deepti (2003) Design and Evaluation of Matrix Diffusion Controlled Transdermal Patches of Verapamil Hydrochloride, 29, 495-503.
[3] https://www.caymanchem.com/product/14288
[4] Yuveraj Singh Tanwar, Pushpendra Singh Naruka, Garima Rani Ojha (2007) Development and evaluation of floating microspheres of verapamil hydrochloride, 43, 529-534
Chemical Properties
White Powder
Uses
A calcium channel blocker. Antihypertensive; antianginal; antiarrhythmic (class IV)
Uses
Calcium antagonists
brand name
Calan (Searle); Covera (Searle); Isoptin (FSC); Isoptin (Par); Verelan (Elan).
Clinical Use
Calcium-channel blocker:
Supraventricular arrhythmias
Angina
Hypertension
Cluster headaches (unlicensed)
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Veterinary experience with this agent is somewhat limited, but in dogs and cats verapamil may be useful for supraventricular tachycardias and, possibly, treatment of atrial flutter or fibrillation.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Aminophylline and theophylline: enhanced effect of
aminophylline and theophylline.
Anaesthetics: increased hypotensive effect.
Anti-arrhythmics: increased risk of amiodaroneinduced bradycardia, AV block and myocardial
depression; increased risk of myocardial depression
and asystole with disopyramide and flecainide;
increased risk of bradycardia and myocardial
depression with dronedarone.
Antibacterials: metabolism increased by rifampicin;
metabolism possibly inhibited by erythromycin,
clarithromycin and telithromycin (increased risk of
toxicity).
Anticoagulants: possibly increases dabigatran
concentration - reduce dabigatran dose.
Antidepressants: enhanced hypotensive effect with
MAOIs; concentration of imipramine and possibly
other trycyclics increased; concentration significantly
reduced by St John’s wort.
Antiepileptics: effect probably reduced by
barbiturates, phenytoin and primidone; enhanced
effect of carbamazepine.
Antifungals: negative inotropic effect possibly
increased with itraconazole.
Antihypertensives: enhanced hypotensive effect,
increased risk of first dose hypotensive effect of postsynaptic alpha-blockers.
Antipsychotics: possibly increases concentration of
lurasidone.
Antivirals: concentration possibly increased by
atazanavir and ritonavir; use telaprevir with caution.
Avanafil: concentration of avanafil increased.
Beta-blockers: enhanced hypotensive effect; risk of
asystole, severe hypotension and heart failure if coprescribed with beta-blockers.
Cardiac glycosides: increased levels of digoxin.
Increased AV block and bradycardia.
Ciclosporin: variable reports of decreased
nephrotoxicity and potentiated effect; may also
increase ciclosporin levels.
Colchicine: possibly increased risk of colchicine
toxicity - suspend or reduce colchicine, avoid
concomitant use in renal or hepatic failure.
Cytotoxics: possibly increased bosutinib,
doxorubicin, ibrutinib concentration - reduce dose
of bosutinib and ibrutinib; possibly increased risk
of bradycardia with crizotinib; concentration of
both drugs may be increased in combination with
everolimus - consider reducing everolimus dose;
concentration of olaparib possibly increased - avoid
or reduce olaparib dose.
Fingolimod: increased risk of bradycardia.
Grapefruit juice: concentration increased - avoid
concomitant use.
Ivabradine: concentration of ivabradine increased -
avoid concomitant use.
Lenalidomide: possibly increases lenalidomide
concentration.
Lipid-lowering agents: increased myopathy with
atorvastatin and simvastatin - reduce dose of
atorvastatin, do not exceed 20 mg of simvastatin1
,
concentration of verapamil increased by atorvastatin;
concentration of lomitapide increased - avoid.
Sirolimus: concentration of both drugs increased.
Tacrolimus: may increase tacrolimus levels.
Metabolism
Verapamil undergoes considerable first pass loss and is
extensively metabolised in the liver. 12 metabolites have been
identified. Of these only norverapamil has any significant
activity (approximately 20
% that of the parent compound).
Norverapamil represents about 6
% of the dose eliminated
in urine and reaches steady-state plasma concentrations
approximately equal to those of verapamil. About 70
%
of a dose is excreted by the kidneys in the form of its
metabolites but about 16
% is excreted in the bile into the
faeces. Less than 4
% is excreted unchanged.
Purification Methods
The salt is purified by dissolving it in EtOH, filtering (if insoluble particles are present) and adding Et2O, filtering the salt, washing it with Et2O and drying it in vacuo. It has the following solubilities: hexane (0.001%), CH2Cl2 (~10%), MeOH (~10%), EtOH (20%) and H2O (8.3%). It has UV max at 232 and 278nm. The free base is a viscous yellow oil b 243-246o/0.01mm (n 25D 1.5448) and is almost insoluble in H2O but soluble in organic solvents. It is a Ca channel antagonist and is a coronary vasodilator. [Ramuz Helv Chim Acta 58 2050 1975, Harvey et al. Biochem J 257 95 1989.]
Verapamil hydrochloride Preparation Products And Raw materials
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Shaanxi TNJONE Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd | +8618740459177 | sarah@tnjone.com | China | 1143 | 58 |
| career henan chemical co | +86-0371-86658258 +8613203830695 | factory@coreychem.com | China | 29825 | 58 |
| Longyan Tianhua Biological Technology Co., Ltd | 0086 18039857276 18039857276 | CHINA | 2783 | 58 | |
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co.,Ltd. | +86-0551-65418671 +8618949823763 | sales@tnjchem.com | China | 34571 | 58 |
| Shaanxi Dideu Medichem Co. Ltd | +86-029-89586680 +86-18192503167 | 1026@dideu.com | China | 8840 | 58 |
| Wuhan Fortuna Chemical Co., Ltd | +86-027-59207850 | info@fortunachem.com | China | 5989 | 58 |
| Baoji Guokang Bio-Technology Co., Ltd. | 0917-3909592 13892490616 | gksales1@gk-bio.com | China | 9319 | 58 |
| Wuhan Golt Biotech Co., Ltd. | +8615389281203 | maria@goltbiotech.com | China | 980 | 58 |
| SUZHOU SENFEIDA CHEMICAL CO.,LTD | +86-0512-83500002 +8615195660023 | sales@senfeida.com | China | 23053 | 58 |
| LEAPCHEM CO., LTD. | +86-852-30606658 | market18@leapchem.com | China | 43348 | 58 |
View Lastest Price from Verapamil hydrochloride manufacturers
| Image | Update time | Product | Price | Min. Order | Purity | Supply Ability | Manufacturer | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
2024-09-06 | Verapamil hydrochloride
23313-68-0
|
US $0.00 / KG | 1KG | 99%,USP | 500kg/month | WUHAN FORTUNA CHEMICAL CO., LTD | |
 |
2024-05-07 | Verapamil Hydrochloride
23313-68-0
|
US $0.00 / kg | 1kg | 99% | 10000kg | Shaanxi TNJONE Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd | |
 |
2021-07-10 | Verapamil hydrochloride
23313-68-0
|
US $15.00-10.00 / KG | 1KG | 99%+ HPLC | Monthly supply of 1 ton | Zhuozhou Wenxi import and Export Co., Ltd |
-

- Verapamil hydrochloride
23313-68-0
- US $0.00 / KG
- 99%,USP
- WUHAN FORTUNA CHEMICAL CO., LTD
-

- Verapamil Hydrochloride
23313-68-0
- US $0.00 / kg
- 99%
- Shaanxi TNJONE Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd
-

- Verapamil hydrochloride
23313-68-0
- US $15.00-10.00 / KG
- 99%+ HPLC
- Zhuozhou Wenxi import and Export Co., Ltd
23313-68-0(Verapamil hydrochloride)Related Search:
1of4