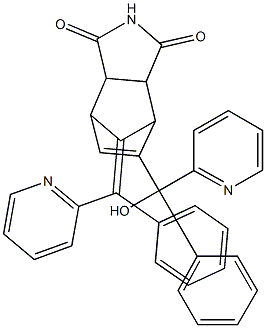
NORBORMIDE
- CAS No.
- 991-42-4
- Chemical Name:
- NORBORMIDE
- Synonyms
- s6999;Shoxin;mcn1025;s-6,999;raticide;Raticate;ent51,762;nobormide;mcneil1025;NORBORMIDE
- CBNumber:
- CB2693460
- Molecular Formula:
- C33H25N3O3
- Molecular Weight:
- 511.57
- MOL File:
- 991-42-4.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2023/5/4 15:14:08
| Melting point | 190-198° |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 598.31°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.2065 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.7800 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Amber Vial, -20°C Freezer, Under inert atmosphere |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly, Heated) |
| form | Solid |
| color | Crystals |
| Water Solubility | 60mg/L(room temperature) |
| Stability | Light Sensitive |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Norbormide (991-42-4) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Warning |
| Hazard statements | H302 |
| Precautionary statements | P264-P270-P301+P312-P330-P501 |
| Hazard Codes | Xn |
| Risk Statements | 22 |
| RIDADR | 2588 |
| HazardClass | 6.1(a) |
| PackingGroup | I |
| Toxicity | LD50 in rats (mg/kg): 5.3 orally; 0.65 i.v. (Roszkowski) |
NORBORMIDE Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Description
Norbormide was first introduced on the market in 1964 as a selective raticide, but does not have a current registration for commercial use in the European Union or North America. Current use as a pesticide is minimal to nonexistent worldwide. This compound’s toxicity is highly specific for rats.
Chemical Properties
White solid. Insoluble in water; soluble in dilute acids.
Uses
Norbormide is used as a rodenticide. It acts as a vasoconstrictor and calcium channel blocker, but is selectively toxic to rats and has relatively low toxicity to other species, due to a species specific action of opening the permeability transition pores in rat mitochondria.
Definition
A rodenticide specific for rats, supposedly nontoxic to other animals or to humans .
General Description
Colorless to off-white crystalline powder. Used as a selective rat poison.
Reactivity Profile
When heated to decomposition, NORBORMIDE emits toxic fumes of nitrogen oxides. Avoid alkalis. [EPA, 1998].
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion.
Health Hazard
Moderately to highly toxic to humans. Probable human lethal dose is 50 to 500 mg/kg, or 1 teaspoon to 1 pint for a 150 lb. person.
Fire Hazard
When heated to decomposition, NORBORMIDE emits toxic fumes of nitrogen oxides. Avoid alkalies.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion andintravenous routes. A rodenticide. When heated todecomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Potential Exposure
This material is used as a selective, fast acting rat poison.
Environmental Fate
Because of its use as a rodenticide, norbormide may have entered the environment, particularly as a soil contaminant. The vapor pressure for norbormide is estimated to be 4.3 ×10-22 mmHg at 25 ℃, while Henry’s constant is 2.7 × 10-23 atmm3 mol-1. Therefore, volatilization from wet or dry soil is not likely to occur. If present in contaminated soil, norbormide may be transported in the air and undergo wet or dry deposition. Also, with a Koc of 2000, there would be some minor soil mobility. The high Koc coupled with a bioconcentration factor (BCF) of 290 predicts that norbormide contaminating aquatic systems would adsorb to suspended solids or sediments and would bioconcentrate.
Shipping
UN2588 Pesticides, solid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Incompatibilities
Compounds of the carboxyl group react with all bases, both inorganic and organic (i.e., amines) releasing substantial heat, water and a salt that may be harmful. Incompatible with arsenic compounds (releases hydrogen cyanide gas), diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, and sulfides (releasing heat, toxic and possibly flammable gases), thiosulfates and dithionites (releasing hydrogen sulfate and oxides of sulfur).
Waste Disposal
Small amounts may be treated with alkali, then landfilled. Large amounts should be incinerated . In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.
NORBORMIDE Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CLEARSYNTH LABS LTD. | +91-22-45045900 | Hyderabad, India | 6351 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 | China | 21667 | 55 | Inquiry |
| Shenzhen Nexconn Pharmatechs Ltd | +86-755-89396905 +86-15013857715 | China | 10311 | 58 | Inquiry |
| TargetMol Chemicals Inc. | +1-781-999-5354 +1-00000000000 | United States | 19892 | 58 | Inquiry |
| SUZHOU SENFEIDA CHEMICAL CO.,LTD | +86-0512-83500002 +8615195660023 | China | 23048 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Aladdin Scientific | +1-+1(833)-552-7181 | United States | 52927 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Nantong Zhonghe Chemical New Materials Co., Ltd | 13003551299 13003551299 | China | 7567 | 58 | Inquiry |
| LGC Science (Shanghai) Ltd. | 17717235263 | China | 11677 | 58 | Inquiry |
| TargetMol Chemicals Inc. | 4008200310 | China | 23980 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Crescent Chemical Co., Inc. | 631 348 0333 | United States | 4599 | 68 | Inquiry |
991-42-4(NORBORMIDE)Related Search:
1of3
chevron_right




