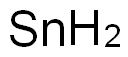주석
|
|
주석 속성
- 녹는점
- 231.9 °C (lit.)
- 끓는 점
- 2270 °C (lit.)
- 밀도
- 7.310 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
- 증기압
- 1Pa at 1223.85℃
- 인화점
- 2270°C
- 저장 조건
- no restrictions.
- 용해도
- H2O: 용해성
- 물리적 상태
- 철사
- 색상
- 은회색
- Specific Gravity
- 7.31
- Flame Color
- Blue-white
- 비저항
- 11 μΩ-cm, 20°C
- 수용성
- 차가운 묽은 HCl, 묽은 HNO3, 뜨거운 묽은 H2SO4와 천천히 반응합니다. 진한 HCl, 왕수 [MER06]로 쉽게 사용 가능
- Crystal Structure
- Cubic, Alpha-Tin; Diamond Structure - Space Group Fd3m
- Merck
- 13,9523
- 노출 한도
- ACGIH: Ceiling 2 ppm
OSHA: Ceiling 5 ppm(7 mg/m3)
NIOSH: IDLH 50 ppm; Ceiling 5 ppm(7 mg/m3)
- 안정성
- 안정적인. 강한 산화제와 호환되지 않습니다. 분말로서 가연성이 높습니다. 분말 형태로 분진 폭발을 일으킬 수 있음. 수분에 민감합니다.
- InChIKey
- OLGIDLDDXHSYFE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
- CAS 데이터베이스
- 7440-31-5(CAS DataBase Reference)
- EPA
- Tin (7440-31-5)
안전
- 위험 및 안전 성명
- 위험 및 사전주의 사항 (GHS)
| 위험품 표기 | Xi,F,C | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 위험 카페고리 넘버 | 36/37/38-36/37-11-36/38-34-20/21/22 | ||
| 안전지침서 | 26-24/25-22-36/37/39-33-16-36/37-45 | ||
| 유엔번호(UN No.) | UN 3264 8/PG 2 | ||
| OEB | B | ||
| OEL | TWA: 2 mg/m3 [*Note: The REL also applies to other inorganic tin compounds (as Sn) except tin oxides.] | ||
| WGK 독일 | 1 | ||
| RTECS 번호 | XP7320000 | ||
| F 고인화성물질 | 10 | ||
| TSCA | Yes | ||
| 위험 등급 | 4.1 | ||
| 포장분류 | III | ||
| HS 번호 | 80070080 | ||
| 유해 물질 데이터 | 7440-31-5(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| 기존화학 물질 | KE-33838 |
주석 C화학적 특성, 용도, 생산
물성
탄소족에 속하는 전이후 금속의 하나로 은백색의 고체 금속이다. 연성과 전성이 크고 쉽게 산화되지 않으며 부식에 대한 저항성이 있어 녹슬지 않는다.개요
Tin has a long, colorful history. The extraction and use of tin began during the Bronze Age around 3000 BC when early craftsmen discovered that bronze – a noncorrosive metal that is extremely hard and strong enough to be used for spears, swords, arrows, and other especially important objects at that time – could be produced by smelting tin with copper. Tin is also the primary constituent of pewter. Long ago, people developed the belief that trace amounts of tin seemed to help prevent fatigue and depression, and that drinking out of tin cups could help combat these ailments. Tin toys, tin coated cans, and tin roofs have also enjoyed great popularity in the past.화학적 성질
Tin is a gray to almost silver-white, ductile, malleable, lustrous metal.물리적 성질
Tin is a soft, silvery-white metal located in the carbon group, similar in appearance to freshcutaluminum. When polished, it takes on a bluish tint caused by a thin protective coatingof oxidized tin. This property makes it useful as a coating for other metals. It is malleable andductile, meaning it can be pounded, rolled, and formed into many shapes, as well as “pulled”into wires through a die.There are two allotropes of tin. One is known as gray or alpha (α) tin, which is not verystable. The other is known as white tin or beta (β), which is the most common allotrope. Thetwo forms (allotropes) of tin are dependent on temperature and crystalline structure. Whitetin is stable at about 13.2°C. Below this temperature, it turns into the unstable gray alphaform. There is also a lesser-known third allotrope of tin called “brittle tin,” which exists above161°C. Its name is derived from its main property.
Tin’s melting point is 231.93°C, its boiling point is 2,602°C, and the density is 5.75 g/cm3for the gray allotrope (alpha) and 7.287 g/cm3 for the white allotrope (beta).
Isotopes
There are 49 isotopes of tin, 10 of which are stable and range from Sn-112to Sn-124. Taken together, all 10 stable isotopes make up the natural abundance of tinfound on Earth. The remaining 39 isotopes are radioactive and are produced artificially innuclear reactors. Their half-lives range from 190 milliseconds to 1×10+5 years.Origin of Name
The name “tin” is thought to be related to the pre-Roman Etruscan god Tinia, and the chemical symbol (Sn) comes from stannum, the Latin word for tin.출처
Tin is the 49th most abundant element found in the Earth’s crust. Although tin is nota rare element, it accounts for about 0.001% of the Earth’s crust. It is found in deposits inMalaysia, Thailand, Indonesia, Bolivia, Congo, Nigeria, and China. Today, most tin is minedas the mineral ore cassiterite (SnO2), also known as tinstone, in Malaysia. Cassiterite is tin’smain ore. There are no significant deposits found in the United States, but small deposits arefound on the southeast coast of England. To extract tin from cassiterite, the ore is “roasted” ina furnace in the presence of carbon, thereby reducing the metal from the slag.Characteristics
Although tin is located in group 14 as a metalloid, it retains one of the main characteristicsof metals: in reacting with other elements, it gives up electrons, forming positive ions just asdo all metals.Tin has a relatively low melting point (about 231°C or 4,715°F), and it reacts with someacids and strong alkalis, but not with hot water. Its resistance to corrosion is the main characteristicthat makes it a useful metal.
There is an interesting historical event related to the two main allotropes of tin. At temperaturesbelow 13 degrees centigrade, “white” tin is slowly transformed into “gray” tin, whichis unstable at low temperatures, and during the brutally cold winter of 1850 in Russia, thetin buttons sewn on soldiers’ uniforms crumbled as the tin changed forms. In the 1800s, tinwas also widely used for pots, pans, drinking cups, and dinner flatware. However, at very lowtemperatures, these implements also disintegrated as their chemical structure was altered.
용도
Chiefly for tin-plating and manufacture of food, beverage and aerosol containers, soldering alloys, babbitt and type metals, manufacture of tin salts, collapsible tubes, coating for copper wire. Principle component in pewter. Alloys as dental materials (silver-tin-mercury), nuclear reactor components (tin-zirconium), aircraft components (tin-titanium), bronze (copper-tin), brass.정의
Metallic element of atomic number 50, group IVA of the periodic system, aw 118.69, valences of 2, 4; 10 isotopes.생산 방법
Tin is relatively rare, composing only about 0.0006% in the earth’s crust. The major tin ore is cassiterite, a naturally occurring tin (IV) oxide (SnO2). The other major tin-containing minerals are stannate, teallite, cylindrite, and canfieldite that are sulfides of tin.일반 설명
White TIN is an almost silver-white, ductile, malleable, lustrous solid. Mp 232°C; bp: 2507°C. Density: 7.3 g cm-3. Pure white TIN becomes non-metallic powdery gray TIN if held for a sustained period at temperatures less than 13°C.반응 프로필
TIN is a reducing agent. Stable in massive form in air, but oxidizes (corrodes) in air as a powder, especially in the presence of water. Dissolve slowly in dilute strong acids in the cold. Dissolves in hot aqueous KOH and other strongly basic solutions. Incompatible with acids and base. Incompatible with chlorine and turpenTINe.위험도
Tin, as the elemental metal, is nontoxic. Most, but not all of tin’s inorganic salts and compoundsare also nontoxic.In contrast, almost all organic tin compounds (tin compounds composed of carbon andhydrocarbons) are very toxic and should be avoided. If they are used, special equipment andcare must be taken in handling.
(Note: When chemical formulas use the letter “R” preceding an element’s symbol, it designatessome form of organic compound—for example, R4Sn. If the letter “X” follows theelement’s symbol in a formula, it designates some form of inorganic compound—for example,SnX2. Thus, a whole series of tin compounds could be designated as R4Sn2, R2Sn, or SnX4,SnX2, and so forth.)
건강위험
Inorganic tin salts are irritants of the eyes and skin. No systemic effects have been reported from industrial exposure. Some inorganic tin compounds can cause skin or eye irritation because of acid or alkaline reaction produced with water. Tin tetrachloride, stannous chloride, and stannous sulfate are strong acids; sodium and potassium stannate are strong alkalies.공업 용도
Hot-dip coatings can be applied to fabricatedparts made of mild and alloy steels, cast iron,and copper and copper alloys to improveappearance and corrosion resistance. Like zinc,the coatings consist of two layers — a relativelypure outer layer and an intermediate alloy layer.An invisible surface film of stannic oxideis formed during exposure, which helps toretard, but does not completely prevent, corrosion.The coatings have good resistance to tarnishingand staining indoors, and in most rural,marine, and industrial atmospheres. They alsoresist foods. Corrosion resistance in all casescan be markedly improved by increasing thicknessand controlling porosity. Typical applicationswhere they can be used are milk cans,condenser and transformer cans, food and beveragecontainers, and various items of sanitaryequipment such as cast iron mincing machinesand grinders.
Safety Profile
An inhalation hazard. Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic data by implant route. Combustible in the form of dust when exposed to heat or by spontaneous chemical reaction with Br2, BrF3, Cl2, ClF3, Cu(NO3), K2O2, S. See also POWDERED METALS and TIN COMPOUNDS.잠재적 노출
The most important use of tin is as a protective coating for other metals, such as in the food and beverage canning industry; in roofing tiles; silverware, coated wire; household utensils; electronic components; and pistons. Common tin alloys are phosphor bronze; light brass; gun metal; high tensile brass; manganese bronze; die-casting alloys; bearing metals; type metal; and pewter. These are used as soft solders, fillers in automobile bodies; and as coatings for hydraulic brake parts; aircraft landing gear and engine parts. Metallic tin is used in the manufacture of collapsible tubes and foil for packaging. Exposures to tin may occur in mining, smelting, and refining; and in the production and use of tin alloys and solders. Inorganic tin compounds are important industrially in the production of ceramics; porcelain, enamel, glass; and inks; in the production of fungicides; anthelmintics, insecticides; as a stabilizer it is used in polyvinyl plastics and chlorinated rubber paints; and it is used in plating baths.Carcinogenicity
Limited animal testing with stannous chloride has not revealed evidence of carcinogenic potential. Mixed results have been observed in genotoxic assays.운송 방법
UN3089 Metal powders, flammable, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 4.1; Labels: 4.1-Flammable solid.Purification Methods
Tin powder is purified by adding it to about twice its weight of 10% aqueousNaOH and shaking vigorously for 10minutes. (This removes oxide film and stearic acid or similar material that is sometimes added for pulverisation.) It is then filtered, washed with water until the washings are no longer alkaline to litmus, rinsed with MeOH and dried in air. [Sisido et al. J Am Chem Soc 83 538 1961.]비 호환성
TIN is a reducing agent. Stable in bulk form in air, but as powder it corrodes (oxidizes) in air, especially in the presence of moisture. Keep away from strong oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Incompatible with acids, alkalies, bases, chlorine, turpentine; reacts violently with acetic aldehyde, ammonium nitrate, ammonium perchlorate, hexachloroethane. Strong reducing agents may react violently with halogens, bromine fluoride, chlorine trifluoride, copper nitrate, disulfur dichloride, nitrosyl fluoride, potassium dioxide, sodium peroxide, sulfur, and other chemicals. May form explosive compounds with hexachloroethane, pentachloroethane, picric acid, potassium iodate, potassium peroxide, 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene-1,3,5-triol.주석 준비 용품 및 원자재
원자재
준비 용품
2-(티엔-2-일)피롤리딘
5,7-디클로로옥사졸로[5,4-d]피리미딘
염화 제일석
6-HYDROXY-2-NAPHTHALENEBORONIC ACID
아주석 옥토산염
3,4-DIAMINOTHIOPHENE디히드로클로라이드
7-hydroxyquinazolin-4(3H)-one
NAPHTHOL AS-BI PHOSPHATE
트리시클로헥실 (1,2,4-트리아졸-1-일) 주석
디부틸 틴 옥사이드
2,4,5-트리메톡시아닐린
주석염화물
피레녹신
4-chloroquinazolin-7-ol
2-클로로-p-페닐렌다이아민
4-티오펜-2-일페닐아민
4-Aminobenzamidine dihydrochloride
불화붕산 나트륨
4-(브로모메틸)-2,1,3-벤조티아디아졸
산화 펜브타틴
에틸2-(4-클로로퀴나졸린-7-일옥시)아세테이트
산화주석(II)
Azocyclotin suspensoid
불화붕산 주석
2,3,5-트리메틸-1,4-벤즈아민
S탄NOUS 염화
6-Methoxy-2-naphthaldehyde
트리페닐틴 클로라이드
주석 황산염
4-hydroxy-2-nitrobenzoic acid
다이메틸주석 비스(2-에틸헥실티오글리콜산염)
산화제이석
Azocyclotin W.P.
6-에톡시-2-메르캅토벤조티아졸
메타주석산
주석 공급 업체
글로벌( 365)공급 업체
| 공급자 | 전화 | 이메일 | 국가 | 제품 수 | 이점 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yujiang Chemical (Shandong) Co.,Ltd. | +8617736087130 |
catherine@yjchem.com.cn | China | 994 | 58 |
| Watson Biotechnology Co.,Ltd | +86-18186686046 +86-18186686046 |
sales01@watsonbiotech.cn | China | 5849 | 58 |
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 |
info@tianfuchem.com | China | 21628 | 55 |
| career henan chemical co | +86-0371-86658258 +8613203830695 |
sales@coreychem.com | China | 29859 | 58 |
| Hubei Jusheng Technology Co.,Ltd. | 18871490254 |
linda@hubeijusheng.com | CHINA | 28172 | 58 |
| Cangzhou Wanyou New Material Technology Co.,Ltd | 18631714998 |
sales@czwytech.com | CHINA | 904 | 58 |
| Hubei xin bonus chemical co. LTD | 86-13657291602 |
linda@hubeijusheng.com | CHINA | 22963 | 58 |
| CONIER CHEM AND PHARMA LIMITED | +8618523575427 |
sales@conier.com | China | 49732 | 58 |
| Antai Fine Chemical Technology Co.,Limited | 18503026267 |
info@antaichem.com | CHINA | 9636 | 58 |
| SIMAGCHEM CORP | +86-13806087780 |
sale@simagchem.com | China | 17365 | 58 |
주석 관련 검색:
아주석 옥토산염 틴(II) 메탄설폰산염 산화 펜브타틴 주석염화물 주석 황산염 산화제이석 질화 타이타늄(질화 티타늄) 염화제이석 5수 S탄NOUS 염화 염화 제일석 산화주석(II)
TIN II 2,3-NAPHTHALOCYANINE
TIN II BIS(HEXAMETHYLDISILAZIDE)
TIN ANTIMONIDE
TIN(II)-2,4-PENTANEDIONATE,TIN (II) ACETYLACETONATE
4-AMINO-2,6-DIBROMOPHENOL TIN(II)CHLORIDE HYDROCHLORIDE
TIN (II) ACETYLACETONATE,TIN(II)-2,4-PENTANEDIONATE
TIN-CADMIUM ALLOY