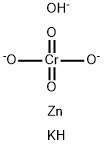
potassium hydroxyoctaoxodizincatedichromate(1-)
- CAS No.
- 11103-86-9
- Chemical Name:
- potassium hydroxyoctaoxodizincatedichromate(1-)
- Synonyms
- ZINCPOTASSIUMCHROMATES;Zinc Potassium Chromate;Potassium zinc chromate hydroxide;POTASSIUM ZINC CHROMATE HYDROXIDE, as Cr;POTASSIUMHYDROXYOCTAOXODIZINCATEDICHROMATE;potassium hydroxyoctaoxodizincatedichromate(1-);Chromate(1-), hydroxyoctaoxodizincatedi-, potassium;Potassium zinc chromate hydroxide (KZn2(CrO4)2(OH))
- CBNumber:
- CB3931275
- Molecular Formula:
- CrH2KO5Zn-3
- Molecular Weight:
- 238.49
- MOL File:
- 11103-86-9.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2024/12/18 14:08:52
| Water Solubility | 500mg/L at 20℃ |
|---|---|
| EPA Substance Registry System | Potassium zinc chromate hydroxide (11103-86-9) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS08,GHS09,GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H317-H302-H341-H410-H400-H361-H335-H350-H330 |
| Precautionary statements | P273-P391-P501-P201-P202-P281-P308+P313-P405-P501-P264-P270-P301+P312-P330-P501-P273-P391-P501-P261-P272-P280-P302+P352-P333+P313-P321-P363-P501-P201-P202-P281-P308+P313-P405-P501-P260-P271-P284-P304+P340-P310-P320-P403+P233-P405-P501 |
| RIDADR | 3288 |
| HazardClass | 6.1(a) |
| PackingGroup | II |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 11103-86-9(Hazardous Substances Data) |
potassium hydroxyoctaoxodizincatedichromate(1-) Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Uses
Zinc potassium chromate is one of several chromates used as anticorrosive agents in the formulation of coatings and primers. Chromates are widely used as inhibitors of corrosion and rust because of their unique ability to react at the metal coating interface to inhibit corrosion, especially galvanic couple corrosion (a chemical reaction that involves electron exchange between different metals). For example, using stainless steel screws on an aluminum part provides a high potential for electron transfer (galvanic couple corrosion). Even when present in very low concentrations, chromate has the unique ability to actively suppress electron transfer at both cathodic and anodic sites when different metallic parts are in contact. Active protection against rust depends on the ability of the inhibitor to migrate to the exposed surface once the protective coating has been scratched or damaged. Inhibitors dissolve in water and migrate to the exposed surface. If the inhibitor’s solubility is too great it may be washed away, if the solubility is too low the inhibitor will have low activity. According to the literature, strontium chromate has an ideal solubility (1.06 g l-1); zinc potassium chromate has similar solubility (0.5–1.5 g l-1) and is a very effective inhibitor. No single nonchrome inhibitor tested thus far acts in this way.
Safety Profile
Confirmed carcinogen. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of ZnO and K2O. Used as a corrosion inhibiting pigment and in steel priming. See also CHROMIUM COMPOUNDS and ZINC COMPOUNDS.
Environmental Fate
Chromium (both trivalent and hexavalent) enters the environment
from numerous natural and anthropogenic sources.
The health hazards of environmental exposure depend on the
oxidation state, with Cr(VI) being most toxic. Cr(VI) contamination
of groundwater typically occurs from industrial sources
such as electroplating or corrosion protection. Contamination
of surface water is commonly the result of particulate
discharges into the air from manufacturing and cooling towers,
with the particulates ultimately settling to either soil or surface
waters. For years, Cr(VI) was thought to arise environmentally
only as an industrial pollutant but recently unpolluted ground
and surface waters have been found to contain Cr(VI) in
concentrations that exceed the World Health Organization
limit for drinking water (50 mg l-1).
Much of the Cr(VI) in the environment is ultimately reduced
to the less toxic Cr(III). The reduction may be mediated by
various reducing agents such as sulfide compounds, and divalent
iron (Fe(II)). In addition, organic matter (e.g., humic acid and fulvic acid) in water or soil may mediate the reduction
process. Microbial processes also convert Cr(VI) to Cr(III).
potassium hydroxyoctaoxodizincatedichromate(1-) Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
Preparation Products
potassium hydroxyoctaoxodizincatedichromate(1-) Suppliers
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Trinity Pigment Industries | +91-9879558532 +91-7926444141 | Gujarat, India | 53 | 58 | Inquiry |
| XIAMEN AMITY INDUSTRY AND TRADE CO., LTD. | +8618950047208 | China | 43416 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Camida | +353-52-25455 | Europe | 3704 | 71 | Inquiry |
| CHEMICAL LAND21 | 82- 2 -783 - 8063 | South Korea | 6303 | 74 | Inquiry |
| Yick-Vic Chemicals & Pharmaceuticals (HK) Ltd | (852)2541 2772 | China | 6206 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Service Chemical Inc. | 888-895-6920 | Germany | 6350 | 71 | Inquiry |
| HONEST JOY HOLDINGS LIMITED | +86-755-26404303 | United States | 6675 | 54 | Inquiry |
| Portail Substances Chimiques | 10 20 0000 | France | 6024 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Hubei Xinyang Medical Technology Co., Ltd | 15347293736 15347293736 | China | 8932 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Shaanxi Dideu Newmaterial Co., Ltd. | 029-87576359 15353716720 | China | 10009 | 58 | Inquiry |





