Mifamurtide hydrate C화학적 특성, 용도, 생산
개요
Mifamurtide (also referred to as MTP-PE) was approved by the EC
in 2009 for the treatment of high-grade nonmetastatic osteosarcoma
patients between the ages 2 and 30 in combination with postoperative
multiagent chemotherapy.
Mifamurtide is the first new drug approved for the treatment of osteosarcoma
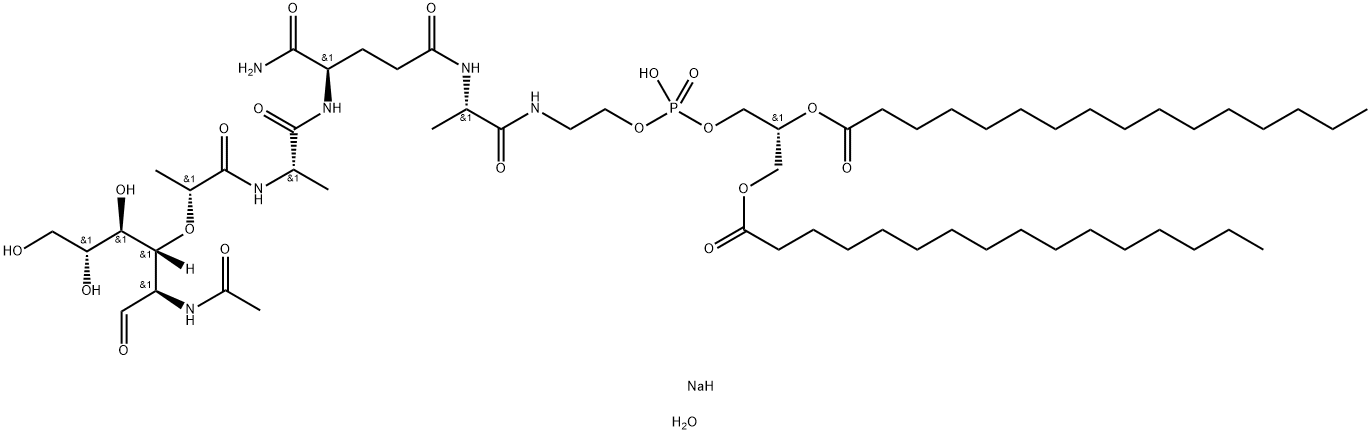
in over 20 years. The active component of mifamurtide is
muramyl dipeptide (MDP), a component of bacterial cell walls, which
is linked via an alanine moiety to phosphatidyl ethanolamine (PE) to
form the tripeptide MTP-PE. Mifamurtide is combined with a liposome
formulation consisting of synthetic phospholipids dioleoyl phosphatidyl
serine and 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl phosphatidyl choline in a ratio of
3:7. This liposome formulation (L-MTP-PE) allows for the specific
in vivo targeting of monocytes and macrophages in the liver, spleen,
and lungs by mifamurtide . In vitro and in vivo studies have shown
that activation of monocytes and macrophages by mifamurtide leads to
the production of proinflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6, IL-8,
NO, prostaglandin E2 and PGD
2, and adhesion molecules such as LFA-1
and ICAM-1. MTP-PE is a ligand for nucleotide-binding oligomerization
domain (Nod)-2 receptor, and it has been postulated that the activation
of monocytes and macrophages is mediated by Nod-2 following phagocytosis
of L-MTP-PE and liberation of MDP. In vitro, human
monocytes treated with MTP-PE had tumoricidal activity on allogeneic
and autologous tumor cells but were nontoxic toward normal cells.
용도
Osteosarcoma.
Mifamurtide hydrate 준비 용품 및 원자재
원자재
준비 용품