RHENIUM
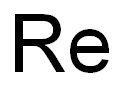
- CAS No.
- 7440-15-5
- Chemical Name:
- RHENIUM
- Synonyms
- RPMI;RHENIUM;RE005140;RE005110;RE005105;RE005115;RE005125;RE005130;RE005108;RE005106
- CBNumber:
- CB5179886
- Molecular Formula:
- Re
- Molecular Weight:
- 186.21
- MOL File:
- 7440-15-5.mol
- MSDS File:
- SDS
- Modify Date:
- 2024/5/31 14:34:02
| Melting point | 3180 °C (lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | 5596 °C (lit.) 5627 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 21.02 g/cm3 (lit.) |
| storage temp. | Flammables area |
| solubility | insoluble in HCl |
| form | wire |
| color | Silver-gray |
| Specific Gravity | 21.04 |
| Water Solubility | Insoluble in water. |
| Merck | 13,8261 |
| Exposure limits |
ACGIH: TWA 1 mg/m3 OSHA: TWA 15 mg/m3; TWA 5 mg/m3 |
| InChIKey | WUAPFZMCVAUBPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7440-15-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Rhenium (7440-15-5) |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 460 GPa |
|---|---|
| Poissons Ratio | 0.296 |
| Shear Modulus | 176 GPa |
| Hardness, Vickers | 550, 15% Cold-Worked |
| Hardness, Brinell | 500, Converted from Vickers for 3000 kg load/10 mm ball Brinell test. |
| Hardness, Rockwell A | 76, Converted from Vickers. |
| Hardness, Rockwell B | 85, Converted from Vickers. |
| Hardness, Rockwell C | 50, Converted from Vickers. |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |  GHS05 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger | |||||||||
| Hazard statements | H290-H314 | |||||||||
| Precautionary statements | P234-P280-P303+P361+P353-P304+P340+P310-P305+P351+P338-P363 | |||||||||
| Hazard Codes | C,F,Xi | |||||||||
| Risk Statements | 34-11-36/38 | |||||||||
| Safety Statements | 16-45-36/37/39-26-33-27 | |||||||||
| RIDADR | UN 3178 4.1/PG 2 | |||||||||
| WGK Germany | 3 | |||||||||
| RTECS | VI0780000 | |||||||||
| TSCA | Yes | |||||||||
| HazardClass | 8 | |||||||||
| PackingGroup | III | |||||||||
| HS Code | 8112993090 | |||||||||
| NFPA 704 |
|
RHENIUM price More Price(39)
| Manufacturer | Product number | Product description | CAS number | Packaging | Price | Updated | Buy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 83672 | Rhenium standard for AAS analytical standard, ready-to-use, in nitric acid | 7440-15-5 | 100ML | ₹6849.5 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 267317 | Rhenium foil, thickness 0.25?mm, 99.98% trace metals basis | 7440-15-5 | 3.3G | ₹34720.8 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 459984 | Rhenium foil, thickness 1.0?mm, 99.98% trace metals basis | 7440-15-5 | 13G | ₹64746.3 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| Sigma-Aldrich(India) | 267317 | Rhenium foil, thickness 0.25?mm, 99.98% trace metals basis | 7440-15-5 | 13.2G | ₹86457.9 | 2022-06-14 | Buy |
| ALFA India | ALF-014169-BW | Rhenium wire, 1.0mm (0.04in) dia, 99.97% (metals basis) | 7440-15-5 | 50cm | ₹69897 | 2022-05-26 | Buy |
RHENIUM Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
Depending on the process used to isolate and process it,
rhenium may appear as a brown-black powder or a silvery
white solid metal. Rhenium is among the least common of the
natural elements comprising 0.5–1 ppb of earth’s crust; it
generally occurs as a trace element in molybdenite, columbite,
gadolinite, and platinum ores. A sulfide mineral of
rhenium, rhenite exists but is very rare.
There are two naturally occurring isotopes, 185 (37%),
which is stable, and 187 (63%), which has a halftime of 1011
years, and several synthetic radioisotopes whose half-lives
range from ,<1 μs to 2×105 year. Rhenium has 11
valence states that range from 0 to 7.
Physical properties
Rhenium ranges in color from silvery-white to gray to a black powder. It is a rather denseelement. As a refined metal, rhenium is ductile, but because it is rather rare, its properties havenot found many uses. Rhenium does have the widest range of valences. In addition to its commonvalences of 4, 6, and 7, it also has the uncommon valences of 2, –1, and –7.
Rhenium has a high melting point of 3,180°C, a boiling point of 5,627°C, and a densityof 21.04 g/cm3.
Isotopes
There are 45 isotopes of rhenium. Only one of these is stable: Re-185, whichcontributes 37.40% to the total amount of rhenium found on Earth. Re-187, which isradioactive with a very long half-life of 4.35×10+10 years, contributes 62.60% to rhenium’sexistence on Earth. The remaining 43 isotopes are radioactive with relatively shorthalf-lives and are artificially manufactured.
Origin of Name
Derived from the Latin word Rhenus, which stands for the Rhine River in Western Europe.
Occurrence
Rhenium is the 78th most common element found on Earth, which makes it somewhatrare. During the early twentieth century, it required the processing of about a 1,000 poundsof earth to secure just one pound of rhenium, resulting in a price of about $10,000 per gram.Thus, there were few uses for rhenium. Later in the century, improved mining and refiningtechniques reduced the price. Today, the United States produces about 1,000 pounds of rheniumper year, and the world’s total estimated supply is only about 400 tons.
The main sources of rhenium are the molybdenite and columbite ores. Some rhenium isrecovered as a by-product of the smelting of copper sulfide (CuS) ores. Molybdenum sulfide(MoS2) is the main ore and is usually associated with igneous rocks and, at times, metallic-likedeposits. Molybdenite is found in Chile, as well as in the states of New Mexico, Utah, andColorado in the United States.
Characteristics
Rhenium is one of the transition elements, which range from metals to metal-like elements.Its chemical and physical properties are similar to those of technetium, which is aboveit in the periodic table. It is not very reactive. When small amounts are added to molybdenum,it forms a unique type of semiconducting metal. It is also noncorrosive in seawater.
Uses
Small quantities of rhenium are alloyed with iron to form steel that is both hard and resistantto wear and high-temperatures. Because of its high melting point, rhenium is used inmany applications where long-wearing, high-temperature electrical components are required,such as electrical contacts and switches and high-temperature thermocouples. This physicalquality makes rhenium alloys ideal for use in rocket and missile engines. It is also used to formthe filaments in photographic flash lamps.
Rhenium’s isotope (187Re) has a very long half-life and decays by both beta and alpharadiation at a very steady rate. This factor makes it useful as a standard to measure the age ofthe universe.
Production Methods
Among the compounds that can be formed with rhenium are sulfides, fluorides, chlorides, bromides, iodides, and oxides. Rhenium(VII) oxide, Re2O7, is the most stable oxide of rhenium. It is formed from rhenium metal powder or other rhenium oxides in dry air or an oxygen atmosphere above 350° °C. Re2O7 is readily soluble in water, forming perrhenic acid, HReO4, which forms salts (MReO4) such as ammonium perrhenate (NH4ReO4). This is an important starting material, which can be reduced to Re metal and used for the production of many other rhenium compounds. Rhenium can also form organometallic compounds such as carbonyls (e.g., Re2(CO)10 and organorhenium compounds such as hexamethylrhenium, Re(CH3)6.
Definition
rhenium: Symbol Re. A silvery white metallic transition element;a.n. 75; r.a.m. 186.2; r.d. 20.53; m.p.3180°C; b.p. 5627 (estimated)°C. Theelement is obtained as a by-productin refining molybdenum, and is usedin certain alloys (e.g. rhenium–molybdenum alloys are superconducting).The element forms a numberof complexes with oxidationstates in the range 1–7. It was discoveredby Walter Noddack (1893–1960)and Ida Tacke (1896–1978) in 1925.
Hazard
Rhenium is flammable in powder form. Rhenium dust and powder and many of its compoundsare toxic when inhaled or ingested.
Industrial uses
The outstanding properties of rhenium and rhenium alloys suggest their use in many specialized applications.Rhenium vs. tungsten thermocouples can be used for temperature measurement and control to approximately 2200 C, whereas previous thermocouple use was limited to temperatures below 1750 C. Indeed, 74% W 26% Re vs. W thermocouples can be used to temperatures of at least 2750 C with a high emf output ensuring accurate precise temperature measurements with excellent reproducibility and reliability.
Rhenium is now widely used for filaments for mass spectrographs and for ion gauges for measuring high vacuum. Its ductility, chemical properties, including the fact that it does not react with carbon to form a carbide, and its emission characteristics make it superior to tungsten for these applications.
Rhenium has received considerable acclaim as an electrical contact material. It possesses excellent resistance to wear as well as arc erosion. Furthermore, the contact resistance of rhenium is extremely stable because of its good corrosion resistance in addition to the fact that possible formation of an oxide film on the contacts would not cause any appreciable change in the contact resistance since the resistivity of the oxide is almost the same as that of the metal. Extensive tests for some types of make-andbreak switching contacts has shown rhenium to have 20 times the life of platinum palladium contacts currently in use.
RHENIUM Preparation Products And Raw materials
| Supplier | Tel | Country | ProdList | Advantage | Inquiry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Otto Chemie Pvt. Ltd. | +91 9820041841 | Mumbai, India | 5873 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Alfa Aesar | 1 800 209 7001 | Maharashtra, India | 6913 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Triveni chemicals | 08048762458 | New Delhi, India | 6093 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Central Drug House(P) Ltd. | 91-11-49404040 | New Delhi, India | 6160 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Aritech Chemazone Private Limited | +91-9034345475 | Punjab, India | 684 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Rare Earth (India) Unit Of Vijay Commercial House | 08046072837 | Mumbai, India | 32 | 58 | Inquiry |
| M/s M.R. Enterprises | 08048372615Ext 959 | Uttar Pradesh, India | 3 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Antarmana creations | 08046060256 | Delhi, India | 2 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Laxmi Narayan & Sons | 08048977891 | Mumbai, India | 22 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Kothari Filaments | 08047302056 | Kolkata, India | 3 | 58 | Inquiry |
| Supplier | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Otto Chemie Pvt. Ltd. | 58 |
| Alfa Aesar | 58 |
| Triveni chemicals | 58 |
| Central Drug House(P) Ltd. | 58 |
| Aritech Chemazone Private Limited | 58 |
| Rare Earth (India) Unit Of Vijay Commercial House | 58 |
| M/s M.R. Enterprises | 58 |
| Antarmana creations | 58 |
| Laxmi Narayan & Sons | 58 |
| Kothari Filaments | 58 |
Related articles
- Rhenium:Discovery,Minerals,Chemistry,Uses,Toxicity
- Rhenium exists as one stable isotope, 185Re, occurring in minority abundance. It is a silvery-white metal with one of the high....
- May 31,2024
- Industrial Applications of Rhenium metal
- Rhenium metal is used as an additive to tungsten and molybdenum-based alloys to impart useful properties at elevated temperatu....
- Sep 30,2019
- Preparation of Rhenium
- Rhenium is obtained commercially from molybdenum roaster-flue dusts obtained from the processing of copper-sulfide ores.
- Sep 29,2019
7440-15-5(RHENIUM)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




