4-Chloro-3,5-Dimethylphenol: Anticancer Activity and Toxicity
Oct 22,2024
General Description
Chloroxylenol (4-Chloro-3,5-Dimethylphenol or PCMX) is an antimicrobial chemical with a long history of safe use in topical antiseptic drug products for over-the-counter human use (FDA, 2013, 1994), and for pesticide use (EPA, 1994, 2009a, b). A human health risk assessment was conducted to evaluate the safety of chloroxylenol used as an active ingredient in rinse-off liquid antimicrobial hand soaps and dish soaps by consumer (adults and children) and in rinsed off antimicrobial liquid hand soaps by health-care workers. This assessment was initiated in response to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) Proposed Rules and reopening of the administrative record on topical antimicrobial drug products for over-the-counter (OTC) human use (FDA, 2013, 2014) (hereafter Proposed Rules), which identified data needed to demonstrate that such antiseptics used in consumer and health-care settings are generally recognized as safe and effective [GRAS/E]. 1

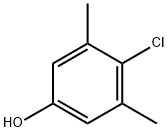
Figure 1. 4-Chloro-3,5-dimethylphenol
Anticancer Activity
Chloroxylenol (4-Chloro-3,5-Dimethylphenol) is the active ingredient of the antibacterial agent Dettol. The anticancer effect and underlying mechanisms of this compound and other common antimicrobial agents have not been clearly elucidated. In the recent study, the effects of chloroxylenol, benzalkonium chloride, benzethonium chloride, triclosan and triclocarban on β‑catenin‑mediated Wnt signaling in colorectal cancer were evaluated using the SuperTOPFlash reporter assay.
It was demonstrated that 4-Chloro-3,5-Dimethylphenol, but not the other antimicrobial agents tested, inhibited the Wnt/β‑catenin signaling pathway by decreasing the nuclear translocation of β‑catenin and disrupting β‑catenin/T‑cell factor 4 complex, which resulted in the downregulation of the Wnt target genes Axin2, Survivin and Leucine‑rich G protein‑coupled receptor‑5. Chloroxylenol effectively inhibited the viability, proliferation, migration and invasion, and sphere formation, and induced apoptosis in HCT116 and SW480 cells. Notably, chloroxylenol attenuated the growth of colorectal cancer in the MC38 cell xenograft model and inhibited organoid formation by the patient‑derived cells. Chloroxylenol also demonstrated inhibitory effects on the stemness of colorectal cancer cells. The results of the present study demonstrated that chloroxylenol could exert anti‑tumor activities in colorectal cancer by targeting the Wnt/β‑catenin signaling pathway, which provided an insight into its therapeutic potential as an anticancer agent.
Toxicity
4-Chloro-3,5-Dimethylphenol has a long history of safe use in topical antiseptic drug products for over-the-counter human use and in hard surface disinfectant use (regulated as a pesticide). The existing data indicate low acute toxicity, lack of genotoxicity and carcinogenicity, and low systemic toxicity.
Momma et al. evaluated dermal carcinogenicity of 4-Chloro-3,5-Dimethylphenol in a combined 18-month dermal toxicity and carcinogenicity study in which a 1% or 10% solution of chloroxylenol was applied twice weekly to shaved skin on the backs of female mice. No treatment related adverse effects were identified. The exclusive use of female mice was a limitation in the investigation, but the lack of hormonally mediated effects within in silico and in vitro studies or in repeated dose studies, reduces the significance of this limitation. In addition, histopathological analyses were not described in detail, however, no adverse findings were reported. Finally, Momma et al. used a two-time-per-week dosing regimen in contrast to the standard seven-day-per-week dosing method. The less frequent dosing used in Momma et al. adds uncertainty to the dataset, but is unlikely to underestimate risks at the doses applied.
Although there is no chronic oral carcinogenicity study, there is substantial evidence for a lack of systemic carcinogenic potential including lack of genotoxicity and carcinogenicity following chronic dermal exposure as identified in Momma et al.. Moreover the dermal exposure route is the most relevant for consumer and health-care worker exposures.1
Wnt signaling and exerts anticancer activity in colorectal cancer. INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ONCOLOGY 63: 121, 2023.References:
[1] LISA J. YOST . Human health risk assessment of chloroxylenol in liquid hand soap and dishwashing soap used by consumers and health-care professionals[J]. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology, 2016, 80: 1-362. DOI:10.1016/j.yrtph.2016.06.003.
[2] QI SUN. Antimicrobial agent chloroxylenol targets β?catenin?mediated Wnt signaling and exerts anticancer activity in colorectal cancer.[J]. International journal of oncology, 2023, 63 5. DOI:10.3892/ijo.2023.5569.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
Supplementation with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate monohydrate can synthesize neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, maintaining a healthy nervous system.....
Nov 4,2025Biochemical EngineeringSodium methyl mercaptide (Sodium thiomethoxide) is a kind of water white strong alkaline liquid that has an off-odour and can be used for the raw material of pesticides, medicine, Pigment Intermediates.....
Aug 1,2024Inorganic salts4-Chloro-3,5-dimethylphenol
88-04-0You may like
4-Chloro-3,5-dimethylphenol manufacturers
- 4-Chloro-3,5-dimethylphenol/PCMX
-

- $0.00 / 25kg
- 2025-12-19
- CAS:88-04-0
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 98.5%min
- Supply Ability: 20 tons
- 4-Chloro-3,5-dimethylphenol
-

- $0.00 / 1kg
- 2025-12-18
- CAS:88-04-0
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 98%
- Supply Ability: Customise
- 4-Chloro-3,5-dimethylphenol
-

- $0.00 / 25KG
- 2025-12-18
- CAS:88-04-0
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 995
- Supply Ability: 500mt