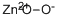Zinc peroxide
- CAS No.
- 1314-22-3
- Chemical Name:
- Zinc peroxide
- Synonyms
- zpo;GYHX;ai3-03965;Zinkperoxid;Zincperoxid;ZINC DIOXIDE;ZINC PEROXIDE;Zinc superoxide;Zinc peroxide,55%;Zinc dioxidanediide
- CBNumber:
- CB9853036
- Molecular Formula:
- O2Zn
- Molecular Weight:
- 97.39
- MDL Number:
- MFCD00137469
- MOL File:
- 1314-22-3.mol
| Melting point | 212 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
|---|---|
| Density | 1.57 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| solubility | insoluble in H2O; reacts with acid solutions,ethanol, acetone |
| form | Powder |
| Specific Gravity | 1.571 |
| color | yellow-white |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble in water. |
| Merck | 14,10149 |
| Exposure limits |
ACGIH: TWA 2 mg/m3; STEL 10 mg/m3 OSHA: TWA 5 mg/m3; TWA 15 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 500 mg/m3; TWA 5 mg/m3; STEL 10 mg/m3; Ceiling 15 mg/m3 |
| LogP | -0.425 (est) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1314-22-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EWG's Food Scores | 2-3 |
| FDA UNII | 0I969DVM77 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Zinc peroxide (Zn(O2)) (1314-22-3) |
| UNSPSC Code | 12352303 |
| NACRES | NA.23 |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS03,GHS07,GHS09 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H271-H315-H319-H410 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P210-P220-P264-P273-P302+P352-P305+P351+P338 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | O,N,Xi | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 9-50/53-8-36/38 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 24/25-27-17-61-60-26 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 1516 5.1/PG 2 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 5.1 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | II | |||||||||
| Hazardous Substances Data | 1314-22-3(Hazardous Substances Data) | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
Zinc peroxide Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
Zinc Peroxide, solid and generally similar in its properties to magnesium peroxide. The commercial product is a pale yellow powder containing about 55% ZnO2 and 9% active oxygen. It is stable in dry air but loses its oxygen in moist air and on heating. It is insoluble in water but dissolves in dilute acid, liberating hydrogen peroxide.
Chemical Properties
White powder containing 45–60% ZnO2, balance ZnO. Decomposes rapidly above 150C. Decomposes in acids, alcohol, acetone; insoluble in water but decomposed by it.
Uses
Zinc peroxide is used as curing agent, rubber accelerator. has been applied in a variety of settings, from medicine to aesthetics.
Uses
Zinc peroxide is used as an accelerator in rubber-compounding, as a curing agent for synthetic elastomers, and as a deodorant for wounds and skin diseases.
Uses
Accelerator in rubber compounding; curing agent for synthetic elastomers. Deodorant for wounds and skin diseases.
General Description
A white powder.
Air & Water Reactions
Slowly decomposed by water.
Reactivity Profile
Zinc peroxide dissolves in dilute acid, liberating hydrogen peroxide [Merck 11th ed. 1989]. Noncombustible but accelerates the burning of combustible material. If the combustible material is finely divided, the mixture may be explosive. Mixtures with combustible material can sometimes be ignited by friction or contact with moisture.The hydrated material (of indefinite composition) explodes at 212°C. Mixtures with aluminum or zinc powder burn brilliantly [Mellor 1940. v. 4, 530].
Health Hazard
TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or contact (skin, eyes) with vapors, dusts or substance may cause severe injury, burns or death. Fire may produce irritating and/or toxic gases. Toxic fumes or dust may accumulate in confined areas (basement, tanks, hopper/tank cars, etc.). Runoff from fire control or dilution water may cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
May explode from friction, heat or contamination. These substances will accelerate burning when involved in a fire. May ignite combustibles (wood, paper, oil, clothing, etc.). Some will react explosively with hydrocarbons (fuels). Containers may explode when heated. Runoff may create fire or explosion hazard.
reaction suitability
reagent type: catalyst
core: zinc
reagent type: oxidant
Safety Profile
Systemic toxicity is similar to zinc oxide. Flammable when SYN: ZINC SUPEROXIDE 212.. Can react.iolently with A. and Zn. Very dangerous, wdl react with water or steam to produce heat. Vigorous reaction with reducing materials. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of ZnO. See also PEROXIDES and ZINC COMPOUNDS.