LUTETIUM
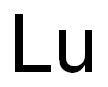
- CAS No.
- 7439-94-3
- Chemical Name:
- LUTETIUM
- Synonyms
- Lu;LUTETIUM;Lutecium;LU006010;Cassiopeum;838Lutetium;Lutetium foil;Lutetiumchips;lutetium atom;LUTETIUM, LUMP
- CBNumber:
- CB2168799
- Molecular Formula:
- Lu
- Molecular Weight:
- 174.97
- MOL File:
- 7439-94-3.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2023/10/17 17:11:56
| Melting point | 1663 °C (lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 3402 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 9.84 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| storage temp. | Flammables area |
| solubility | soluble in dilute acid solutions |
| form | powder |
| color | Silver-gray |
| Specific Gravity | 9.842 |
| Resistivity | 54 μΩ-cm, 20°C |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble in water. |
| Sensitive | Air & Moisture Sensitive |
| Merck | 13,5635 |
| Exposure limits |
ACGIH: TWA 2 ppm; STEL 4 ppm OSHA: TWA 2 ppm(5 mg/m3) NIOSH: IDLH 25 ppm; TWA 2 ppm(5 mg/m3); STEL 4 ppm(10 mg/m3) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7439-94-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Lutetium (7439-94-3) |
| Poissons Ratio | 0.261 |
|---|---|
| Shear Modulus | 27.2 GPa |
| Hardness, Vickers | 44 |
| Bulk Modulus | 47.6 GPa |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS02 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H228 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P210-P240-P241-P280-P370+P378 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | F,Xi | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 11-36/38 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 16-33-36/37/39-26 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 3089 4.1/PG 2 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 4.1 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
LUTETIUM price More Price(16)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALFA India | ALF-012410-06 | Lutetium pieces, distilled dendritic, 99.9% (REO) | 7439-94-3 | 5G | ₹78485 | 2022-05-26 | Buy |
| ALFA India | ALF-012410-03 | Lutetium pieces, distilled dendritic, 99.9% (REO) | 7439-94-3 | 1g | ₹11979 | 2022-05-26 | Buy |
| ALFA India | ALF-010228-FI | Lutetium foil, 0.1mm (0.004in) thick, 99.9% (REO) | 7439-94-3 | 50x50mm | ₹86982 | 2022-05-26 | Buy |
| ALFA India | ALF-010228-FF | Lutetium foil, 0.1mm (0.004in) thick, 99.9% (REO) | 7439-94-3 | 25x25mm | ₹48380 | 2022-05-26 | Buy |
| ALFA India | ALF-000628-06 | Lutetium pieces, 99.9% (REO) | 7439-94-3 | 5G | ₹76039 | 2022-05-26 | Buy |
LUTETIUM Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
grey powder
Physical properties
In the last (17th) position in the lanthanide series, lutetium is the heaviest and largestmolecule of all the rare-earths as well as the hardest and most corrosion-resistant. It has asilvery-white color and is somewhat stable under normal atmospheric conditions.
Its melting point is 1,663°C, its boiling point is 3,402°C, and its density is 9.84g/cm3.
Isotopes
There are a total of 59 isotopes of Lutetium. Only two of these are stable: Lu-175, which makes up 97.41% of all the natural abundance found on Earth. The otheris a long-lived radioisotope (Lu-176) with such a long half-life (4.00×10+10 years) thatit is considered stable: Lu-176 contributes 2.59% to the natural abundance of lutetium.
Origin of Name
Lutetium’s name is derived from the ancient Latin name for Paris, France: Lutecia.
Occurrence
Lutetium is the 60th most abundant element on Earth, and it ranks 15th in the abundanceof the rare-earths. It is one of the rarest of the lanthanide series. It is found in monazite sand(India, Australia, Brazil, South Africa, and Florida), which contains small amounts of all therare-earths. Lutetium is found in the concentration of about 0.0001% in monazite. It is difficultto separate it from other rare-earths by the ion-exchange process. In the pure metallicform, lutetium is difficult to prepare, which makes is very expensive.
Characteristics
Lutetium has had a number of different names over the years. At one time or another,it was called neoytterbium, lutecium, lutetia, lutetium, and cassiopium. Some scientists inGermany still refer to it as cassiopium.
Lutetium reacts slowly with water and is soluble in weak acids. Its crystals exhibit strongmagnetic properties, which are important to the study of magnetism.
History
In 1907, Urbain described a process by which Marignac’s ytterbium (1879) could be separated into the two elements, ytterbium (neoytterbium) and lutetium. These elements were identical with “aldebaranium” and “cassiopeium,” independently discovered by von Welsbach about the same time. Charles James of the University of New Hampshire also independently prepared the very pure oxide, lutecia, at this time. The spelling of the element was changed from lutecium to lutetium in 1949. Lutetium occurs in very small amounts in nearly all minerals containing yttrium, and is present in monazite to the extent of about 0.003%, which is a commercial source. The pure metal has been isolated only in recent years and is one of the most difficult to prepare. It can be prepared by the reduction of anhydrous LuCl3 or LuF3 by an alkali or alkaline earth metal. The metal is silvery white and relatively stable in air. While new techniques, including ion-exchange reactions, have been developed to separate the various rare-earth elements, lutetium is still the most costly of all rare earths. It is priced at about $100/g (99.9%). 176Lu occurs naturally (97.41%) with 175Lu (2.59%), which is radioactive with a very long half-life of about 4 × 1010 years. Lutetium has 50 isotopes and isomers that are now recognized. Stable lutetium nuclides, which emit pure beta radiation after thermal neutron activation, can be used as catalysts in cracking, alkylation, hydrogenation, and polymerization. Virtually no other commercial uses have been found yet for lutetium. While lutetium, like other rare-earth metals, is thought to have a low toxicity rating, it should be handled with care until more information is available.
Uses
Lutetium is the last member of the rare earth series. Unlike most rare earths it lacks a magnetic moment. It also has the smallest metallic radius of any rare earth. It is perhaps the least naturally abundant of the Lanthanides. It is the ideal host for x-ray phosphors because it produces the densest known white material, Lutetium Tantalate (LuTaO4). It is utilized as a dopant in matching lattice parameters of certain substrate garnet crystals, such as Indium-Gallium-Garnet (IGG) crystals due its lack of a magnetic moment.
Lutetium isotopes can data the age of meteorites and are used to target tumors experimentally. Stable lutetium can be used as catalysts in petroleum cracking in refineries and can also be used in alkylation, hydrogenation, and polymerization applications.
Lutetium Metal, is the hardest metal of the rare-earths, used as important additive to some specialty alloy. Stable Lutetium can be used as catalysts in petroleum cracking in refineries and can also be used in alkylation, hydrogenation, and polymerization applications. Lutetium is used as a phosphor in LED light bulbs.
Definition
A silvery element of the lanthanoid series of metals. It occurs in association with other lanthanoids. Lutetium is a very rare lanthanoid and has few uses. Symbol: Lu; m.p. 1663°C; b.p. 3395°C; r.d. 9.84 (25°C); p.n. 71; r.a.m. 174.967.
Hazard
Lutetium fluoride is a skin irritant, and its fumes are toxic if inhaled. The dust and powderof the oxides of some rare-earths, including lutetium, are toxic if inhaled or ingested.
LUTETIUM Preparation Products And Raw materials
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CHEMSWORTH | +91-261-2397244 | New Delhi, India | 6707 | 30 | Inquiry |
| Otto Chemie Pvt. Ltd. | +91 9820041841 | Mumbai, India | 5873 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Alfa Aesar | 1 800 209 7001 | Maharashtra, India | 6913 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Central Drug House(P) Ltd. | 91-11-49404040 | New Delhi, India | 6160 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Aritech Chemazone Private Limited | +91-9034345475 | Punjab, India | 684 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co.,Ltd. | 0551-65418671 | China | 34571 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Shaanxi Dideu Medichem Co. Ltd | +86-029-89586680 +86-18192503167 | China | 9030 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Zhuoer Chemical Co., Ltd | 02120970332; +8613524231522 | China | 3005 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Henan Alfa Chemical Co., Ltd | +8618339805032 | China | 13141 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Alfa Chemistry | United States | 24072 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| CHEMSWORTH | 30 |
| Otto Chemie Pvt. Ltd. | 58 |
| Alfa Aesar | 58 |
| Central Drug House(P) Ltd. | 58 |
| Aritech Chemazone Private Limited | 58 |
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co.,Ltd. | 58 |
| Shaanxi Dideu Medichem Co. Ltd | 58 |
| Zhuoer Chemical Co., Ltd | 58 |
| Henan Alfa Chemical Co., Ltd | 58 |
| Alfa Chemistry | 58 |
7439-94-3(LUTETIUM)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




