- Sodium citrate
-
- $0.00 / 1KG
-
2025-04-16
- CAS:68-04-2
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99.0-101%
- Supply Ability: 500kg/month
- Sodium citrate
-

- $10.00 / 1KG
-
2025-04-16
- CAS:68-04-2
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 100 mt
- Sodium Citrate
-

- $3.60 / 1kg
-
2025-04-15
- CAS:68-04-2
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: ≥99%
- Supply Ability: 3000tons/month
Related articles - Sodium Citrate and Citric Acid
- Sodium citrate and citric acid are both alkalinizing agents that make the urine less acidic. The combination of sodium citrate....
- Feb 1,2023
- Introduction of Sodium citrate
- Sodium citrate is the trisodium salt of citric acid. It has a role as a flavouring agent and an anticoagulant. It contains a c....
- May 7,2022
|
| | Sodium citrate Basic information |
| Product Name: | Sodium citrate | | Synonyms: | Citric acidsodiuM,anhydrous;1,2,3-Propanetricarboxylicacid, 2-hydroxy-, sodiuM salt (1:3);Citric acid trisodium salt Vetec(TM) reagent grade, 98%;CITRIC ACID TRISODIUM SALT, VETEC;1,2,3-Propanetricarboxylicacid,2-hydroxy,trisodiumsalt;1,2,3-propanetricarboxylicacid2hydroxy-trisodiumsalt;2,3-propanetricarboxylicacid,2-hydroxy-trisodiumsalt;citnatin | | CAS: | 68-04-2 | | MF: | C6H9NaO7 | | MW: | 216.12 | | EINECS: | 200-675-3 | | Product Categories: | AnticoagulantsBiological Buffers;Buffers A to ZProteins and Derivatives;Blood;Buffer Convenience Packaging;Buffer SolutionsBiological Buffers;Coagulation Proteins and Reagents;Immune Cell Signaling and Blood;Plasma&Blood Proteins;ReagentsMore...Close...;AlphabeticalMolecular Biology;Biological Buffers;BioUltra Buffers;BioUltraBiological Buffers;Buffer SolutionsBiochemicals and Reagents;ChelatorsProtein Structural Analysis;DNA&RNA Purification;Molecular Biology Reagents;Optimization ReagentsMolecular Biology;X-Ray Crystallography;Buffers A to Z;Cytochemistry Products;Hematology and Histology;Chemistry;FOOD ADDITIVES;bc0001;68-04-2 | | Mol File: | 68-04-2.mol | 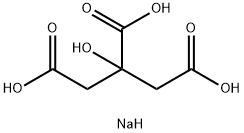 |
| | Sodium citrate Chemical Properties |
| Melting point | 300°C | | density | 1.008 g/mL at 20 °C | | FEMA | 3026 | SODIUM CITRATE | | storage temp. | 2-8°C | | solubility | Water (Slightly) | | form | Liquid | | color | White to off-white | | PH | 8.59(1 mM solution);8.9(10 mM solution);9.04(100 mM solution);9.26(1000 mM solution) | | Odor | at 100.00?%. odorless | | Water Solubility | Soluble in water. | | Sensitive | Hygroscopic | | λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: ≤0.1 | | Stability: | Hygroscopic | | InChIKey | HRXKRNGNAMMEHJ-UHFFFAOYSA-K | | LogP | -0.280 (est) | | CAS DataBase Reference | 68-04-2(CAS DataBase Reference) | | EPA Substance Registry System | Trisodium citrate (68-04-2) |
| | Sodium citrate Usage And Synthesis |
| Description | Trisodium citrate has the chemical formula of Na3C6H5O7.It is some times referred to simply as sodium citrate, though sodium citrate can refer to any of the three sodium salts of citric acid. It possesses a saline, mildly tart flavor. For this reason, citrates of certain alkaline and alkaline earth metals (e.g. sodium and calcium citrates) are commonly known as "sour salt" (occasionally citric acid is erroneously termed sour salt). | | Description | Sodium citrate may refer to any of the sodium salts of citric acid (though most commonly the third):
Mono sodium citrate
Di sodium citrate
Tri sodium citrate
As food additives, the 3 forms of the salt are also collectively known by the E number E331. | | Chemical Properties | Sodium citrate is odorless and has a pleasant, acid taste. Sodium citrate is anhydrous or contains two molecules of water of crystallization | | Chemical Properties | White to off-white crystalline powder | | Occurrence | Citric acid and its salts occur naturally in many plants and animals. | | Uses | Alkalizer (systemic). | | Uses | Sodium citrate is also known as citrate of soda, the white crystals or granular
powder was obtained by neutralizing citric acid with sodium
carbonate. It is soluble in water but less so in alcohol. Sodium
citrate was used as a preservative in albumen papers. | | Uses | Trisodium Citrate is a buffer and sequestrant that is the trisodium
salt of citric acid. see sodium citrate. | | Uses | Sodium Citrate is a buffer and sequestrant obtained from citric acid
as sodium citrate anhydrous and as sodium citrate dihydrate or
sodium citrate hydrous. the crystalline products are prepared by
direct crystallization from aqueous solutions. sodium citrate anhy-
drous has a solubility in water of 57 g in 100 ml at 25°c, while
sodium citrate dihydrate has a solubility of 65 g in 100 ml at 25°c.
it is used as a buffer in carbonated beverages and to control ph in
preserves. it improves the whipping properties in cream and pre-
vents feathering of cream and nondairy coffee whiteners. it pro-
vides emulsification and solubilizes protein in processed cheese. it
prevents precipitation of solids during storage in evaporated milk.
in dry soups, it improves rehydration which reduces the cooking
time. it functions as a sequestrant in puddings. it functions as a
complexing agent for iron, calcium, magnesium, and aluminum.
typical usage levels range from 0.10 to 0.25%. it is also termed
trisodium citrate. | | Uses | sodium citrate may be used in cosmetic formulations as an alkalizer and to bind trace metals in solutions (by means of a chelating action). It is the sodium salt of citric acid. | | Application | 2 – 1 - Food
Sodium citrate is chiefly used as a food additive E331, usually for flavor or as a preservative. Sodium citrate is employed as a flavoring agent in certain varieties of club soda. Sodium citrate is common as an ingredient in Bratwurst, and is also used in commercial ready to drink beverages and drink mixes, contributing a tart flavour.
2 – 2 - Buffer
As a conjugate base of a weak acid, citrate can perform as a buffering agent or acidity regulator, resisting changes in pH. Sodium citrate is used to control acidity in some substances, such as gelatin desserts. It can be found in the mini milk containers used with coffee machines. The compound is the product of antacids, such as Alka- Seltzer, when they are dissolved in water.
2 – 3 - Medical uses
In 1914, the Belgian doctor Albert Hustin and the Argentine physician and researcher Luis Agote successfully used sodium citrate as an anticoagulant in blood transfusions. It continues to be used today in blood collection tubes and for the preservation of blood in blood banks. The citrate ion chelates calcium ions in the blood by forming calcium citrate complexes, disrupting the blood clotting mechanism.
Sodium citrate is used to relieve discomfort in urinary tract infections, such as cystitis, to reduce the acidosis seen in distal renal tubular acidosis, and can also be used as an osmotic laxative. It is a major component of the WHO Oral Rehydration Solution. | | Definition | ChEBI: Sodium citrate is the trisodium salt of citric acid. It has a role as a flavouring agent and an anticoagulant. It contains a citrate(3-). | | Preparation | Produced by the neutralization of citric acid with sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate. May be prepared in an anhydrous state or may contain 2 mole of water per mole of sodium citrate. | | General Description | Citric acid trisodium salt corresponds to a molecular weight of 258 Da. It has high sodium content and sieving coefficients. | | Biochem/physiol Actions | Citrate Concentrated Solution or sodium citrate is an anticoagulant used for collecting blood samples. It is useful in coagulation testing and for the erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Sodium citrate eliminates calcium, which is known to mediate coagulation. | | Food additive | Sodium citrate is some times used as an acidity regulator in drinks, and also as an emulsifier for oils when making cheese. It allows the cheeses to melt with out becoming greasy. Consider the following quote from Modernist Cuisine:
Our modernist version of mac and cheese owes its chemistry to James L. Kraft, who in 1916 patented the first American cheese slice. He showed that sodium phosphate keeps the water and fat droplets mixed when the cheese is melted. We use sodium citrate, which has the same effect and is easier to find. The resulting texture is as smooth as melted American cheese, but as complex and intense in flavor as any of your favorite cheeses. | | Purification Methods | Crystallise the salt from warm water by cooling to 0o. [Beilstein 3 III 1100, 3 IV 1274.] |
| | Sodium citrate Preparation Products And Raw materials |
|