|
|
| | ALOGLIPTIN(ALOGLIPTINE, ALOGLIPTINA) Basic information |
| Product Name: | ALOGLIPTIN(ALOGLIPTINE, ALOGLIPTINA) | | Synonyms: | Alogliptin(free base);Benzonitrile, 2-[[6-[(3R)-3-aMino-1-piperidinyl]-3,4-dihydro-3-Methyl-2,4-dioxo-1(2H)-pyriMidinyl]Methyl]-;(R)-2-[6-(3-aMino-piperidin-1-yl)-3-Methyl-2,4-dioxo-3,4-dihydropyriMidin-1(2H)-yl)Methyl]-benzonitrile;Alogliptin Benzoate API;Alogliptin
2-[[6-[(3R)-3-Amino-1-piperidinyl]-3,4-dihydro-3-methyl-2,4-dioxo-1(2H)-pyrimidinyl]methyl]benzonitrile;ALOGLIPTIN(ALOGLIPTINE, ALOGLIPTINA);Unii-jhc049lo86;2-[[6-[(3R)-3-Amino-1-piperidinyl]-3,4-dihydro-3-methyl-2,4-dioxo-1(2H)-pyrimidinyl]methyl]benzonitrile | | CAS: | 850649-61-5 | | MF: | C18H21N5O2 | | MW: | 339.39 | | EINECS: | 821-899-3 | | Product Categories: | Inhibitor;Intermediates & Fine Chemicals;Pharmaceuticals;intermediat;Inhibitors;Amines;Aromatics;Chiral Reagents;Heterocycles | | Mol File: | 850649-61-5.mol | 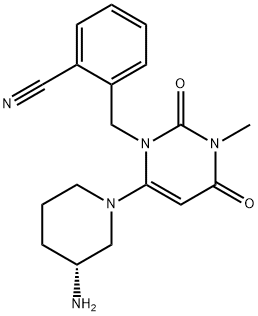 |
| | ALOGLIPTIN(ALOGLIPTINE, ALOGLIPTINA) Chemical Properties |
| Melting point | 127 - 129°C | | Boiling point | 519.2±60.0 °C(Predicted) | | density | 1.342 | | Fp | 267.8℃ | | storage temp. | Refrigerator | | solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Ethyl Acetate (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) | | form | Solid | | pka | 9.89±0.20(Predicted) | | color | White to Off-White |
| | ALOGLIPTIN(ALOGLIPTINE, ALOGLIPTINA) Usage And Synthesis |
| Description | Alogliptin is a dipeptidyl-peptidase IV (DPP-4) inhibitor that was
approved in Japan in 2010 for treatment of type 2 diabetes, a disease in
which insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction lead to hyperglycemia.
As islet function is lost, the severity of insulin resistance
increases. The introduction of DPP-4 inhibitors has brought a novel
class of insulinotropic agents for the treatment options available to type
2 diabetic patients. The therapeutic potential of glucagon-like peptide 1
(GLP-1), an incretin peptide, for the treatment of type 2 diabetes was
realized in the 1990s. The insulinotropic effects of GLP-1 depend closely
on glucose concentrations providing the possibility of glucose normalization
without the risk of hypoglycemia. GLP-1 has other non-insulinotropic
physiological actions that are advantageous. It suppresses glucagon
secretion from a cells and slows gastric emptying, which contributes to
satiety and to a slower passage and reabsorption of carbohydrates. GLP-1
also contributes to satiety via a central mechanism as a neurotransmitter
with effects on the hypothalamus. | | Chemical Properties | White Solid | | Originator | Syrrx Inc. (now Takeda San Diego) (Japan) | | Uses | Alogliptin is an oral antihyperglycemic agent that is a selective inhibitor of the enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4).
Antidiabetic agent. | | Definition | ChEBI: A piperidine that is 3-methyl-2,4-dioxo-3,4-dihydropyrimidine carrying additional 2-cyanobenzyl and 3-aminopiperidin-1-yl groups at positions 1 and 2 respectively (the R-enantiomer). Used in the form of its benzoate salt for treatment of t
pe 2 diabetes. | | Brand name | Nesina | | Clinical Use | Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor:
Treatment of type 2 diabetes in combination with
other therapies | | target | DPP-4 | | Metabolism | Alogliptin does not undergo extensive metabolism. Two
minor metabolites were detected following administration
of an oral dose of [14C]-alogliptin, N-demethylated
alogliptin, M-I (<1% of the parent compound), and
N-acetylated alogliptin, M-II (<6% of the parent
compound). M-I is an active metabolite and is a highly
selective inhibitor of DPP-4 similar to alogliptin; M-II
does not display any inhibitory activity towards DPP-4
or other DPP-related enzymes. In vitro data indicate
that CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 contribute to the limited
metabolism of alogliptin. |
| | ALOGLIPTIN(ALOGLIPTINE, ALOGLIPTINA) Preparation Products And Raw materials |
|