- Alkaline Phosphatase
-
- $0.10 / 1KG
-
2024-08-30
- CAS:9001-78-9
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99.0%
- Supply Ability: 1000 tons
- Alkaline Phosphatase
-
- $0.00 / 1g
-
2023-11-01
- CAS:9001-78-9
- Min. Order: 1g
- Purity: 99% HPLC
- Supply Ability: 100kg
|
| | Alkaline Phosphatase Basic information |
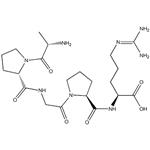
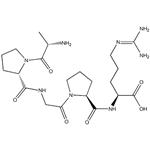
| Product Name: | Alkaline Phosphatase | | Synonyms: | PHOSPHATASE, ALKALINE TYPE XXX FROM*CALF INTESTINAL;ALKALINE PHOSPHATASE YELLOW LI;PHOSPHATASE ALKALINE TYPE XV FROM BOVINE PLACENTA;PHOSPHATASE, ALKALINE TYPE XVIII FROM*PO RCINE INTES;PHOSPHATASE ALK. FROM CALF INTEST. MUC., STAB., ~1000 U/MG*;PHOSPHATASE ALKALINE TYPE VII-S FROM*BOV INE INTESTI;PHOSPHATASE, ALKALINE TYPE VII-NT;PHOSPHATASE, ALKALINE FROM SHRIMP | | CAS: | 9001-78-9 | | MF: | C21H36N8O6 | | MW: | 496.56054 | | EINECS: | 232-631-4 | | Product Categories: | HPLC Fittings;SSI Fittings;Stainless Steel Fittings;enzyme;CAP | | Mol File: | 9001-78-9.mol | 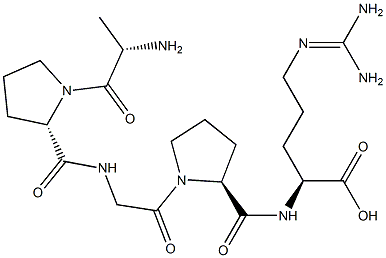 |
| | Alkaline Phosphatase Chemical Properties |
| density | 1.12 g/mL at 20 °C | | storage temp. | -20°C | | form | suspension | | color | white | | Specific Gravity | 1 | | PH | ~7.6 | | biological source | mouse | | Water Solubility | It is soluble in water. | | Specific Activity | 30-90units/mg protein (modified Warburg-Christian, in glycine buffer) | | Stability: | Stability Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents | | EPA Substance Registry System | Alkaline phosphatase (9001-78-9) | | Absorption | 7.6 at 278nm (10 mg AP/ml) |
| Hazard Codes | B,Xi | | Risk Statements | 36/37/38 | | Safety Statements | 26-36-24/25-22-23 | | WGK Germany | 3 | | F | 3-10 | | TSCA | Yes | | HS Code | 35079090 | | Toxicity | An enzyme with an
alkaline pH optimum that hydrolyzes phosphate monoesters.
Elevation of its activity in the serum usually indicates obstructive
jaundice, Paget’s disease (osteitis deformans), or bone
carcinoma. |
| | Alkaline Phosphatase Usage And Synthesis |
| Chemical Properties | solid | | Uses | Alkaline Phosphatase, calf intestine, EIA GradeDephosphorylation of cloning vector DNA to prevent recircularization during ligation, dephosphorylation of DNA prior to end-labeling using T4 Polynucleotide Kinase, treatment of dNTPs in PCR reactions prior to sequencing or SNP analysis, dephosphorylation of DNA and RNA. It is also used to remove the 5?-terminal phosphate from nucleic acids during molecular cloning reactions. | | Uses | Hydrolyzes 5′-terminal monophosphate (dephosphorylation) from DNA and RNA. Prevents fragments from self annealing. 5′-nucleic acid targeting for probes. | | Uses | Alkaline Phosphatase is commonly used to remove the 5′-terminal phosphate from nucleic acids. | | General Description | Alkaline phosphatase from bovine intestinal mucosa is both a phosphomonoesterase and a pyrophosphatase. | | Biochem/physiol Actions | Alkaline phosphatase is a model enzyme for understanding phosphomonoesterase. It is used in various biochemical methods and enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). | | Purification Methods | The E.coli supernatant in sucrose (20%, 33mM) in Tris-HCl pH 8.0 is purified through a DEAE-cellulose column and recrystallised. To the column eluates in 0.125M NaCl is added MgCl2 (to 0.01M) and brought to 50% saturation in (NH4)2SO4 by adding the solid (0.20g/mL). The mixture is centrifuged to remove bubbles and is adjusted to pH 8.0 (with 2N NaOH). Saturated (NH4)2SO4 at pH 8.0 is added dropwise until the solution becomes faintly turbid (~61% saturation). It is set aside at ~25o for 1hour (turbidity will increase). The mixture is placed in an ice bath for several minutes when turbidity disappears and a clear solution is obtained. It is then placed in a large ice bath at 0o (~5L) and allowed to warm slowly to room temperature in a dark room whereby crystals are formed appearing as a silky sheen. The crystals are collected by centrifugation at 25o if necessary. The crystalline solutions are stable at ~25o for many months. They can be stored at 0o, but are unstable when frozen. Cysteine at 10-3M and thioglycolic acid at 10-4M are inhibitory. This is reversed on addition of Zn2+ ions. Many organic phosphates are good substrates for this phosphatase. [Molamy & Horecker Methods Enzymol 9 639 1966, Torriani et al. Methods Enzymol 12b 212 1968, Engstrom Biochim Biophys Acta 92 71 1964.] Alkaline phosphatase from rat osteosarcoma has been purified by Me2CO precipitation and chromatography on DEAE-cellulose, Sephacryl S-200, and hydroxylapatite. [Nair et al. Arch Biochem Biophys 254 18 1987.] Phosphoproteins (various). These are purified by adsorbing onto an iminodiacetic acid substituted agarose column to which are bound ferric ions. This chelate complex acts as a selective immobilised metal affinity adsorbent for phosphoproteins. [Muszyfiska et al. Biochemistry 25 6850 1986.] |
| | Alkaline Phosphatase Preparation Products And Raw materials |
|