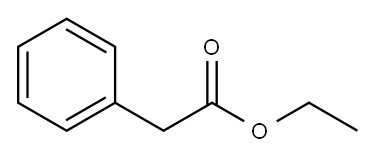
Applications of Ethyl Phenylacetate: Versatility in Fragrance, Flavor, and Beyond
Oct 22,2024
Introduction
Ethyl Phenylacetate, a natural is derived from cane sugar. It is diluted at 35% into the natural fixative benzyl benzoate, which makes it last longer. This honeyed floral base note smells like a garden of blooming sweet peas. Since there are almost no floral base notes, ethyl phenylacaetate is an extremely useful addition to the natural perfumer's palette. Ethyl phenylacetate is a less toxic, greener solvent. It is non-mutagenic. Hence, it could be used in perfumery[1].
The effect of Ethyl Phenylacetate in wine
Interest in high-quality and peculiar products is a recent trend in the enological field; for this reason, consumers request the production of wines from autochthonous vine varieties. Aglianico wine from the Italian region "Basilicata" is an example of a promising product strictly connected to the territory; nevertheless, it is affected by a frequent sweet-like off-flavour.

Ethyl phenylacetate (EPhA) and phenylacetic acid (PhAA) presented sweet honey-like notes and emerged as key aroma compounds. The concentration of these compounds in wines elaborated from infected berries was one order of magnitude above that found in control (healthy) samples, reaching a maximal concentration of 304 and 1668 mg/L of EPhA and PhAA, respectively. Phenylacetic acid is a plant-growth regulator, so it is hypothesized that this compound may be produced as a plant response to an alteration of the grape surface. Phenylacetic acid could then be extracted to the must if a maceration process is used and be further converted to its corresponding ethyl ester (EPhA) during fermentation or bottle ageing. Ethyl phenylacetate has been suggested as being responsible for the 'sweet-like' off odour usually affecting Italian Aglianico del Vulture wines[2-3].
In addition, the effect of sour rot was tested in monovarietal wines produced with the Portuguese red grape variety Trincadeira and in blends of Cabernet Sauvignon and sour, rotten Trincadeira grapes. Wines from damaged berries exhibited clear honey-like notes not evoked by healthy samples. Ethyl phenylacetate and phenylacetic acid, exhibiting sweet honey-like aromas, emerged as key aroma compounds of sour, rotten wines. Their levels were 1 order of magnitude above those found in controls and reached 304 and 1668 ug/L of EPhA and PhAA, respectively, well above the corresponding odour thresholds. Levels of gamma-nonalactone also increased by a factor 3 in sour rot samples. Results also suggest that sour rot greatly affects the secondary metabolism of yeast, decreasing the levels of volatiles related to fatty acids and amino acid synthesis. The highest levels of gamma-decalactone of up to 405 ug/L were also found in all samples, suggesting that this could be a relevant aroma compound in Trincadeira wine aroma.
The Uses and Pollution
Ethyl phenylacetate's production and use in food flavourings and as a chemical intermediate may result in its release to the environment through various waste streams(SRC). Its use in perfumery will result in its direct release to the environment(SRC). Ethyl phenylacetate has been detected in wastewater effluents from publicly-owned water treatment facilities.
[1].Tat, L.; Battistutta, F.; Comuzzo, P.; Zironi, R. In Ethyl Phenylacetate as the probable responsible of honey-like character in Aglianico del Vulture wine, International Workshop on Advances in Grapevine and Wine Research 754, 2005; pp 557-562.
[2].Campo, E.; Saenz‐Navajas, M.; Cacho, J.; Ferreira, V., Consumer rejection threshold of ethyl phenylacetate and phenylacetic acid, compounds responsible for the sweet‐like off odour in wines made from sour rotten grapes. Australian Journal of Grape and Wine Research 2012,18(3), 280-286.
[3].Kikuchi, R.; Mizukami, F.; Niwa, S.-i.; Toba, M.; Ushijima, H.; Itou, K., Hydrogenation of ethyl phenylacetate to 2-phenylethanol by ruthenium/tin/alumina catalysts Elimination of need for high temperature activation of the catalysts with hydrogen; optimum oxidation state of tin. Applied Catalysis A: General 1997,165(1-2), 309-317.
References:
[1] TAT L, BATTISTUTTA F, COMUZZO P, et al. ETHYL PHENYLACETATE AS THE PROBABLE RESPONSIBLE OF HONEY-LIKE CHARACTER IN AGLIANICO DEL VULTURE WINE[C]. 2007. DOI:10.17660/ACTAHORTIC.2007.754.74.
[2] E. CAMPO. Consumer rejection threshold of ethyl phenylacetate and phenylacetic acid, compounds responsible for the sweet-like off odour in wines made from sour rotten grapes[J]. Australian Journal of Grape and Wine Research, 2012, 18 3: 245-360. DOI:10.1111/j.1755-0238.2012.00198.x.
[3] R. KIKUCHI. Hydrogenation of ethyl phenylacetate to 2-phenylethanol by ruthenium/tin/alumina catalysts elimination of need for high temperature activation of the catalysts with hydrogen; optimum oxidation state of tin[J]. Applied Catalysis A: General, 1997, 11 1: 89-93. DOI:10.1016/S0926-860X(97)00211-1.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
Supplementation with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate monohydrate can synthesize neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, maintaining a healthy nervous system.....
Nov 4,2025Biochemical EngineeringMethylthiouracil is a thioamide, closely related to propylthiouracil. It is not used clinically in the United States, it has a similar mechanism of action and side effect to that of propylthiouricil.....
Oct 22,2024APIEthyl phenylacetate
101-97-3You may like
Ethyl phenylacetate manufacturers
- Ethyl phenylacetate
-

- $0.00 / 1kg
- 2025-11-04
- CAS:101-97-3
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 98%
- Supply Ability: 1000
- Ethyl phenylacetate
-

- $5.00 / 200KG
- 2025-11-04
- CAS:101-97-3
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 500mt/year
- Ethyl phenylacetate
-

- 2025-11-04
- CAS:101-97-3
- Min. Order:
- Purity: 0.99
- Supply Ability: