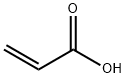
아크릴산
|
|
아크릴산 속성
- 녹는점
- 13 °C (lit.)
- 끓는 점
- 139 °C (lit.)
- 밀도
- 1.051 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
- 증기 밀도
- 2.5 (vs air)
- 증기압
- 4 mm Hg ( 20 °C)
- 굴절률
- n
20/D 1.421
- 인화점
- 130 °F
- 저장 조건
- Store at +15°C to +25°C.
- 용해도
- 1000g/L
- 물리적 상태
- 액체
- 산도 계수 (pKa)
- 4.25(at 25℃)
- 색상
- 투명한
- 냄새
- 매캐한 냄새
- pH 범위
- 1 - 2
- 수소이온지수(pH)
- 3.68(1 mM solution);3.14(10 mM solution);2.63(100 mM solution);
- 폭발한계
- 3.9-19.8%(V)
- 수용성
- 혼용 가능
- 감도
- Air Sensitive
- 최대 파장(λmax)
- 231nm(lit.)
- Merck
- 14,130
- BRN
- 635743
- 노출 한도
- TLV-TWA 10 ppm (30 mg/m3) (ACGIH).
- 안정성
- 안정성 불안정 - p-메톡시페놀을 억제제로 함유할 수 있습니다. 위험한 중합이 발생하기 쉽습니다. 타기 쉬운. 강한 산화제, 강염기, 아민과 호환되지 않습니다. 산화제와 접촉하면 화재가 발생할 수 있습니다. 빛과 공기에 민감합니다. 흡습성.
- LogP
- 0.46 at 25℃
- CAS 데이터베이스
- 79-10-7(CAS DataBase Reference)
- IARC
- 3 (Vol. 19, Sup 7, 71) 1999
안전
- 위험 및 안전 성명
- 위험 및 사전주의 사항 (GHS)
| 위험품 표기 | C,N | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 위험 카페고리 넘버 | 10-20/21/22-35-50 | ||
| 안전지침서 | 26-36/37/39-45-61 | ||
| 유엔번호(UN No.) | UN 2218 8/PG 2 | ||
| WGK 독일 | 1 | ||
| RTECS 번호 | AS4375000 | ||
| F 고인화성물질 | 8-13 | ||
| 자연 발화 온도 | 744 °F | ||
| TSCA | Yes | ||
| 위험 등급 | 8 | ||
| 포장분류 | II | ||
| HS 번호 | 29161110 | ||
| 유해 물질 데이터 | 79-10-7(Hazardous Substances Data) | ||
| 독성 | LD50 orally in rats: 2.59 g/kg (Smyth) | ||
| 기존화학 물질 | KE-29442 | ||
| 사고대비 물질 필터링 | 17 |
아크릴산 C화학적 특성, 용도, 생산
용도
플로피바인드가공용.개요
Acrylic acid (IUPAC: prop-2-enoic acid) is an organic compound with the formula CH2=CHCO2H. It is the simplest unsaturated carboxylic acid, consisting of a vinyl group connected directly to a carboxylic acid terminus. This colorless liquid has a characteristic acrid or tart smell. It is miscible with water, alcohols, ethers, and chloroform. More than one billion kilograms are produced annually.화학적 성질
Acrylic acid is a colorless, flammable, and corrosive liquid or solid (below 13 C) with an irritating, rancid, odor. Sinks and mixes with water; irritating vapor is produced.용도
Acrylic acid is produced by oxidation of acrolein or hydrolysis of acrylonitrile. It is used in the manufacture of plastics; in paints, polishes, and adhesives; and as coatings for leather.정의
An unsaturated liquid carboxylic acid with a pungent odor. The acid and its esters are used to make ACRYLIC RESINS.생산 방법
Acrylic acid is produced from propene which is a by product of ethylene and gasoline production. CH2=CHCH3 + 1.5 O2→ CH2=CHCO2H + H2O Because acrylic acid and its esters have long been valued commercially, many other methods have been developed but most have been abandoned for economic or environmental reasons. An early method was the hydrocarboxylation of acetylene ("Reppe chemistry") : HCCH + CO + H2O → CH2=CHCO2H This method requires nickel carbonyl and high pressures of carbon monoxide. It was once manufactured by the hydrolysis of acrylonitrile which is derived from propene by ammoxidation, but was abandoned because the method cogenerates ammonium derivatives. Other now abandoned precursors to acrylic acid include ethenone and ethylene cyanohydrin.일반 설명
Acrylic acid is a colorless liquid with a distinctive acrid odor. Flash point 130°F. Boiling point 286°F. Freezing point 53°F. Corrosive to metals and tissue. Prolonged exposure to fire or heat can cause polymerization. If polymerization takes place in a closed container, violent rupture may occur. The inhibitor (usually hydroquinone) greatly reduces the tendency to polymerize.공기와 물의 반응
Flammable. Soluble in water. The presence of water, due to different solubilities of the acid and inhibitor (partitioning one from the other), may initiate polymerization.반응 프로필
ACRYLIC ACID may polymerize violently especially when the frozen acid is partially thawed (freezing point 12°C or 53°F). Frozen acid should be melted at room temperature and the process should be well stirred. Do not use heat during the melting process [Kirk-Othmer, 3rd ed., Vol. 1, 1978, p. 330]. Corrodes iron and steel and polymerization may occur on contact with iron salts. The uninhibited acid polymerizes exothermically at ambient temperature and explodes if confined. The inhibitor (usually hydroquinone) greatly reduces the tendency to polymerize. Explosive polymerization can also occur with strong bases, amines, ammonia, oleum, chlorosulfonic acid, and peroxides. Mixing with 2-aminoethanol, 28% ammonium hydroxide, ethylenediamine or ethyleneimine in a closed container causes an increase in temperature and pressure. Can react violently with oxidizing reagents and strong bases [Bretherick, 5th ed., 1995, p. 419].건강위험
Acrylic acid is a corrosive liquid that cancause skin burns. Spill into the eyes candamage vision. The vapors are an irritantto the eyes. The inhalation hazard is oflow order. An exposure to 4000 ppm for4 hours was lethal to rats. The oral LD50values reported in the literature show widevariation. The dermal LD50 value in rabbitsis 280 mg/kg.화재위험
Combustible liquid; flash point (closed cup) 54°C (130°F), (open cup) 68°C (155°F); vapor pressure 31 torr at 25°C (77°F); vapor density 2.5 (air=1); autoignition temperature 360°C (680°F). Vapors of acrylic acid form explosive mixtures with air within the range 2.9–8.0% by volume in air. Fireextinguishing agent: water spray, “alcohol” foam, dry chemical, or CO2; use a water spray to flush and dilute the spill and to disperse the vapors.Acrylic acid may readily polymerize at ambient temperature. Polymerization may be inhibited with 200 ppm of hydroquinone monomethyl ether (Aldrich 2006). In the presence of a catalyst or at an elevated temperature, the polymerization rate may accelerate, causing an explosion. The reactions of acrylic acid with amines, imines, and oleum are exothermic but not violent. Acrylic acid should be stored below its melting point with a trace quantity of polymerization inhibitor. Its reactions with strong oxidizing substances can be violent.
색상 색인 번호
Acrylates are esters from acrylic acid. Occupational contact allergies from acrylates have frequently been reported and mainly concern workers exposed to the glues based on acrylic acid, as well as dental workers and beauticians.Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, skin contact, and intraperitoneal routes. An experimental teratogen. Other experimental reproductive effects. A severe skin and eye irritant. Questionable carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic and tumorigenic data. Corrosive. Flammable liquid. May undergo exothermic polymerization at room temperature. May become explosive if confined. A fire hazard when exposed to heat or flame.Safety
Acrylic acid is severely irritating and corrosive to the skin and the respiratory tract. Eye contact can result in severe and irreversible injury. Low exposure will cause minimal or no health effects, while high exposure could result in pulmonary edema. The LD50 is 340 mg/kg (rat, oral).잠재적 노출
Acrylic acid is chiefly used in manufacture of plastics, acrylates, polyacrylic acids, polymer, and resins; as a monomer in the manufacture of acrylic resins and plastic products, leather treatment, and paper coatings. Also, it is used as a tackifier and flocculant.환경귀착
Acrylic acid is corrosive, and its toxicity occurs at the site of contact.운송 방법
UN2218 Acrylic acid, stabilized, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material, 3-Flammable liquidPurification Methods
It can be purified by steam distillation, or vacuum distillation through a column packed with copper gauze to inhibit polymerisation. (This treatment also removes inhibitors such as methylene blue that may be present.) Azeotropic distillation of the water with *benzene converts aqueous acrylic acid to the anhydrous material. [Beilstein 2 H 397, 2 I 186, 2 II 383, 2 III 1215, 2 IV 1455.]비 호환성
May form explosive mixture with air. Light, heat, and peroxides can cause polymerization. Use MEHQ (monomethyl ether of hydroquinone) as an inhibitor. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Incompatible with sulfuric acid, caustics, ammonia, amines, isocyanates, alkylene oxides; epichlorohydrin, toluene diamine, oleum, pyridine, methyl pyridine, n-methyl pyrrolidone, 2-methyl-6-ethyl aniline, aniline, ethylene diamine, ethyleneimine, and 2aminoethanol. Severely corrodes carbon steel and iron; attacks other metals. May accumulate static electrical charges and may cause ignition of its vapors.폐기물 처리
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. Incineration. 100 500 ppm potassium permanganate will degrade acrylic acid to a hydroxy acid which can be disposed of at a sewage treatment.아크릴산 준비 용품 및 원자재
원자재
아크롤레인
2-Amino-3-chlorobenzoic acid
락토니트릴
olefine ketone
프로필렌
톨루엔
아크릴아마이드
니켈카르보닐
에틸렌 클로로히드린
비스무트
암모늄 이황산염
폴리아크릴산
아크릴로나이트릴
황산
준비 용품
Carboxy styrene-butadiene latex
water stabilizing agent YSS-93
3-Hydrazinyl-N-methylpropanamide
Acrylic latex
Water quality stabilizer
AMPS-Acrylate copolymer
아크릴산 2-에틸헥실
2-포스포노-1,2,4-부탄트리카복실산
2-하이드록시프로필아크릴레이트
4-CHLORO-8-(TRIFLUOROMETHYL)QUINOLINE
1,2,3,4-Tetrahydro-9-methylcarbazol-4-one
아크릴산 4-하이드록시부틸
Pressure sensitive adhesive
Latex paint for interior and exterior wall
nonformaldehyde resin finishing agent CN-NF^{3^}
N-ACRYLOXYSUCCINIMIDE
2-(2-CARBOXYETHYL)THIO-4,6-DIMETHYLPYRIMIDINE
아크릴산/아크릴산 나트륨 공중합체
Acrylic acid-hydroxypropyl acrylate copolymer
Antiscale and inhibitor
acrylic resin coating finish
Viscosity increaser
Antiscale dispersant
Thickening agent
PAINT
펜타에리스리톨 트리아크릴레이트
Ce^<4+^> initiated starch-g-acrylic acid water absorbent agent (I)
scale inhibitor and dispersant TS-1615
conductive coating-composite system of acrylic copolymer and cuprous iodide
아크릴산이 있는 말레익산 폴리머
3-(1H-1,2,4-TRIAZOL-1-YL)PROPANOIC ACID
트리메틸올프로판 EO 변성 트리아크릴레이트
Styrene-acrylic latex
Water treatment disinfectant
Binder for coating printing
corrosion and scale inhibitor CW-1901
surfactant ASMS
아크릴산에틸
acrylate resin emulsion s-1
폴리아크릴산소다
아크릴산 공급 업체
글로벌( 729)공급 업체
| 공급자 | 전화 | 이메일 | 국가 | 제품 수 | 이점 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Auschemicals Pty Ltd | +61406202619 |
info@auschemicals.com | Australia | 431 | 58 |
| Hebei Mojin Biotechnology Co., Ltd | +8613288715578 |
sales@hbmojin.com | China | 12471 | 58 |
| Yujiang Chemical (Shandong) Co.,Ltd. | +86-17736087130 +86-18633844644 |
catherine@yjchem.com.cn | China | 351 | 58 |
| Capot Chemical Co.,Ltd. | 571-85586718 +8613336195806 |
sales@capotchem.com | China | 29797 | 60 |
| Shanghai Daken Advanced Materials Co.,Ltd | +86-371-66670886 |
forrest.lee@dakenchem.com | China | 15956 | 58 |
| Henan Tianfu Chemical Co.,Ltd. | +86-0371-55170693 +86-19937530512 |
info@tianfuchem.com | China | 21689 | 55 |
| Hefei TNJ Chemical Industry Co.,Ltd. | +86-0551-65418679 +86-18949832763 |
info@tnjchem.com | China | 2989 | 55 |
| Yancheng Green Chemicals Co.,Ltd | +undefined-86-25-86655873 |
info@royal-chem.com | China | 114 | 58 |
| Hubei Jusheng Technology Co.,Ltd. | 18871490254 |
linda@hubeijusheng.com | CHINA | 28180 | 58 |
| Jinan Finer Chemical Co., Ltd | +86-531-88989536 +86-15508631887 |
sales@finerchem.com | China | 2966 | 58 |