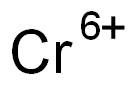크롬 6가 C화학적 특성, 용도, 생산
화학적 성질
Elemental chromium is a transition-group metal belonging to group VIB of the periodic table and has oxidation states ranging from –2 to +6, of which the divalent (+2, II), trivalent (+3, III), and hexavalent (+6, VI) forms are the most important. Elemental chromium does not occur naturally in the environment. The divalent (chromous) state is readily oxidized to the more stable trivalent (chromic) state. Although the hexavalent state (including chromates) is more stable than the divalent state, it is rarely found in nature. Chromium(VI) compounds are strong oxidizing agents and are highly corrosive. In the environment, they generally are reduced to chromium(III) compounds. The chromium(VI) compounds most commonly encountered in industry are calcium chromate, chromium trioxide, sodium chromate and dichromate, potassium chromate and dichromate, lead chromate, strontium chromate, and zinc chromate (IARC 1990, Costa 1997). However, this listing applies to all hexavalent chromium compounds,
not just to those specified above.
Calcium chromate occurs as yellow crystals or a bright-yellow powder. It is slightly soluble in water and soluble in dilute acids, and it reacts with acids and ethanol. Although calcium chromate is not flammable, toxic chromium fumes may be formed in fires, and mixtures with boron burn violently when ignited. Chromium trioxide (also known as chromic trioxide) occurs as dark-red or brown crystals, flakes, or granular powder and is soluble in water, ethyl alcohol, ethyl ether, sulfuric acid, and nitric acid. Contact of chromium trioxide with organic chemicals may result in violent or explosive reactions, and fires with chromium trioxide may produce irritating, corrosive, and toxic gases (ATSDR 2000, HSDB 2009). Lead chromate occurs as yellow, orange, or red crystals or a yellow or orange-yellow powder that is insoluble in water, acetic acid, and ammonia but soluble in dilute nitric acid. When heated, it emits highly toxic fumes, and it may react explosively with azo dyes. The term “lead chromate” is also used to refer to various commercial lead chromate pigments (IARC 1980, 1990, HSDB 2009). Potassium chromate occurs as yellow crystals and is soluble in water but insoluble in ethanol. Potassium dichromate occurs as red or orange-red crystals and is soluble in water but insoluble in ethanol and acetone. It poses a dangerous fire risk when in contact with organic materials or finely divided combustible materials, such as sawdust (ATSDR 2000, HSDB 2009).
Sodium chromate occurs as yellow crystals and is soluble in water and slightly soluble in methanol. Although it is not flammable, toxic chromium oxide fumes may be formed in fires with sodium chromate (ATSDR 2000, HSDB 2009). Sodium dichromate occurs as bright orange-red or red hygroscopic crystals and is soluble in water and methanol. It reacts explosively with hydrazine, acetic anhydride, boron, silicon, and other materials (IARC 1980, HSDB 2009). Strontium chromate occurs as yellow monoclinic crystals or a yellow powder. It is slightly soluble in water and soluble in dilute hydrochloric acid, nitric acid, and acetic acid. It is not flammable but reacts explosively with hydrazine (HSDB 2009). Zinc chromate occurs as lemonyellow crystals or powder. It is insoluble in cold water and acetone, sparingly soluble in hot water, and soluble in acid and liquid ammonia. Zinc chromate reacts explosively with hydrazine. The term “zinc chromate” is also used to refer to various commercial zinc and zinc potassium chromates (IARC 1990, HSDB 2009). Physical and chemical properties of these chromium(VI) compounds are listed in the following table, along with their chemical formulas.
용도
The steel industry is the major consumer of chromium. In 2007, estimated consumption of chromium in the United States by end use was 78% in stainless and heat-resisting steel, 13.8% for other steel uses, 3.7% in superalloys, and 4.5% in other alloys and end uses (Papp 2009). Alloys of stainless steel and chromium typically contain between 11.5% and 30% chromium (ATSDR 2000). Chromium(VI) compounds are widely used as corrosion inhibitors, in the manufacture of pigments, in metal finishing and chrome plating, in stainless steel production, in leather tanning, and in wood preservatives (Costa 1997, ATSDR 2000). In 1996, about 52% of all chromium compounds used in the U.S. chemical industry were used in production of wood preservatives; the rest were used in leather tanning (13%), metals finish-ing (13%), pigments (12%), refractories (linings for high-temperature industrial furnaces) (3%), and other uses (7%) (ATSDR 2000). The use of chromium(VI) compounds in wood preservatives increased dramatically from the late 1970s to the early 2000s; however, this use is expected to decrease because of a voluntary phase-out of all residential uses of wood treated with chromated copper arsenate (pressure-treated wood) that went into effect December 31, 2003 (Brooks 2009). Chromium(VI) compounds are also used in textile-dyeing processes, printing inks, drilling muds, pyrotechnics, water treatment, and chemical synthesis (HSDB 2009).
Calcium chromate is used primarily as a corrosion inhibitor and as a depolarizer in batteries (IARC 1973, 1990, HSDB 2009). Chromium trioxide is used primarily in chrome plating and other metal finishing (particularly in the production of automobiles and military aircraft), in production of wood preservatives, as a corrosion inhibitor, and in production of organic chemicals and catalysts. Lead chromate has been used in paints and printing inks and as a colorant in vinyl, rubber, and paper. Potassium chromate is used in production of dyes and in textile-dyeing processes. Potassium dichromate has largely been replaced by sodium dichromate in many applications; however, it is still used in photomechanical processes and production of pigments and wood preservatives. Sodium chromate is used as a corrosion inhibitor and in textile dyeing processes, inks, paints, leather tanning, wood preservatives, drilling muds, cutting oils, water treatment, and production of other chromium compounds. Sodium dichromate is the primary base material for the production of chromium compounds and is used as a corrosion inhibitor, in metal treatments, in drilling muds, and in the production of dyes, wood preservatives, synthetic organic chemicals, and catalysts. Strontium chromate is used as a corrosion inhibitor and metal conditioner, in aluminum flake coatings, as a colorant in polyvinyl chloride, in pyrotechnics, in chrome plating, and for sulfate ion control in electrochemical processes. Zinc chromates are used as corrosion inhibitors and metal conditioners and in paints, varnishes, and oil colors.
Carcinogenicity
Chromium hexavalent (VI) compounds are known to be human carcinogens based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in humans.
크롬 6가 준비 용품 및 원자재
원자재
준비 용품