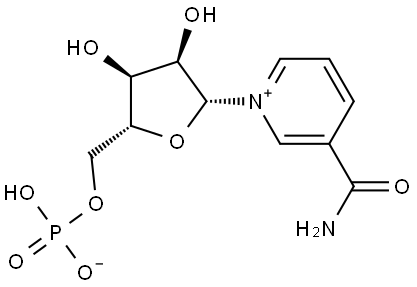
β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide: Benefits and Side Effects
Jun 18,2024
β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN) is one of the key precursors of coenzyme I (NAD+). β-NMN is widely present in various organisms, and the β-isomer is its active form. Studies have shown that β-NMN plays a key role in a variety of physiological and metabolic processes, and has been shown to be effective in slowing down aging, repairing DNA and ameliorating metabolic diseases.
Benefits of β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide
Anti-ageing
Numerous studies have shown that increasing NAD+ levels increases insulin sensitivity, reverses mitochondrial dysfunction, and extends life span. NAD+ levels can be increased by activating enzymes that stimulate NAD+ synthesis, inhibiting enzymes that degrade NAD+ (CD38), and supplementing with NAD precursors including nicotinamide riboside (NR) and nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN). Therefore, NMN supplementation is an effective nutraceutical anti-aging intervention with benefits for a variety of physiological functions.
Neuroprotection
Amyloid-β (Aβ) oligomers are considered to be the major neurotoxic substances in Alzheimer's disease (AD). Impaired brain energy metabolism and oxidative stress are associated with cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease. Studies have shown that NMN can restore cognitive performance in AD model rats.The beneficial effects of NMN are produced by improving neuronal survival, improving energy metabolism, and reducing ROS accumulation.NMN is a potentially effective drug for the treatment of AD.
Promoting cell proliferation and hair growth
In a study of the effect of NMN on hair growth in mice, the results showed that NMN reversed dihydrotestosterone (DHT)-induced follicular atrophy, hair thinning, and hair thinning states compared to minoxidil. The mechanism of action of hair growth is related to the reduction of oxidative stress and related inflammatory factors.
Promoting intestinal health
NMN can improve intestinal epithelial cell pathology and intestinal permeability by up-regulating the expression of intestinal tight junction proteins and the number of thrush cells, increasing the release of anti-inflammatory factors, and increasing beneficial intestinal bacteria. Supplementation with NMN may delay frailty in old age, aid healthy ageing and slow intestinal ageing.
In addition, NMN has benefits such as preventing heart disease and cancer and improving the quality of in vitro-frozen ram sperm.
Side Effects
NMN is safe and well-tolerated in healthy adult males and females aged 20-65 years at an oral dose of 1250 mg once daily for 4 weeks without serious adverse events. However, NMN users may experience mild side effects including abdominal pain, diarrhoea, flatulence and upper respiratory health problems.
References:
[1] XU C, DAI J, AI H, et al. β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Promotes Cell Proliferation and Hair Growth by Reducing Oxidative Stress[J]. Molecules, 2024. DOI:10.3390/molecules29040798.
[2] XIAONAN WANG . Nicotinamide mononucleotide protects against β-amyloid oligomer-induced cognitive impairment and neuronal death[J]. Brain Research, 2016. DOI:10.1016/j.brainres.2016.04.060.
[3] GU Y, GAO L, HE J, et al. β-Nicotinamide mononucleotide supplementation prolongs the lifespan of prematurely aged mice and protects colon function in ageing mice†[J]. Food & Function, 2024. DOI:10.1039/D3FO05221D.
[4] YUICHIRO FUKAMIZU. Safety evaluation of β-nicotinamide mononucleotide oral administration in healthy adult men and women.[J]. Scientific Reports, 2022. DOI:10.1038/s41598-022-18272-y.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Preparation of β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Jan 4, 2024
The one-step conversion of nicotinamide riboside (NR) to β-NMN has been considered to be the most promising synthetic route for β-NMN.
- Anti-aging effects and safety of β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide Nov 15, 2023
NMN has gained widespread attention as an anti-aging product in China, where it is used as a dietary supplement and is widely used in cosmetics.
- ANH, NPA ask FDA to reverse position on NMN supplements Aug 7, 2023
FDA has taken the position that NMN does not meet the definition of a dietary ingredient under DSHEA and should be classified as a drug.
Methyl orange serves as a catalyst in biodiesel production and an adsorbent in wastewater treatment, showcasing dual functionality in sustainable applications.....
Jun 18,2024APISuperoxide dismutase (SOD) is a key endogenous and exogenous cellular antioxidant.....
Jun 18,2024Antioxidantsβ-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide
1094-61-7You may like
β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide manufacturers
- β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide
-

- $1.00 / 1kg
- 2024-07-14
- CAS:1094-61-7
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 20 tons
- β-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide
-

- $0.00 / 1kg
- 2024-07-14
- CAS:1094-61-7
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 500
- α-NMN,BETA-Nicotinamide Mononucleotide
-

- $0.00 / 1G
- 2024-07-14
- CAS:1094-61-7
- Min. Order: 1G
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 20