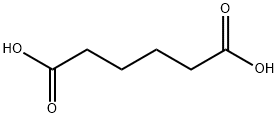
Adipic Acid: A Versatile Industrial Compound
Dec 16,2024
Uses and Synthesis
Adipic acid is an important chemical reagent that has been widely used in the production of thermoplastic polyurethane resins, nylon 6-6, adhesives, synthetic lubricants, and plasticizers. Currently, adipic acid is derived from petrochemical sources and is mainly produced by the oxidation of KA oil (cyclohexanol and cyclohexanone) catalyzed by nitric acid. However, this preparation method produces greenhouse gases and serious environmental pollution. Therefore, researchers began to look for biosynthesis of adipic acid, including: (1) bioaccumulation of adipic acid precursors such as d-glucaric acid and cis-, cis-muconic acid, which are further catalyzed to produce adipic acid; (2) direct synthesis of adipic acid from carbon sources.

Figure 1 Characteristics of Adipic acid
In addition, researchers found that modifying ATP metabolism can enhance adipic acid production in Escherichia coli. Through the reverse adipic acid degradation pathway (RADP), and by overexpression of control genes (panK and acs) to fine-tune the ATP consumption cycle to balance ATP consumption and adipic acid production. As a result, a significant increase in adipic acid production (19.5-fold) was achieved, reaching 1093.11 mg/L in shake flasks, compared to the control strain (wild-type E. coli containing RADP). Our transcriptome analysis suggests that regulation of ATP metabolism as well as balanced supply of pathway precursors influence metabolic fluxes, leading to enhanced adipic acid biosynthesis in E. coli.
Adipic acid, when used as an additive in limestone FGD systems, can greatly improve SO2/sub 2/ removal and limestone utilization. Most existing limestone scrubbers can benefit from the addition of adipic acid without major process changes. No major operational issues or adverse environmental impacts were found.
Metabolism
When radioactive adipic acid was fed to fasted rats, metabolites such as urea, glutamate, lactate, β-ketoadipate, and citric acid were found in the urine along with adipic acid. Adipic acid is metabolized in a manner very similar to fatty acids via β-oxidation. Further evidence was provided by the appearance of succinate in the urine of rats fed radioactive adipic acid (1-C14) and injected with malonate. The presence of radioacetyl-γ-phenyl-α-aminobutyric acid after feeding γ-phenyl-α-aminobutyric acid and C14-labeled adipic acid provided very strong evidence that acetate was a metabolite of adipic acid. Radioactive glycogen was isolated after feeding glucose and radioactive adipic acid. Some of the metabolites found in the urine are certainly not direct degradation products of adipic acid, such as urea, but contain radioactive carbon derived from the carbon dioxide in the adipic acid. This was confirmed by experiments in which radioactive carbon dioxide was fed, and traces of some of the same metabolites were subsequently isolated in the urine.
References:
[1] YU DENG ?Yin M ?Lizhou Ma. Biological production of adipic acid from renewable substrates: Current and future methods[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 105: 1-320. DOI:10.1016/j.bej.2015.08.015.
[2] SOO YOUNG MOON . Coordinated reprogramming of ATP metabolism strongly enhances adipic acid production in Escherichia coli[J]. Metabolic engineering, 2024, 86: 1-. DOI:10.1016/j.ymben.2024.10.010.
[3] Adipic acid enhanced limestone flue gas desulfurization process - an assessment[C]. 1981. DOI:10.1080/00022470.1981.10465353.
[4] I.I. RUSOFF. Intermediary metabolism of adipic acid[J]. Toxicology and applied pharmacology, 1960, 2 3: 243-352. DOI:10.1016/0041-008X(60)90060-0.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Adipic acid: Physicochemical properties, production host screening and toxicity May 20, 2024
Adipic acid is an odourless, white crystalline powder with a wide range of roles in chemical generation and manufacture.
- Adipic acid: Uses and Synthesis Nov 16, 2022
This passage describes that Adipic acid is used in medicine and foods, and also introduces the laboratory and industrial synthesis of it.
Adipic acid
124-04-9You may like
- Adipic acid
-

- $2.00 / 25KG
- 2025-04-22
- CAS:124-04-9
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: ≥99.5%
- Supply Ability: 1000mt/year
- Adipic Acid
-

- $150.00 / 1kg
- 2025-04-22
- CAS:124-04-9
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 500kg
- ADIPIC ACID
-

- $1.00 / 1kg
- 2025-04-21
- CAS:124-04-9
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 10 mt