|
|
| | Ethylenediamine-N,N'-bis((2-hydroxyphenyl)acetic acid) Basic information |
| Product Name: | Ethylenediamine-N,N'-bis((2-hydroxyphenyl)acetic acid) | | Synonyms: | CHEL-138;EDHPA;Ethylenebisiminobis(2-hydroxyphenylacetic acid);N,N'-(1,2-Ethanediyl)bis[(2-hydroxyphenyl)carboxymethylamine];α,α'-(1,2-Ethanediyldiimino)bis(2-hydroxybenzeneacetic acid);EDDHA;EthylenediaMine-N,N;2,2'-(Ethane-1,2-diylbis(azanediyl))-bis(2-(2-hydroxyphenyl)acetic acid) | | CAS: | 1170-02-1 | | MF: | C18H20N2O6 | | MW: | 360.37 | | EINECS: | 214-625-3 | | Product Categories: | | | Mol File: | 1170-02-1.mol | 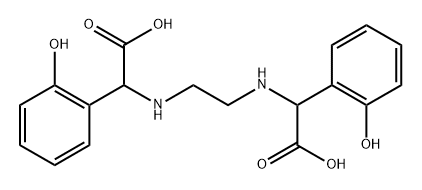 |
| | Ethylenediamine-N,N'-bis((2-hydroxyphenyl)acetic acid) Chemical Properties |
| | Ethylenediamine-N,N'-bis((2-hydroxyphenyl)acetic acid) Usage And Synthesis |
| Uses | EDDHA is used as an inorganic fertilizer. | | Agricultural Uses | EDDHA is short for Ethylenediamine-N,N'-bis((2-hydroxyphenyl)acetic acid. It is a chelating agent (C18H20O6N2) that forms a chelate, which complexes with metal ions. Fe-EDDHA, which is stable over an entire pH range, is commonly used as an iron fertilizer because of its affinity to iron. The comparison of a soil treated with iron chelates, such as EDTA (ethylenediamine tetra- aceticacid), DTPA (diethylenetriaminepentaaceticacid) or EDDHA shows that EDDHA is most effective in making iron available to plants. | | Purification Methods | Purify it by extensive Soxhlet extraction with acetone. [Bonadies & pK Est( 2) pK Est( 3) Carrano J Am Chem Soc 108 4088 1986]. |
| | Ethylenediamine-N,N'-bis((2-hydroxyphenyl)acetic acid) Preparation Products And Raw materials |
|