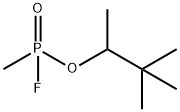
소만 C화학적 특성, 용도, 생산
개요
Soman was first synthesized in 1944 by the German chemist
Richard Kuhn. It was the third of a family of related organophosphate
or organophosphorus (OP) compounds that were
developed for use as chemical warfare agents during World
War II (tabun (GA) and sarin (GB) were developed several
years earlier). Unlike tabun and sarin, soman was not
produced in large quantities or loaded into munitions during
World War II due to its late discovery and difficulties associated
with scaling up the manufacturing process. After the war,
other nations including the United States, United Kingdom,
and former Soviet Union were also quick to realize the
weaponization potential of OP nerve agents and establish
research and development programs of their own. Soman was
never mass produced by the United States due to the difficulty
and cost of large-scale production as well as concerns over the
lack of effective antidotes (compared to tabun and sarin).
However, it was manufactured in large quantities and loaded
into munitions by the former Soviet Union beginning in the
1960s. In the 1990s, the production, stockpiling, and use of
chemical weapons (including soman) by nations were banned
by the Chemical Weapons Convention (CWC), an international
agreement that entered into force in 1997. The CWC is
implemented by the Organisation for the Prohibition of
Chemical Weapons (OPCW) and requires the destruction of
existing chemical weapons stockpiles. Nearly all of the nations
in the world are members of the OPCW, and destruction of
existing chemical weapons stockpiles was ongoing at the time
of this writing in 2012.
화학적 성질
Colorless liquid. Evolves odorless gas.
용도
Chemical warfare agent.
일반 설명
Colorless liquid, odorless to fruity.
공기와 물의 반응
Hydrolyzed by water, rapidly hydrolyzed by dilute aqueous sodium hydroxide. Water alone removes Fluoride atom producing nontoxic acid.
반응 프로필
Acidic conditions produce hydrogen fluoride; alkaline conditions produce isopropyl alcohol and polymers. When heated to decomposition or reacted with steam, Soman. emits very toxic fumes of fluorides and oxides of phosphorus. Slightly corrosive to steel. Hydrolyzed by water.
위험도
Highly toxic by ingestion, inhalation, and
skin absorption; may be fatal on short exposure;
cholinesterase inhibitor; military nerve gas; fatal
dose (man) 0.01 mg/kg.
건강위험
Median lethal dose (mg-min/m3): 2500 by skin (vapor) or 350 (liquid); 35 inhaled. Median incapacitating dose: 25 inhaled. Eye/skin toxicity: Very high. Rate of action: Very rapid. Physiological action: Cessation of breath-death may follow. Detoxification rate: Low, essentially cumulative. (ANSER)
잠재적 노출
Agent GD, an organic fluoride compound, is a quick-acting chemical warfare nerve agent (nerve gas). Medical treatment of soman is difficult because it permanently binds to receptors in the body in minutes. Large amounts of the vapor or liquid can hurt you in minutes, and can quickly lead to death.
운송 방법
UN2810 Toxic liquids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poison Inhalation Hazard, Technical Name Required. Military driver shall be given full and complete information regarding shipment and conditions in case of emergency. AR 50-6 deals specifically with the shipment of chemical agents. Shipments of agent will be escorted in accordance with AR 740-32
비 호환성
Hydrolyzed by water to form hydrogen fluoride and the nontoxic phosphonic acid derivative. It is rapidly hydrolyzed by dilute aqueous NaOH Stable after storage in steel for 3 months @ 65 C. Raising the pH increases the rate of decomposition significantly. GD decomposes slowly in water; will hydrolyze to form HF-H-H-O-CH3 and (CH3)3-C-C-O-P-OH. GD reacts readily with bases and weak acids. Under acid conditions, GD hydrolyzes, forming hydrofluoric acid (HF). Flammable hydrogen gas produced by the corrosive vapors reacting with metals, concrete, etc., may be present. Corrosive to steel and possibly other ferrous metals. GD corrodes steel at the rate of 1×10-5 in/month. When heated to decomposition or on contact with steam, it emits very toxic fumes of fluorides and oxides of phosphorus.
소만 준비 용품 및 원자재
원자재
준비 용품