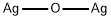은(I) 산화물 C화학적 특성, 용도, 생산
화학적 성질
Silver(I) oxide, Ag2O, is made by action of oxygen under pressure on silver at 300 °C, or by precipitation of a silver salt with carbonate-free alkali metal hydroxide; it is covalent, each silver atom (in solid Ag2O) having two collinear bonds and each oxygen atom four tetrahedral ones; two such interpenetrating lattices constitute the structure.
물리적 성질
Brownish-black cubic crystals; density 7.14 g/cm
3 at 16°C; begins to decompose around 200°C, decomposition becoming rapid at 250 to 300°C; insoluble in water and ethanol; soluble in acids and alkalis; sparingly soluble in solutions of caustic alkalis; insoluble in alcohol.
용도
Polishing glass, coloring glass yellow, catalyst, purifying drinking water, lab reagent, carbon dioxide scrubber, and chemical sensors. It is used in the preparation of other silver compounds, and silver-oxide batteries. In organic chemistry, silver oxide finds use as an oxidizing agent for aldehyes to produce carboxylic acids.
제조 방법
Silver(I) oxide is precipitated by mixing solutions of silver nitrate and caustic soda: 2AgNO
3 + 2NaOH → Ag2O + 2NaNO
3 + H
2O.
일반 설명
Odorless brown-black solid. Sinks in water.
반응 프로필
Hydrogen sulfide is rapidly oxidized and may ignite in contact with Silver oxide [Bretherick 1979 p. 977]; Mixtures of metal sulfides, gold(III) sulfide, antimony sulfide or mercury (II) sulfide, phosphorus, sulfur, selenium, and selenium disulfide ignite on grinding with the oxide. Ammonia or hydrazine slowly react with Silver oxide forming silver nitride or in the presence of alcohol, silver fulminate may also be produced [Bretherick 1979 p. 203]. Oxidation of magnesium is explosive when warmed with Silver oxide.
위험도
Fire and explosion risk in contact with
organic materials or ammonia.
건강위험
Contact with eyes causes mild irritation. If continued for a long period, ingestion or inhalation of silver compounds can cause permanent discoloration of the skin (argyria).
화재위험
Behavior in Fire: Decomposes into metallic silver and oxygen. If large quantities are involved, the oxygen might increase the intensity of the fire.
Safety Profile
A poison by intraperitoneal route. Moderately toxic by ingestion. Flammable by chemical reaction; an oxidizing agent. Explodes in contact with ammonia. Incompatible with CuO, (NH3 + ethanol), (hydrazine + ethanol), CO, HzS, Mg, auric sulfide, Sb sulfide, Hg sulfide, nitroalkanes, Se, S, P, K, Na, NaK, seleninyl chloride. See also SILVER COMPOUNDS.
Purification Methods
Leach the oxide with hot water in a Soxhlet apparatus for several hours to remove any entrained electrolytes. [Glemser & Sauer in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry (Ed. Brauer) Academic Press Vol II p 1037 1965.]
은(I) 산화물 준비 용품 및 원자재
원자재
준비 용품