- 1-Fluoronaphthalene
-

- $0.00 / 1kg
-
2025-04-16
- CAS:321-38-0
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99.99%
- Supply Ability: 20 tons
- 1-Fluoronaphthalene
-

- $0.00 / 1kg
-
2025-04-16
- CAS:321-38-0
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 98
- Supply Ability: 1000
- 1-Fluoronaphthalene
-

- $1.00 / 1KG
-
2025-04-16
- CAS:321-38-0
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 10 mt
Related articles - Applications of 1-Fluoronaphthalene
- 1-Fluonaphthalene (321-38-0) is a colorless to pale yellow transparent liquid. 1-Fluoronaphthalene is an organofluorine chemic....
- Nov 1,2019
|
| | 1-Fluoronaphthalene Basic information |
| | 1-Fluoronaphthalene Chemical Properties |
| Melting point | -13 °C (lit.) | | Boiling point | 215 °C (lit.) | | density | 1.1322 g/mL at 20 °C (lit.) | | refractive index | n20/D 1.593(lit.) | | Fp | 150 °F | | storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature | | solubility | slightly soluble in water, well soluble in chloroform, ethyl acetate, and methanol. | | form | Oil | | color | Colourless to Yellow | | Specific Gravity | 1.332 | | Water Solubility | Not miscible or difficult to mix in water. | | BRN | 1906413 | | Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. | | InChIKey | CWLKTJOTWITYSI-UHFFFAOYSA-N | | CAS DataBase Reference | 321-38-0(CAS DataBase Reference) | | NIST Chemistry Reference | Naphthalene, 1-fluoro-(321-38-0) | | EPA Substance Registry System | 1-Fluoronaphthalene (321-38-0) |
| Hazard Codes | Xi | | Risk Statements | 36/37/38 | | Safety Statements | 26-36 | | RIDADR | UN2810 | | WGK Germany | 3 | | RTECS | QJ7100000 | | Hazard Note | Flammable | | TSCA | T | | HazardClass | IRRITANT | | HS Code | 29039990 |
| | 1-Fluoronaphthalene Usage And Synthesis |
| Chemical Properties | clear slightly yellow to yellow-brown liquid | | Uses | 1-Fluoronaphthalene is a fluorinated naphthalene derivative that is metabolized by fungal monooxygenase-epoxide hydrolase. It is also used as a pharmaceutical intermediate. It is Duloxetine impurity. | | Application | 1-Fluoronaphthalene was used in t-BuLi-mediated synthesis of 6-substituted phenanthridines. It was also used in the synthesis of LY248686, a potent inhibitor of serotonin and norepinephrine uptake. | | Preparation | The preparation of 1-Fluoronaphthalene is as follows:1) Diazotization reaction: 1500 g of hydrochloric acid (mass concentration: 25%) and 300 g of naphthylamine were added to a 3000 mL three-necked flask, stirred and heated to 75 ° C to dissolve, and the temperature was lowered to below 5 ° C, and 148 g was slowly added at this temperature. Sodium nitrite, stirred at low temperature for 0.3 hours after the addition, to obtain a diazonium salt solution;2) Substitution reaction: 360 g of fluoroboric acid solution (concentration: 45%) was added to the resulting solution obtained in the step 1), stirred for 0.25 h, filtered, and the filter cake was dried at a temperature of 50 ° C for 0.2 h to obtain Dry naphthylamine diazonium salt fluoroborate double salt;3) Hot air decomposition: the dried diazonium salt fluoroborate double salt is slowly added to the reactor through which hot air (hot air temperature is 85-90 ° C), and the dried powdered naphthylamine diazonium salt fluoroborate double salt is The hot air blows up the dispersion and absorbs the heat for thermal decomposition to obtain a 1-fluoronaphthalene solution containing a small amount of solid impurities;4) Purification treatment: the 1-fluoronaphthalene solution obtained in the step 3) is first washed with pure water for 3 to 6 times, then neutralized with a soda ash to a pH of 6.8 to 7.2, and finally the oil layer is separated by filtration, and the filtrate is taken. The distillation treatment gave 210 g of a naphthalene-based fluorine-containing intermediate 1-fluoronaphthalene in an amount of 99.8%. 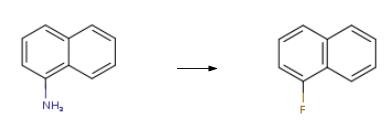
| | Air & Water Reactions | Insoluble in water. | | Reactivity Profile | Simple aromatic halogenated organic compounds, such as Fluoronaphthalene, are very unreactive. Reactivity generally decreases with increased degree of substitution of halogen for hydrogen atoms. Materials in this group may be incompatible with strong oxidizing and reducing agents. Also, they may be incompatible with many amines, nitrides, azo/diazo compounds, alkali metals, and epoxides. |
| | 1-Fluoronaphthalene Preparation Products And Raw materials |
| Preparation Products | 4-Fluoronaphtalene-1-boronic acid-->2-(1-FLUORONAPHTHALEN-4-YL)-4,4,5,5-TETRAMETHYL-1,3,2-DIOXABOROLANE-->(R)-N,N-dimethyl-3-(naphthalen-1-yloxy)-3-(thiophen-2-yl)propan-1-amine-->Duloxetine-->3-Bromo-1-fluoronaphthalene-->(S)-(+)-N,N-Dimethyl-3-(1-naphthalenyloxy)-3-(2-thienyl)propanamine-->2-(1-NAPHTHYLENE)-4,4,5,5-TETRAMETHYL-1,3,2-DIOXABOROLANE-->1-fluoro-2-iodonaphthalene-->4-FLUORONAPHTHALENE-1-SULFONYL CHLORIDE-->(S)-N,N-DIMETHYL-[3-(2-THIENYL)-3-(1-NAPHTHYLOXY)PROPYL]AMINE--PHOSPHORIC ACID (1:1)-->3-Bromo-1-fluoro-2-iodonaphthalene-->(S)-N,N-DIMETHYL-[3-(2-THIENYL)-3-(1-NAPHTHYLOXY)PROPYL]AMINE--PHOSPHORIC ACID (1:1)-->Duloxetine Impurity 4 |
|