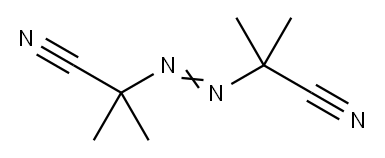
2,2'-Azobis(2-methylpropionitrile): Application and Related Research
Apr 22,2024
Application of 2,2'-Azobis(2-methylpropionitrile)
2,2'-Azobis(2-methylpropionitrile) (AIBN) is a monoazo compound that promotes or initiates free radical reactions. It is insoluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol, and soluble in methanol, toluene, and acetone. AIBN has a wide range of uses as a foaming agent for elastomers and plastics, a catalyst for vinyl polymerisation reactions, a curing agent for unsaturated polyester resins, a fumigant (when heated), and an initiator of free-radical reactions.Solutions of AIBN are also used in the preparation of silicon-carbide glass and in the synthesis of poly[N-(p-vinylbenzyl)phthalimide N-(p-vinylbenzyl)phthalimide] synthesis.

Related Research of 2,2'-Azobis(2-methylpropionitrile)
Preparation and characterization of polyaniline microcapsule loaded with 2,2′-azobis(2-methylpropionitrile) initiator and its controlled release
The thermal curing of acrylate adhesive consisting of acrylate monomer or prepolymer and 2,2′-azobis(2-methylpropionitrile) (AIBN) initiator is quite common. However, the two-component adhesive is not suitable for large areas, large gap bonding, or potting because of its fast-curing speed and intense heat release. To solve these problems, microencapsulating the initiator AIBN in the adhesive and controlling its release is proposed. Here, a new series of polyaniline microcapsules loaded with AIBN for the preparation of delayed-release initiator were synthesized via an emulsification-polymerization method. The coumarone indene resins were doped in polyaniline to control the release of the encapsulated AIBN. The characterization results indicate that the coumarone indene resin had been successfully mixed into the microcapsule polyaniline shell, and the interior of the microcapsules doped with resin had a rich pore structure. When a Span 80 and Tween 80 composite emulsifying system was used and its concentration was controlled at 0.1%–1.0%, the resulting microcapsules were homogeneous with good dispersibility. The release of the microcapsule was slow, and the release rate and release time could be precisely controlled by adjusting the type and doping amount of coumarone indene resin in the microcapsule shell material as well as the external temperature. For example, when the doping amount of coumarone indene resins in the PANI shell material increased from 0.2 to 1.0 g or when the temperature ranges from 75to 85°C, the release time of AIBN from the microcapsule decreased from 9 to 2 h and 12 to 3 h, respectively. With increasing demands for high performance delayed-release initiators, the prepared polyaniline microcapsules loaded with AIBN show great potential for practical applications in adhesive, self-healing coating, and petroleum exploitation.
Preparation of microcapsules
AIBN initiator microcapsules were prepared by the
emulsification-polymerization method. The typical AIBN
initiator microcapsules were prepared as follows: aniline
(1 g), AIBN (0.5 g), and coumarone indene resins (0.4 g)
were mixed with magnetic stirring for 10 min as the discontinuous phase (oil phase). The Span 80 (0.05 g) and
Tween 80 (0.1 g) were then mixed with 50 mL of
deionized water to form a continuous phase (aqueous
phase). The discontinuous phase (oil phase) was then
dropped into the continuous phase (water phase) slowly
and dispersed at a high speed (15,000 rpm) for 2 min to
form oil-in-water (O/W) emulsion. Next, the emulsion
was transferred to a 600-rpm mechanical stirrer for further stirring and dispersion, and the initiator APS aqueous solution was slowly added to the O/W emulsion for
further stirring and reaction for 4 h. The product was
washed with deionized water and ethanol three times to
remove the unwrapped core material, monomer, and
emulsifier. AIBN microcapsules were obtained after drying at 50C for 24 h.
An in situ study of the thermal decomposition of 2,2′-azobis(2-methylpropionitrile) radical chemistry using a dual-mode EPR resonator
A custom-built dual-mode EPR resonator was used to study the radical chemistry of AIBN thermal decomposition. This resonator enables both simultaneous in situ heating using microwaves and EPR measurements to be performed. The thermal decomposition of AIBN was compared following conventional heating methods and microwave-induced (or dielectric) heating methods. Under both heating conditions, the radicals formed and detected by EPR include the 2-cyano-2-propyl (CP●) and 2-cyano-2-propoxyl (CPO●) radicals. Under aerobic conditions, the observed relative distribution of these radicals as observed by EPR is similar following slow heating by conventional or dielectric methods. In both conditions, the kinetically favoured CPO● radicals and their adducts dominate the EPR spectra up to temperatures of approximately 80–90 °C. Under anaerobic conditions, the distribution can be altered as less CPO● is available. However, the observed results are notably different when rapid heating (primarily applied using a MW-induced T-jump) is applied. As the higher reaction temperatures are achieved on a faster timescale, none of the ST●-CPO adducts are actually visible in the EPR spectra. The more rapid and facile heating capabilities created by microwaves may therefore lead to the non-detection of radical intermediates compared to experiments performed using conventional heating methods.
References:
[1] QIFAN ZHANG. Preparation and characterization of polyaniline microcapsule loaded with 2,2′-azobis(2-methylpropionitrile) initiator and its controlled release[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science, 2021. DOI:10.1002/app.51603.
[2] GIUSEPPINA MAGRI. An in situ study of the thermal decomposition of 2,2′-azobis(2-methylpropionitrile) radical chemistry using a dual-mode EPR resonator[J]. Research on Chemical Intermediates, 2022. DOI:10.1007/s11164-022-04861-z.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- 2,2'-Azobis(2-methylpropionitrile): Reactions, synthesis and safety May 17, 2023
2,2'-Azobis(2-methylpropionitrile) is used as an initiator in polymer radical polymerization because its molecules can easily undergo split reactions and form molecules with high activation energy.
- What is 2,2'-Azobis(2-methylpropionitrile)? Feb 25, 2020
2,2'-Azobis(2-methylpropionitrile) is used as an initiator in polymer radical polymerization because its molecules can easily undergo split reactions and form molecules with high activation energy.
- Uses of Azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN) Dec 16, 2019
Azobisisobutyronitrile (abbreviated AIBN) is an organic compound with the formula [(CH3)2C(CN)]2N2. This white powder is soluble in alcohols and common organic solvents but is insoluble in water.
You may like
2,2'-Azobis(2-methylpropionitrile) manufacturers
- 2,2'-Azobis(2-Methylpropionitrile)
-

- $100.00 / 25kg
- 2025-04-22
- CAS:78-67-1
- Min. Order: 1000kg
- Purity: 0.98
- Supply Ability: 5000 Metric Ton/Metric Tons per Year
- 2,2'-Azobis(2-methylpropionitrile)
-

- $50.00 / 1kg
- 2025-04-21
- CAS:78-67-1
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99.9%
- Supply Ability: 10000 Kilogram/Kilograms per Day
- 2,2'-Azobis(2-methylpropionitrile)
-

- $10.00 / 20kg
- 2025-04-21
- CAS:78-67-1
- Min. Order: 20kg
- Purity: 99.5%
- Supply Ability: 100 TON