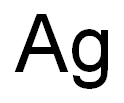Applications and Preparation of Silver
Sep 30,2019
Silver is one of the oldest metals, known since ancient times. It is a precious metal worldwide, used in ornaments, coins, and utensils.
Raw materials for the production of silver are, for primary sources, rich silver, galena, and all byproducts arising from gold bullion smelting in mines and containing small amounts of gold such as slag, flue dust, furnace linings, and crucibles. Secondary sources include activated carbon, sweeps, ashes, concentrates, and computer scrap.

Industrial Preparation
The end product of the smelting process is doré bullion, a mixture of ca. 30 wt.% Au and 70 wt.% Ag, which is sent to the refining section.
The chlorides produced in the gold refining process contain ca. 50 wt.% Ag and are treated to recover this. This silver (99 wt.% Ag) is dried in a centrifuge, then melted in a resistance furnace, from which silver anodes are cast. These slab anodes are refined by electrorefining to produce silver crystals containing at least 99.9 wt.% Ag, which are either vacuum dried and sold or cast into roughly 31.103477 kg (i.e., exactly 1000 troy oz.) bars for sale.
Applications
The uses and applications of silver alloys are important and various. In fact, the high thermal and electrical conductivities, associated with the high reflectivity and ductility of silver and silver alloys, encourage their use despite their high cost.
Jewelry and silverware.
Because of its high reflectivity, sterling silver (i.e., a silver-copper alloy) is extensively used for jewelry, silverware, and tableware where appearance is paramount. Sometimes, a protective rhodium coating is electrodeposited onto thin nickel-plated silver objects to avoid tarnishing. Sterling-silver alloy contains roughly 92.5 wt.% Ag, the remainder being copper or some other metals.
Photography.
Silver is of the utmost importance in photography, about 30% of the industrial consumption going into this application. Actually, the use of silver in photography is due to the ability of silver-halide crystals (i.e., especially silver bromide) to be photosensitive and undergo a secondary image amplification called development.
Dentistry.
Silver is also used in dentistry either as Ag-Sn-Hg or Ag-Sn-Cu-Hg silver alloys owing to their small expansion during setting, which is suitable for making dental amalgams.
Brazing filler metals.
Owing to its low melting point and its good wettability of several base metals, silver is a major component for making solder and brazing alloys.
Electronics.
Due to its high conductivity, both electrical and thermal, and low surface contact resistance, electrodeposited silver is also used for making electric contacts.
Primary batteries.
Silver compounds such as AgO are used as cathode materials for making high-capacity silver-zinc and silver-cadmium primary batteries. Silver paints are used for making printed circuits.
Explosives.
Silver fulminate, AgCNO, is a powerful primary explosive.
Meteorology.
Hexagonal crystals of silver iodide, AgI, are used in seeding clouds to produce artificial rain.
Other.
For centuries silver has been used traditionally for coinage by many countries of the world. Today, however, silver coins of other countries have largely been replaced with coins made of other metals.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- 10 Interesting Facts About Silver Mar 5, 2024
Silver (Ag), atomic number 47, is a rare metal resource with dull-white color. In nature, most of the silver resources are associated with Lead-Zinc ores, except for a small portion in the form of simple substance or silver minerals.
- What is the charge of silver? Feb 18, 2024
Silver typically has a +1 charge when involved in an ionic bond. Although silver can form both +1 and +2 cations, the +2 is so rare that we usually name Ag + as silver ion, not silver(I) ion.
- Flame test and chemical principles of silver Jan 25, 2024
Silver do not produce a characteristic flame test color. There are several possible explanations for this.
From a chemical point of view, silver is stable in pure air and water in comparison with copper, but it readily tarnishes when exposed to ozone, O3, hydrogen sulfide, H2S, or air containing sulfur dioxide, SO2.....
Sep 30,2019Inorganic chemistryFirst things first. Let’s clear up what this mysterious rhodium is. Rhodium is a precious metal – like gold, silver, or platinum – only more expensive! In fact, it is the most expensive of all the precious metals.....
Sep 30,2019Inorganic chemistrySilver
7440-22-4You may like
- Silver
-

- 2025-11-16
- CAS:7440-22-4
- Min. Order:
- Purity: 0.99
- Supply Ability:
- Silver
-

- $685.00 / 1ton
- 2025-09-26
- CAS:7440-22-4
- Min. Order: 1ton
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 900ton
- Silver
-

- $188.00 / 1KG
- 2025-09-25
- CAS:7440-22-4
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%, 99.5% Sublimated
- Supply Ability: g-kg-tons, free sample is available