(1R,4R)-4-(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)cyclopent-2-enecarboxylic Acid: Applications in Medicinal Chemistry and its Preparation Method
Aug 23,2024
General Description
(1R,4R)-4-(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)cyclopent-2-enecarboxylic acid is a key compound in medicinal chemistry, primarily utilized for synthesizing enzyme inhibitors targeting E1 activating enzymes implicated in cancer. Its unique cyclopentene structure enhances bioavailability and facilitates functionalization. (1R,4R)-4-(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)cyclopent-2-enecarboxylic acid is synthesized from N-Boc-(−)-amino acid methyl ester, involving controlled reactions and selective hydrolysis to isolate the desired trans isomer using Candida rugosa lipase. The isolation process employs extraction with organic solvents and characterization through techniques like GC-MS ensures high purity. Future research focuses on its therapeutic potential across various diseases linked to abnormal cell proliferation, aiming to optimize selectivity and minimize toxicity.

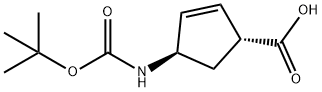
Figure 1. (1R,4R)-4-(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)cyclopent-2-enecarboxylic acid
Applications in Medicinal Chemistry
(1R,4R)-4-(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)cyclopent-2-enecarboxylic acid has garnered significant interest in medicinal chemistry due to its structural properties and reactivity. This compound serves as a fundamental building block for the synthesis of various bioactive molecules, particularly in the development of enzyme inhibitors. Its unique cyclopentene structure imparts specific steric and electronic characteristics that can enhance the bioavailability of potential drug candidates. These features are particularly relevant in the design of inhibitors targeting E1 activating enzymes, which are crucial in regulating cell proliferation and have implications in the treatment of cancer. The incorporation of the tert-butoxycarbonyl protecting group facilitates further functionalization, allowing for the introduction of diverse pharmacophores, thereby expanding the scope of its applications in medicinal chemistry. 1
Synthesis of E1 Activating Enzyme Inhibitors
The versatility of (1R,4R)-4-(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)cyclopent-2-enecarboxylic acid is highlighted in the synthesis of 4-(7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7-yl)-2-(hydroxymethyl)cyclopentanol derivatives. These derivatives have been identified as promising E1 activating enzyme inhibitors, which play a critical role in cancer biology by influencing cellular growth and proliferation. The synthesis involves the reaction of (1R,4R)-4-(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)cyclopent-2-enecarboxylic acid with pyrimidine derivatives under basic conditions, followed by cyclization. This process exemplifies how (1R,4R)-4-(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)cyclopent-2-enecarboxylic acid can be transformed into more complex structures with significant biological activity, making it a valuable compound in drug discovery. 1
Future Directions and Therapeutic Potential
The therapeutic potential of (1R,4R)-4-(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)cyclopent-2-enecarboxylic acid extends beyond E1 activating enzyme inhibition. Ongoing research aims to explore its efficacy against various diseases characterized by abnormal cell proliferation, including different cancer types. By optimizing the synthetic routes involving (1R,4R)-4-(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)cyclopent-2-enecarboxylic acid, researchers are likely to uncover novel compounds with enhanced selectivity and lower toxicity profiles. Additionally, incorporating this compound into combinatorial chemistry strategies may lead to the discovery of new therapeutic classes. Ultimately, (1R,4R)-4-(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)cyclopent-2-enecarboxylic acid's role as a pivotal intermediate in the drug development process underscores its significance in the field of medicinal chemistry. 1
Preparation Method
The synthesis of (1R,4R)-4-(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)cyclopent-2-enecarboxylic acid begins with the preparation of its precursor, N-Boc-(−)-amino acid methyl ester. This is achieved through the reaction of (−)-2-azabicyclo[2.2.1]hept-5-en-3-one dissolved in methanol. To initiate the reaction, thionyl chloride is added dropwise to the cooled solution, ensuring the temperature remains below 5°C to facilitate controlled reactivity. Following overnight stirring, the solution is concentrated under reduced pressure, yielding an off-white solid. The next step involves the formation of a suspension with (−)-4-aminocyclopent-2-ene-1-carboxylic acid methyl ester hydrochloride. Utilizing dichloromethane as a solvent, triethylamine and di-tert-butyl dicarbonate are sequentially added, creating a reaction mixture that is stirred for an additional hour before extraction. 2
Selective Hydrolysis of Diastereomeric Esters
The crucial step in preparing (1R,4R)-4-(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)cyclopent-2-enecarboxylic acid involves a selective hydrolysis process. This is conducted on a mixture of diastereomeric esters, which were formed in the previous reactions. A screening of five different enzymes demonstrates the potential for selectively hydrolyzing either the cis or trans isomers of the product. Among the enzymes tested, Candida rugosa lipase exhibits the highest selectivity, leading to the efficient conversion of the desired trans isomer, (1R,4R)-4-(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)cyclopent-2-enecarboxylic acid, while minimizing the formation of the unwanted cis isomer. The hydrolysis reaction is performed in a buffered solution at pH 7, with continuous agitation to enhance enzyme efficiency. 2
Isolation and Purification
Following the selective hydrolysis of the diastereomeric esters, the next critical step involves the isolation and purification of (1R,4R)-4-(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)cyclopent-2-enecarboxylic acid. The reaction mixture undergoes extraction, typically using an organic solvent such as ethyl acetate, followed by drying over magnesium sulfate to remove residual moisture. The solvent is then evaporated under reduced pressure, yielding a purified product. The final compound can be characterized using techniques such as Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) to confirm its purity and enantiomeric specificity. This meticulous process ensures a high yield and purity of (1R,4R)-4-(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)cyclopent-2-enecarboxylic acid, making it suitable for further applications in medicinal chemistry and biologically relevant studies. 2
Reference
1. Armitage I, Elliott EL, Langston M, Langston SP, McCubbin Q, Mizutani H, Stirling M, Zhu Lei. Process for the synthesis of 4-(7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-7-yl)-2-(hydroxymethyl)cyclopentanol derivatives as E1 activating enzyme inhibitors. 2009; Patent Number: US20090036678.
2. Taylor S, John C, Lloyd M. The preparation of trans-4-amino-2-cyclopentene-1-carboxylic acid derivatives. 2000; Patent Number: WO2000058500.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- (1R,4R)-4-(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)cyclopent-2-enecarboxylic acid:Synthesis,Application Mar 28, 2023
The (1R,4R)-4-(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)cyclopent-2-enecarboxylic acid contain an α-BOC-amino group, which can be used to access α-BOC-aminoketones.
Supplementation with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate monohydrate can synthesize neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, maintaining a healthy nervous system.....
Nov 4,2025Biochemical EngineeringPraziquantel, a broad-spectrum anthelmintic, targets trematodes and cestodes by binding to TRPMPZQ channels, causing muscle paralysis and tegument damage.....
Aug 23,2024APIYou may like
(1R,4R)-4-(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)cyclopent-2-enecarboxylic acid manufacturers
- (1R,4R)-4-(tert-butoxycarbonylamino)cyclopent-2-enecarboxylic acid
-

- $1.00 / 1KG
- 2019-12-20
- CAS:298716-03-7
- Min. Order: 100g
- Purity: 98%
- Supply Ability: 200KG