FORMETANATE HYDROCHLORIDE
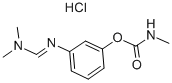
- CAS No.
- 23422-53-9
- Chemical Name:
- FORMETANATE HYDROCHLORIDE
- Synonyms
- ep332;ep-332;CARZOL;sn36056;carzolsp;DICARZOL;ent-27566;Nsc379585;mortonep332;nor-amep332
- CBNumber:
- CB8372321
- Molecular Formula:
- C11H16ClN3O2
- Molecular Weight:
- 257.72
- MOL File:
- 23422-53-9.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2025/1/27 9:38:02
| Melting point | 201℃ (decomposition) |
|---|---|
| Density | 1.3616 (rough estimate) |
| vapor pressure | 1.6 x 10-6 Pa (25 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.5270 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly), Water (Slightly) |
| pka | 8.0 (base) |
| Water Solubility | 822,000 mg l-1 (25 °C) |
| Stability | Hygroscopic |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Formetanate hydrochloride (23422-53-9) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |   GHS06,GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H300+H330-H317-H410 |
| Precautionary statements | P273-P280-P301+P310+P330-P302+P352-P304+P340+P310 |
| Hazard Codes | T+,N |
| Risk Statements | 26/28-43-50/53 |
| Safety Statements | 24-28-37/39-45-60-61 |
| RIDADR | 2757 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | FC2514000 |
| HazardClass | 6.1(a) |
| PackingGroup | II |
| HS Code | 29252900 |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 23422-53-9(Hazardous Substances Data) |
FORMETANATE HYDROCHLORIDE Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
Formetanate hydrochloride is a white or yellowish, crystalline solid or powder with a faint odor.
Uses
Formetanate is an insecticide and acaricide with contact and stomach action. It is used to control spider mites and some insects (Diptera, Hemiptera and Thysanoptera) on ornamentals, fruit, vegetables and alfalfa.
General Description
White powder with a faint odor. Used as a plant insecticide, acaricide, and miticide.
Air & Water Reactions
Hydrolyzed at pH less than 4 [EPA, 1998].
Reactivity Profile
FORMETANATE HYDROCHLORIDE is a carbamate ester. Carbamates are chemically similar to, but more reactive than amides. Like amides they form polymers such as polyurethane resins. Carbamates are incompatible with strong acids and bases, and especially incompatible with strong reducing agents such as hydrides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen is produced by the combination of active metals or nitrides with carbamates. Strongly oxidizing acids, peroxides, and hydroperoxides are incompatible with carbamates.
Health Hazard
Extremely toxic to humans. Not absorbed through contact with skin. Inhalation or ingestion may cause poisoning. Inhibits cholinesterase activity so effects are in relation to action on nervous system and can result in death.
Fire Hazard
FORMETANATE HYDROCHLORIDE may burn but does not ignite readily. Container may explode in heat of fire. Hydrolyzed at pH less than 4
Agricultural Uses
Insecticide, Acaricide: Registered for use in the U.S. Not listed for use in EU countries. An insecticide used for thrips and true bug control on fruit crops.
Trade name
CARZOL®; CARZOL® SP; DICARZOL®; ENT 27566®; EP-332®; MORTON® EP332; NOR-AM® EP 332; SCHERING® 36056; SN 36056®
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Mddly toxic by skin contact. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NOx and HCl.
Potential Exposure
A potential danger to those involved in the manufacture, formulation, and application of this plant insecticide, acaricide and miticide.
Metabolic pathway
Formetanate is hydrolysed rapidly in field and laboratory soils under aerobic and anaerobic conditions. It is metabolised by similar pathways in plants and animals. It is hydrolytically deaminated to produce a formyl derivative and subsequently hydrolysed at the carbamate ester to give a phenolic product. The phenol is deformylated to 3-aminophenol and acetylated to 3-acetamidophenol. Formetanate and most phase 1 metabolites are found conjugated. Its metabolism has been reviewed by Cool and Jankowski (1985), Fukuto (1972) and Kuhr and Dorough (1976).
Shipping
UN2757 Carbamate pesticides, solid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials. UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Incompatibilities
Carbamates are incompatible with strong acids and bases, and especially incompatible with strong reducing agents such as hydrideds and active metals. Contact with active metals or nitrides form flammable gas eous hydrogen. Incompatible with strongly oxidizing acids, peroxides, and hydroperoxides.
Waste Disposal
In accordance with 40CFR 165 recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by follow ing package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office. Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations gov erning storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal.





