|
|
| | N-(2-Methylphenyl)thiourea Basic information |
| Product Name: | N-(2-Methylphenyl)thiourea | | Synonyms: | (2-methylphenyl)-thioure;1-(2-methylphenyl)thiourea;1-o-Tolyl-2-thiourea;2-thio-1-o-tolyl-ure;2-tolylthiourea;N-(o-Tolyl)thiourea;ortho-Tolylthiourea;Thiourea, (2-methylphenyl)- | | CAS: | 614-78-8 | | MF: | C8H10N2S | | MW: | 166.24 | | EINECS: | 210-395-3 | | Product Categories: | API intermediates | | Mol File: | 614-78-8.mol | 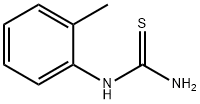 |
| | N-(2-Methylphenyl)thiourea Chemical Properties |
| | N-(2-Methylphenyl)thiourea Usage And Synthesis |
| General Description | Crystalline solid. | | Reactivity Profile | When heated to decomposition, N-(2-Methylphenyl)thiourea emits very toxic fumes of oxides of nitrogen and sulfur. [EPA, 1998]. Organosulfides are incompatible with acids, diazo and azo compounds, halocarbons, isocyanates, aldehydes, alkali metals, nitrides, hydrides, and other strong reducing agents. Reactions with these materials generate heat and in many cases hydrogen gas. Many of these compounds may liberate hydrogen sulfide upon decomposition or reaction with an acid. | | Health Hazard | The material is highly toxic if orally ingested. | | Fire Hazard | When heated to decomposition, N-(2-Methylphenyl)thiourea emits very toxic fumes of oxides of nitrogen and sulfur. |
| | N-(2-Methylphenyl)thiourea Preparation Products And Raw materials |
|