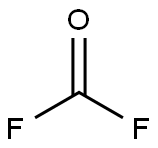
CARBONYL FLUORIDE
- CAS No.
- 353-50-4
- Chemical Name:
- CARBONYL FLUORIDE
- Synonyms
- COF2;Fluorophosgene;Difluorophosgene;Fluophosgene;Difluoro ketone;CARBONYL FLUORIDE;Difluoromethanone;carbonoxyfluoride;Carbon oxyfluoride;Carbon oxyfiuoride
- CBNumber:
- CB9253542
- Molecular Formula:
- CF2O
- Molecular Weight:
- 66.01
- MOL File:
- 353-50-4.mol
- Modify Date:
- 2025/1/6 13:21:43
| Melting point | -114°C |
|---|---|
| Boiling point | -84°C |
| Density | 1,139 g/cm3 |
| solubility | reacts with H2O |
| form | colorless gas |
| color | colorless |
| Water Solubility | instantly hydrolyzed by H2O [MER06] |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Carbonic difluoride (353-50-4) |
SAFETY
Risk and Safety Statements
| Symbol(GHS) |    GHS05,GHS04,GHS06 |
|---|---|
| Signal word | Danger |
| Hazard statements | H280-H330 |
| Precautionary statements | P410+P403-P260-P271-P284-P304+P340-P310-P320-P403+P233-P405-P501 |
| Hazard Codes | T |
| Risk Statements | 8-23/24/25-34 |
| Safety Statements | 3/7-9-36/37/39-38-45 |
| RIDADR | 2417 |
| OEB | B |
| OEL | TWA: 2 ppm (5 mg/m3), STEL: 5 ppm (15 mg/m3) |
| Hazard Note | Highly Toxic |
| HazardClass | 2.3 |
| Hazardous Substances Data | 353-50-4(Hazardous Substances Data) |
CARBONYL FLUORIDE Chemical Properties,Uses,Production
Chemical Properties
Carbonyl fluoride is colorless or light yellow, hygroscopic, compressed liquefied gas. Pungent, highly irritating and suffocating odor.
Physical properties
Colorless gas; pungent odor; hygroscopic; unstable; liquid density 1.139 g/mL (at -114°C); liquefies at -83.1°C; solidifies at -114°C; decomposes in water.
Uses
Organic synthesis.
Preparation
Carbonyl fluoride is prepared by the reaction of carbon monoxide with fluorine gas or silver fluoride:
CO + F2 → COF2
Also, it may be produced by the action of carbon monoxide with bromine trifluoride, BrF3.
General Description
A colorless gas with a pungent odor. Very toxic by inhalation. Prolonged exposure of the containers to fire or heat may result in violent rupturing and rocketing.
Air & Water Reactions
Reacts with water or steam to produces corrosive and toxic hydrofluoric acid fumes.
Reactivity Profile
CARBONYL FLUORIDE is an acid fluoride. Incompatible with water, with bases (including amines), with strong oxidizing agents, with alcohols. Reacts violently with hexafluoroisopropylideneaminolithium. High temperature causes decomposition to toxic carbon monoxide gas and fluorine. May react vigorously or explosively if mixed with diisopropyl ether or other ethers in the presence of trace amounts of metal salts [J. Haz. Mat., 1981, 4, 291].
Hazard
Toxic by inhalation, strong irritant to skin. Lower respiratory tract irritant. Bone damage.
Health Hazard
Irritates lungs, causing delayed pulmonary edema. Slight gassing produces dryness or burning sensation in the throat, numbness, pain in the chest, bronchitis, and shortness of breath.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Toxic gas is generated when heated.
Safety Profile
A poison. Moderately toxic by inhalation. A powerful irritant. Hydrolyzes instantly to form HF on contact with moisture. See also CARBONYLS, HYDROFLUORIC ACID, and FLUORINE. Incompatible with hexafluoroisoprop ylideneamino-lithium. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of CO and F-. See CARBON MONOXIDE for fire and explosion hazard.
Potential Exposure
Carbonyl fluoride is a carboxy halide. The major source of exposure to COF2 results from the thermal decomposition of fluoro carbon plastics, such as PTFE in air. Carbonyl fluoride is used for synthesizing fluoroalkanes, difluoroisocyanates, and fluorinated alkyl isocyanates. It may have been used as a military poison gas.
Shipping
UN2417 Carbonyl fluoride, Hazard class: 2.3; Labels: 2.3-Poisonous gas, 8-Corrosive material, Inhalation Hazard Zone B. Cylinders must be transported in a secure upright position, in a well-ventilated truck. Protect cylinder and labels from physical damage. The owner of the compressed gas cylinder is the only entity allowed by federal law (49CFR) to transport and refill them. It is a violation of transportation regulations to refill compressed gas cylinders without the express written permission of the owner.
Incompatibilities
Reacts with water to form toxic and corrosive HF gas. HF gas is highly reactive and forms explosive hydrogen gas on contact with metals. Do not use cast iron or malleable fittings with carbonyl fluoride. Carbonyl fluoride decomposes on heating above 450C producing toxic gases, including HF. Not compatible with hexafluoroisopropylidene-amino lithium; reaction may be dangerous.
Waste Disposal
Return refillable compressed gas cylinders to supplier.
CARBONYL FLUORIDE Preparation Products And Raw materials
Raw materials
1of2
chevron_rightPreparation Products
353-50-4(CARBONYL FLUORIDE)Related Search:
1of4
chevron_right




