硫酸水素 化学特性,用途語,生産方法
外観
無色澄明の液体
定義
本品は、次の化学式で表される無機酸である。
溶解性
水に混和, アルコールに可溶。水及びエタノールと任意の割合で混和する。
解説
硫酸水素,市販の濃硫酸は,通常96% 水溶液で,密度1.84 g cm-3,17.95 mol L-1 である.純硫酸は粘ちゅうな液体.融点10.5 ℃.密度1.834 g cm-3.ほとんどの金属を溶かす.水には多量の熱を発して溶け,自由に混和する.水溶液では強酸となるが,二塩基酸としての第二電離定数Ka2 は2×10-2 で,比較的小さい値を示す.濃硫酸は脱水作用があり,熱すると強い酸化作用を示す.有機化合物と脱水,酸化,スルホン化などの反応を行う.工業的に大規模に生産され,有機反応助剤,硫安,リン酸肥料,薬品,化学繊維,金属精錬,紙・パルプなどの製造に用いられている.腐食性で皮膚,粘膜をおかす.有毒.
用途
ゲルベルブチロメーターによる乳脂肪の測定用
用途
汎用試薬、有機及び無機合成原料、調製液製造原料、乾燥剤。
用途
ほう素定量用試料前処理試薬。
用途
大量の酸を用いる試料の前処理、高感度比色分析、高感度機器分析、臨床試薬等。
用途
横河NP1000全窒素全りん自動測定装置専用試薬。
用途
一般分析試液
用途
一般分析用試液、試液調製原料、塩基性物質中和剤。
用途
汎用試薬、臨床試薬、調製液原料。
用途
汎用試薬。
用途
有害金属分析のための試料の前処理。
用途
硫酸は化学工業の基礎原料で、特に肥料工業、繊維、無機薬品工業をはじめ金属製錬、製鋼、紡織、製紙、食料品工業など広範囲に使用される、化粧品原料(清浄用化粧品)
製法
硫酸水素,水溶液濃度が90% 以上のものを濃硫酸といい,それ以下の濃度のものを希硫酸という.二酸化硫黄から無水硫酸をつくり,水と反応させて濃硫酸をつくる.
化粧品の成分用途
pH調整剤
効能
酸性化剤
特徴
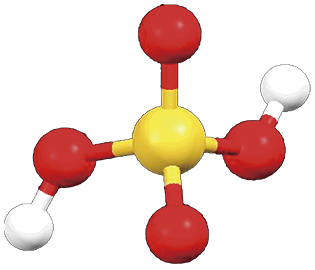
四面体.107 KでS-O 141.9 pm,S-OH 152.8(5) pm,∠OSO 103.7˚,∠HOSOH 118.3˚
主な用途/役割
ユリア樹脂系接着剤、メラミン樹脂系接着剤、フェノール樹脂系接着剤の触媒として使用される。
使用上の注意
強く水分を吸収する。
説明
Reactivity
Sulfuric acid is very reactive and dissolves most metals, it is
a concentrated acid that oxidizes, dehydrates, or sulfonates
most organic compounds, often causes charring.
Sulfuric acid reacts violently with alcohol and water to release
heat. It reacts with most metals, particularly when diluted with
water, to form flammable hydrogen gas, which may create an
explosion hazard. Sulfuric acid is not combustible, but it is
a strong oxidizer that enhances the combustion of other substances,
does not burn itself. During fire, poisonous gases are
emitted. Hazardous decomposition products are as follows:
sulfur dioxide, sulfur trioxide, and sulfuric acid fumes.
Note: Use great caution in mixing with water due to heat
release that causes explosions. Always add the acid to water,
never the reverse.
Where Found
l Car battery acid
l Certain detergents
l Chemical munitions
l Some fertilizers
l Some toilet bowl cleaners
Derivation
Sulfuric acid is made from sulfur, pyrite (FeS2), hydrogen
sulfide, or sulfur-containing smelter gases by the contact process
(vanadium pentoxide catalyst). The first step is combustion of
elemental sulfur, or roasting of iron pyrites, to yield sulfur
dioxide. Then follows the critical reaction, catalytic oxidation of
sulfur dioxide to sulfur trioxide.
化学的特性
Sulfuric acid is a colorless to dark brown, odorless, oily liquid which is commercially sold @ 93% to 98% H2SO4, the remainder being water.
来歴
Sulfuric acid is a colorless, oily, dense liquid that is one of the most important industrial chemicals. More than 40 million tons are produced in the United States annually and approximately 170 million tons are produced globally. Sulfuric acid has a long history and was first produced by ancient alchemists. Its discovery is credited to the Persian physician Mohammad Ibn Zakariya al-Razi (Rhazes, 854 925), who produced sulfuric acid from the dry distillation of minerals. Dry distillation typically involves heating a substance in a closed container to limit oxygen and combustion. As the substance is heated, it decomposes and the volatile components can be captured. Because sulfuric acid was obtained from distilling minerals, it is called a mineral acid. The ancient method of sulfuric acid production involved heating either iron (II) sulfate heptahydrate (FeSO4 7H2O), which was called green vitriol, or copper (II) sulfate pentahydrate (CuSO4 5H2O), called blue vitriol. When minerals containing these compounds were heated, the products included sulfur trioxide (SO3) and water. The combination of sulfur trioxide and water produced sulfuric acid: SO3(g) + H2O(l) H2SO4(aq). The production of sulfuric acid from natural minerals called vitriols and its oily appearance led to the common name oil of vitriol for sulfuric acid.
使用
Sulfuric Acid is an acidulant that is a clear, colorless, odorless liquid
with great affinity for water. it is prepared by reacting sulfur dioxide
with oxygen and mixing the resulting sulfur trioxide with water, or
by reacting nitric oxide with sulfur dioxide in water. it is very cor-
rosive. it is used as a modifier of food starch and is used in caramel
production and in alcoholic beverages.
調製方法
Sulfuric acid may be prepared industrially by either the contact process or the chamber process.
Contact Process
2SO2+O2→2SO3
SO3+H2O→H2SO4
Chamber Process
2NO+O2→2NO2
NO2+SO2+H2O→H2SO4+NO
一般的な説明
Sulphuric acid may be prepared by catalytic oxidation of sulphur dioxide. It is a very strong electrolyte and has high affinity to water.
空気と水の反応
Reaction with water is negligible unless acid strength is above 80-90% then heat from hydrolysis is extreme, may cause severe burns [Merck, 11th ed. 1989]. During sulfonation of mononitrobenzene by fuming Sulfuric acid , a leak from an internal cooling coil permitted water to enter the reaction tank. A violent eruption occurred due to the heat of solution [MCA Case History 944 1963].
危険性
Strong irritant to tissue. Pulmonary function
inhibitor. Confirmed carcinogen.
健康ハザード
Concentrated sulfuric acid is a highly corrosive liquid that can cause severe, deep burns upon skin contact. The concentrated acid destroys tissue because of its dehydrating action, while dilute H 2SO4 acts as a skin irritant because of its acid character. Eye contact with concentrated H2SO4 causes severe burns, which can result in permanent loss of vision; contact with dilute H2SO4 results in more transient effects from which recovery may be complete. Sulfuric acid mist severely irritates the eyes, respiratory tract, and skin. Because of its low vapor pressure, the principal inhalation hazard from sulfuric acid involves breathing in acid mists, which may result in irritation of the upper respiratory passages and erosion of dental surfaces. Higher inhalation exposures may lead to temporary lung irritation with difficulty breathing. Ingestion of sulfuric acid may cause severe burns to the mucous membranes of the mouth and esophagus. Animal testing with sulfuric acid did not demonstrate carcinogenic, mutagenic, embryotoxic, or reproductive effects. Chronic exposure to sulfuric acid mist may lead to bronchitis, skin lesions, conjunctivitis, and erosion of teeth.
火災危険
Sulfuric acid is highly reactive and capable of igniting finely-divided combustible materials on contact. When heated, Sulfuric acid emits highly toxic fumes. Avoid heat; water and organic materials. Sulfuric acid is explosive or incompatible with an enormous array of substances. Can undergo violent chemical change at elevated temperatures and pressure. May react violently with water. When heated, Sulfuric acid emits highly toxic fumes. Hazardous polymerization may not occur.
燃焼性と爆発性
Sulfuric acid is noncombustible but can cause finely divided combustible substances
to ignite. Sulfuric acid reacts with most metals, especially when dilute, to produce
flammable and potentially explosive hydrogen gas.
化学性质
硫酸は強い二塩基酸で,解離度は0.5 mol L?1で約51%,0.05 mol L?1で約59%である。希硫酸はイオン化傾向が水素より大きい金属と反応して,金属の硫酸塩を生成し,水素を遊離する。イオン化傾向が水素より小さい金属は希硫酸とは反応しないが,熱濃硫酸とは反応して金属の硫酸塩を生成し,二酸化硫黄を発生する。硫酸は有機化合物とはニトロ化,スルホン化,脱水,水和,硫酸エステル化などの反応を起こす。
応用例(製薬)
Sulfuric acid is used as an acidifying agent in a variety of
pharmaceutical and food preparations. It may also be used to
prepare dilute sulfuric acid, which, in addition to its use as an
excipient, has some therapeutic use for the treatment of gastric
hypoacidity, as an astringent in diarrhea, or to stimulate appetite.
Sulfuric acid has been used in parenteral, oral, topical, and
ophthalmic pharmaceutical formulations.
工業用途
Sulfuric acid (H
2SO
4) is the most widely used acid for pH control in mineral flotation.
Sulfuric acid can be manufactured by several processes including the burning of pure
sulfur, roasting of pyrite and from the recovery of SO
2 stack gas from a smelter operation.
Sulfuric acid is a colorless to amber, slightly cloudy and oily liquid with a specific
gravity of 1.84 at 95% strength.
In mineral flotation, sulfuric acid is used in almost all applications involving acid pH
control. It is also used as a pulp pretreatment chemical during flotation of oxidic and
industrial minerals. Pulp pretreatment with sulfuric acid improves flotation of ilmenite,
perovskite, phenacite, beryl and other minerals.
安全性
Sulfuric acid is widely used in a variety of pharmaceutical
formulations. Although concentrated sulfuric acid is very corrosive,
it is normally used well diluted in formulations. Concentrated
sulfuric acid will react violently with water and much heat is
generated. When diluting sulfuric acid, the acid should always be
added to the other liquid with great caution.
The concentrated solution is extremely corrosive and can cause
severe damage or necrosis on contact with the eyes and skin.
Ingestion may cause severe injury or death. Inhalation of
concentrated vapors can cause serious lung damage.
LD50 (rat, oral): 2.14 g/kg
職業ばく露
Used as a chemical feedstock in the manufacture of acetic acid, hydrochloric acid; citric acid; phosphoric acid; aluminum sulfate; ammonium sulfate;barium sulfate; copper sulfate; phenol, superphosphates, titanium dioxide; as well as synthetic fertilizers, nitrate explosives; artificial fibers; dyes, pharmaceuticals, detergents, glue, paint, and paper. It finds use as a dehydrating agent for esters and ethers due to its high affinity for water; as an electrolyte in storage batteries; for the hydrolysis of cellulose to obtain glucose; in the refining of mineral and vegetable oil; and in the leather industry. Other uses include fur and food processing; carbonization of wool fabrics; gas drying; uranium extraction from pitchblende; and laboratory analysis. Sulfuric acid is among the highestvolume produced chemical in the United States.
発がん性
Strong inorganic acid mists containing sulfuric acid are known to be human carcinogens based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity
from studies in humans.
環境運命予測
Although sulfuric acid can be extremely harmful, it is a naturally
occurring compound. The release of sulfur into the
biosphere is not from anthropogenic sources. It is also a major
compound that is released in volcanic eruptions when oxides
of sulfur are emitted:
Sulfur trioxide will dissolve in rainwater to form sulfuric
acid
SO3 + H2O → H2SO4:
Sulfur dioxide will dissolve in rainwater to form sulfurous
acid (H2SO3), and is then oxidized to form sulfuric acid,
which leads to acid rains.
The presence of sulfuric acid is related with the natural
ability of microorganisms that can be found in or isolated from
acid mine water or from sulfur and iron sulfide mines as well as
volcanoes.
The examples of such bacteria are:
Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans (Thiobacillus ferrooxidans) that
lives in pyrite deposits, metabolizing iron and sulfur and
producing sulfuric acid.
Acidithiobacillus thiooxidans (Thiobacillus thiooxidans, Thiobacillus
concretivorus) that utilizes sulfur and produces
sulfuric acid.
貯蔵
Splash goggles and rubber gloves should be worn when
handling this acid, and containers of sulfuric acid should be stored in a wellventilated
location, separated from organic substances and other combustible
materials. Containers of sulfuric acid should be stored in secondary plastic trays to
avoid corrosion of metal storage shelves due to drips or spills. Water should never
be added to sulfuric acid because splattering may result; always add acid to water
輸送方法
UN1830 Sulfuric acid with >51% acid or sulfuric acid with not >51% acid, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material. UN1831 Sulfuric acid, fuming with 30% or more free sulfur trioxide and Sulfuric acid, fuming, with <30% free sulfur trioxide, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material. UN1832 Sulfuric acid, spent, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material.
合成方法
硫酸の原料構成は,世界的には硫黄約60%,硫化鉄鉱約8%,その他(おもに,非鉄金属硫化物からの非鉄製錬ガスなど)約30%であるが,国内では非鉄製錬ガス約75%,硫黄約22%,その他(廃酸,排煙脱硫など)約3%となっている。
純化方法
Sulfuric acid, and also 30% fuming H2SO4, can be distilled in an all-Pyrex system, optionally from potassium persulfate. It has been purified by fractional crystallisation of the monohydrate from the liquid. It has a very strong dehydrating action and attacks skin—wash immediately with cold H2O; otherwise the skin can be scarred for life. It is very hygroscopic and has been used as a desiccant in desiccators. Dilution with H2O is highly exothermic, and because the concentrated acid is much more dense than H2O it is diluted by running the concentrated acid down the side of the container of H2O with slowly stirring while cooling the outside of the container. If these precautions are not taken, the H2O is likely to boil vigorously.
不和合性
Avoid storage in close proximity to water, most common metals,
organic materials, strong reducing agents, combustible materials,
strong bases, carbonates, sulfides, cyanides, strong oxidizing agents,
and carbides.
Sulfuric acid is a powerful oxidizer and may ignite or explode on
contact with many materials.
It can react violently with the evolution of a large amount of
heat. Oxides of sulfur and hydrogen can be generated during
reactions.
Great care must be exercised when mixing with other liquids.
Always add sulfuric acid to the diluent with great caution.
廃棄物の処理
Add slowly to solution of soda ash and slaked lime with stirring; flush to drain with large volumes of water. Recovery and reuse of spent sulfuric acid may be a viable alternative to disposal, and processes are available.
規制状況(Regulatory Status)
GRAS listed. Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe.
Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (IM, IV, and IP
injections, inhalation solutions, irrigation solutions, nasal, ophthalmic
solutions and suspensions, oral solutions, and topical emulsions
and creams). Included in nonparenteral and parenteral medicines
licensed in Europe. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable
Non-medicinal Ingredients.
The United Nations Convention Against Illicit Traffic in
Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (1988) lists sulfuric
acid as a chemical frequently used in the illicit manufacture of
narcotic drugs or psychotropic substances. In the USA, sulfuric
acid is included in the list of essential or precursor chemicals
established pursuant to the Chemical Diversion and Trafficking Act.
Accordingly, transactions of sulfuric acid such as imports, exports,
sales, and transfers are subject to regulation and monitoring by the
Drug Enforcement Administration.
参考文献
P.-Y. Yu, T.C.W. Mak, J. Cryst. Mol. Struct., 8, 193 (1978), DOI: 10.1007/BF01297663.
硫酸水素 上流と下流の製品情報
原材料
準備製品
2-アミノ-4-メチル-5-ニトロピリジン
4-Nitro-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzoyl chloride
2-ヒドロキシ-4-(トリフルオロメチル)キノリン
tert-アミルベンゼン
5-スルホ-2-ヒドロキシ安息香酸
7-アミノナフタレン-1,3,6-トリスルホン酸
2-ニトロチオフェン-4-カルボキシアルデヒド
4-CHLOROMETHYL-7-METHOXY-CHROMEN-2-ONE
トリコサン酸メチル
硫酸ジルコニウム 四水和物
セサモール
トリエンチン·2塩酸塩
1-ベンゾチオフェン-3-スルホニルクロリド
2,6-ジメチル-3-ニトロピリジン
2-アミノ-5-(ジエチルアミノ)トルエン一塩酸塩
3-BROMOQUINOLINE-8-SULFONIC ACID
N4-エチル-N4-(2-ヒドロキシエチル)-2-メチル-1,4-フェニレンジアミン硫酸塩
N,N-ジエチル-1,4-フェニレンジアミン硫酸塩
ジプロピレン グリコール
6-AMINO-5-METHYLPYRIDINE-3-SULFONIC ACID
コバルト(II)
2-ethyl-5-nitrobenzenamine
3,3'-ジニトロベンゾフェノン
クマリン酸
アミカシン 硫酸塩
2,6-ジフルオロ-4-ニトロアニリン
4-クロロ-3,5-ジニトロ安息香酸
Vat Blue BC
Dispersing agent DN
2-アミノ-5-ブロモ-3-ニトロピリジン
硫酸チタニル
3-ブロモ安息香酸 エチル
2,2'-チオジグリコール酸
アミカシン硫酸塩
Sulfur-magnesium fertilizer
Conditioner for metal surface
3-ブロモ-4-メチル安息香酸メチル
2-ニトロチオフェン-4-カルボン酸
6-フルオロ-4-(トリフルオロメチル)-2(1H)-キノリノン
2-メチル-5-ニトロベンゾニトリル