Uric acid suppliers
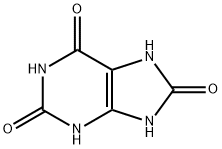
URIC ACID
- CAS:
- 69-93-2
- MF:
- C5H4N4O3
- MW:
- 168.11
Suppliers by country/region
Company Type
Properties
- Melting point:
- >300 °C (lit.)
- Boiling point:
- 297.02°C (rough estimate)
- Density
- 1,9 g/cm3
- refractive index
- 1.9900 (estimate)
- storage temp.
- Sealed in dry,2-8°C
- solubility
- Aqueous Base (Sparingly, Heated)
- form
- crystalline
- pka
- 3.89(at 12℃)
- color
- White to off-white
- Odor
- Odorless
- biological source
- animal (seabird feces (guano))
- Water Solubility
- Soluble in 1M sodium hydroxide solution. Slightly soluble in water. Insoluble in ether and alcohol.
- Merck
- 14,9875
- BRN
- 156158
- Stability:
- Stable. Incompatible with acids, bases, oxidising agents.
- LogP
- -1.730 (est)
- CAS DataBase Reference
- 69-93-2(CAS DataBase Reference)
- EPA Substance Registry System
- Uric acid (69-93-2)
Safety Information
- Symbol(GHS)

GHS07
- Signal word
- Warning
- Hazard statements
- H302-H315-H319-H332-H335
- Precautionary statements
- P261-P280-P305+P351+P338
- Hazard Codes
- Xi
- Risk Statements
- 33-36/37/38
- Safety Statements
- 24/25-36-26
- WGK Germany
- 3
- RTECS
- YU7050080
- TSCA
- Yes
- HS Code
- 29339900
- Toxicity
- A nitrogenous end product and the principal excretory product of purine metabolism in mammals. In birds and reptiles, it is the principal end product of nitrogen metabolism in general. Defects in uric acid metabolism and excretion appear to be associated with a number of disease states, and it frequently occurs as a component of renal calculi. It has not been associated closely with toxic insults except in the case of lead poisoning. Lead causes an elevation in blood uric acid concentration (uric acidemia) and a decrease in uric acid excretion.
Use
The normal or reference levels of uric acid are 2.4-6.0 mg/dL for females and 3.4-7.0 mg/dL for males. However, these normal values vary from different laboratory data[7]. Altered serum uric acid concentrations, both above and below normal levels, have been proven to be linked to some diseases[4]. In addition, both high and low levels of uric acid increase mortality rates, showing an U-shaped association between serum uric acid levels and all-cause, cardiovascular, and cancer mortality[8]. According to available epidemiological data, hyperuricaemia is associated with a greater risk of target organ damage and of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality[9]. Elevated uric acid (hyperuricemia) was reported to contribute to gout, kidney stones, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome, kidney ailments, lympho-proliferative disorders, chronic hemolytic anemias [10]. Besides, more recent results also suggested an association between uric acid and bipolar disorder[11]. Historically, uric acid has been considered as a marker of these disease states. Moreover, recent research results have provided evidence that uric acid may actually play a role in the development or progression of such diseases[4]. The mechanisms between hyperuricemia and mortality can be explained by the correlation of the oxidative stress and the inflammasome. Hyperuricemia can activate the NLRP3 inflammasome and induce the production of interleukin-1, which in turn result in an inflammatory cascade[12]. The amount of urate in the blood depends on the dietary intake of purines, urate biosynthesis, and the rate of urate excretion[4]. Diets consisting of food and drinks that are high in purines may cause an imbalance in the body where higher amounts of uric acid are being produced, but not enough is getting removed as waste. Foods that contain high levels of purines mainly include wild game (veal, venison, and duck), red meat, seafood, organ meat. Alcoholic beverages also contain high purines and alcohol consumption can also raise uric acid levels in blood. In another aspect, alcohol causes dehydration of the body and slow down the uric acid circulation. Besides, high-fat foods intake also decrease uric acid being excreted by holding uric acid in the kidneys[13]. The imbalance caused by high purine foods intake can lead to higher than normal uric acid levels in the blood, which can form crystals and result in painful gout and attacks. Impaired renal function also leads to increased uric acid concentrations[14].
218 supplier list of "URIC ACID"
- Product Name:Uric Acid;2,6,8-Trihydroxypurine;2,6,8-Trioxypurine;Urate;2,6,8-Trioxopurine;Lithic acid
- Products Intro:Purity: 99.52% | Package: 500mg;42USD | CustNote: REAGENT;FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY
- Company Type: Trader
- Country/Region: UNITED STATES
- Main Products: Compound Libraries,Noval Small Molecucles,Nature Compounds,Inhibitory Antibodies,Life science Kits
- Product Name:Uric acid
- Company Type: Reagent
- Country/Region: CHINA
- Main Products: Gamma-butyrolactone
- Product Name:Uric acid
- Products Intro:CustNote: https://surfactant.alfa-chemistry.com/product/uric-acid-cas-69-93-2-321079.html
- Company Type: Reagent
- Country/Region: UNITED STATES
- Main Products: Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API),Insect Pheromone,Boronic Compounds,Material & Chemicals,Lipid Compounds