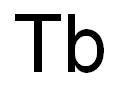터븀(테르븀) C화학적 특성, 용도, 생산
화학적 성질
silvery-white chip or ingot, or grey powder
물리적 성질
There are two allotropic (crystal forms) of terbium, both of which are dependent on itstemperature. The alpha ((α) form exists at room temperatures and up to temperatures of1,298°C, and the beta (β) form exists beyond these temperatures. Although terbium is a silverymetal that resembles aluminum and feels like lead, it is much heavier than either of thesetwo elements. It is placed in the yttrium subgroup (lanthanide series) of the rare-earths. It isalso resistant to corrosion.
Its melting point is 1,356.9°C, its boiling point is 3,230°C, and its density is 8.23g/cm
3.
Isotopes
There are a total of 52 isotopes of terbium, and only one of these is stable (Tb-159). Terbium-59 makes up 100% of the element found in the Earth’s crust.
Origin of Name
Named for a village in Sweden.
출처
Of all the 17 rare-earths in the lanthanide series, terbium is number 14 in abundance.Terbium can be separated from the minerals xenotime (YPO
4) and euxenite, a mixture of thefollowing: (Y, Ca, Er, La, Ce, Y, Th)(Nb, Ta, Ti
2O
6). It is obtained in commercial amountfrom monazite sand by the ion-exchange process. Monazite may contain as much as 50%rare-earth elements, and about 0.03% of this is terbium.
Characteristics
Terbium is not found in great quantities on Earth. In fact, minerals where terbium is foundcontain about 0.03% terbium. Not much of the stable isotope is found as a free metal; rathermost of it is mixed with other rare-earths or are in compound forms.
역사
Discovered by Mosander in 1843. Terbium is a member of the lanthanide or “rare earth” group of elements. It is found in cerite, gadolinite, and other minerals along with other rare earths. It is recovered commercially from monazite in which it is present to the extent of 0.03%, from xenotime, and from euxenite, a complex oxide containing 1% or more of terbia. Terbium has been isolated only in recent years with the development of ion-exchange techniques for separating the rareearth elements. As with other rare earths, it can be produced by reducing the anhydrous chloride or fluoride with calcium metal in a tantalum crucible. Calcium and tantalum impurities can be removed by vacuum remelting. Other methods of isolation are possible. Terbium is reasonably stable in air. It is a silver-gray metal, and is malleable, ductile, and soft enough to be cut with a knife. Two crystal modifications exist, with a transformation temperature of 1289°C. Forty-two isotopes and isomers are recognized. The oxide is a chocolate or dark maroon color. Sodium terbium borate is used as a laser material and emits coherent light at 0.546 μm. Terbium is used to dope calcium fluoride, calcium tungstate, and strontium molybdate, used in solid-state devices. The oxide has potential application as an activator for green phosphors used in color TV tubes. It can be used with ZrO2 as a crystal stabilizer of fuel cells that operate at elevated temperature. Few other uses have been found. The element is priced at about $40/g (99.9%). Little is known of the toxicity of terbium. It should be handled with care as with other lanthanide elements.
용도
There are few uses for terbium. However, terbium can be used as an activator for greenphosphor in TV tubes, and some of its compounds are used to produce laser lights. It is alsoused to “dope” (coat) some forms of solid-state instruments, as a stabilizer in fuel cells so thatthey can operate at high temperatures, and as a metal for control rods in nuclear reactors.
제조 방법
Terbium is recovered from the minerals, monazite, xenotime, and euxenite. The recovery processes are quite similar to those of other lanthanide elements (See individual lanthanide elements). The metal is separated from other rareearths by ion exchange methods, which are relatively easy and faster than fractional crystallization techniques.
Terbium metal is obtained from its anhydrous trifluoride, TbF
3, or trichloride, TbCl
3, by thermal reduction with calcium, carried out in a tantalum crucible. Terbium produced by such methods may contain traces of calcium and tantalum. High purity metal can be prepared by various methods such as vacuum remelting, distillation, amalgam formation, floating zone melting, and various chemical processes.
정의
terbium: Symbol Tb. A silverymetallic element belonging to thelanthanoids; a.n. 65; r.a.m. 158.92;r.d. 8.23 (20°C); m.p. 1356°C; b.p.3123°C. It occurs in apatite and xenotime,from which it is obtained by anion-exchange process. There is onlyone natural isotope, terbium–159,which is stable. Seventeen artificialisotopes have been identified. It isused as a dopant in semiconductingdevices. It was discovered by CarlMosander (1797–1858) in 1843.
위험도
The halogens (group VIIA) of terbium are strong irritants. Most of the compounds aretoxic and some are explosive. A vacuum or inert atmosphere must be maintained when workingwith the metal because of its strong oxidation properties.
터븀(테르븀) 준비 용품 및 원자재
원자재
준비 용품