Doxorubicin Hydrochloride: Anticancer Mechanisms and Highly Sensitive Determination
Jul 4,2024
General Description
Doxorubicin hydrochloride, a potent chemotherapeutic agent, exerts its anti-cancer effects through various mechanisms, including DNA intercalation, induction of DNA damage, generation of reactive oxygen species, and promotion of multiple forms of cell death like apoptosis and autophagy. Additionally, it plays an immunomodulatory role by enhancing the immune system's ability to target tumor cells. On the other hand, the development of an innovative electrochemical sensor utilizing a nanocomposite with gold nanoparticles and multi-walled carbon nanotubes enables highly sensitive determination of doxorubicin hydrochloride, with a detection limit as low as 6.5 picomolar. This advancement holds promise for improved therapeutic monitoring and pharmacokinetic studies.

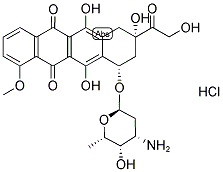
Figure 1. Doxorubicin hydrochloride
Anticancer Mechanisms
Doxorubicin hydrochloride is a potent chemotherapeutic agent widely recognized for its efficacy in the treatment of various cancers. As a cornerstone of many anti-cancer regimens, Doxorubicin hydrochloride has multiple modes of action that contribute to its therapeutic effects.
DNA Interference and Apoptosis Induction
This drug operates primarily by intercalating into DNA, disrupting the synthesis and function of the genetic material, and ultimately leading to cell death. One of the key mechanisms through which Doxorubicin hydrochloride exerts its effect is by inducing DNA damage. By inserting itself between DNA base pairs, Doxorubicin hydrochloride interferes with the normal replication processes. This interference can trigger a cascade of harmful cellular events, culminating in apoptosis, or programmed cell death. Apoptosis is crucial for removing cancerous cells and is a primary pathway by which Doxorubicin hydrochloride achieves its anti-cancer effects.
Oxidative Stress and Multifaceted Cell Death
Moreover, Doxorubicin hydrochloride is known to generate reactive oxygen species (ROS). These ROS contribute to oxidative stress within the cell, further damaging cellular components, including lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. The accumulation of oxidative damage is another pathway through which Doxorubicin hydrochloride promotes cancer cell death. In addition to apoptosis and oxidative stress, Doxorubicin hydrochloride also promotes other forms of cell death, such as autophagy, senescence, ferroptosis, and pyroptosis. These varied forms of cell death reflect the drug’s pleiotropic nature, enabling it to effectively target cancer cells through multiple avenues. This multi-faceted approach helps in tackling tumor cells that may be resistant to one form of cell death but are susceptible to another.
Immunomodulation and Enhanced Antitumor Responses
Furthermore, Doxorubicin hydrochloride plays an immunomodulatory role. It can alter the tumor microenvironment, enhancing the immune system's ability to recognize and destroy tumor cells. This immunomodulation is crucial, as it can potentially improve the overall outcomes of cancer treatment by not only directly killing cancer cells but also by enabling the immune system to play a more active role in cancer eradication. Overall, the application of Doxorubicin hydrochloride in cancer therapy is critical due to its multifaceted mechanisms of action. Its ability to induce multiple forms of cell death, coupled with its effects on the immune system, underscores its importance in modern oncology. Despite its broad utility, ongoing research into the precise mechanisms and optimization of its use continues to enhance its effectiveness and reduce associated side effects. 1
Highly Sensitive Determination
Innovative Electrochemical Sensor with Nanocomposite
The highly sensitive determination of doxorubicin hydrochloride, a potent antitumor agent, has been significantly advanced through the development of an innovative electrochemical sensor. This sensor utilizes a nanocomposite consisting of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) that are adorned with gold nanoparticles. These components are meticulously integrated onto a glassy carbon electrode, which facilitates a groundbreaking approach in the electrochemical sensing of doxorubicin hydrochloride. The nanocomposite was thoroughly evaluated using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and electrochemical methods such as cyclic and linear sweep voltammetry. These analyses confirmed the structure and functional efficacy of the nanocomposite in catalyzing the electrochemical reduction of doxorubicin hydrochloride. Notably, the presence of gold nanoparticles enhances the catalytic reduction process, resulting in a significant amplification of the peak current density and a notable decrease in the reduction over-potential. This enhanced sensitivity allows the electrode to detect doxorubicin hydrochloride over a broad concentration range, from extremely low (1×10^-11 M) to higher concentrations (1×10^-6 M), with a detection limit reaching as low as 6.5 picomolar.
Implications for Therapeutic Monitoring
The functionalized MWCNTs with gold nanoparticles demonstrate excellent selectivity, reproducibility, and repeatability, alongside long-term stability, making this sensor a promising tool for tracing minute quantities of doxorubicin hydrochloride in various pharmaceutical and clinical settings. This method marks a significant step forward in the highly sensitive determination of doxorubicin hydrochloride, potentially enhancing therapeutic monitoring and pharmacokinetic studies. 2
Reference
1. Kciuk M, Gielecińska A, Mujwar S, et al. Doxorubicin-An Agent with Multiple Mechanisms of Anticancer Activity. Cells. 2023; 12(4): 659.
2. Sharifi J, Fayazfar H. Highly sensitive determination of doxorubicin hydrochloride antitumor agent via a carbon nanotube/gold nanoparticle based nanocomposite biosensor. Bioelectrochemistry. 2021; 139: 107741.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Doxorubicin Hydrochloride Injection Jun 28, 2024
Doxorubicin Hydrochloride Injection, USP, has been used successfully to produce regression in disseminated neoplastic conditions.
- Adverse reactions of doxorubicin hydrochloride Mar 30, 2022
Doxorubicin hydrochloride is an anti-tumor antibiotic.
- What is Doxorubicin hydrochloride? Sep 2, 2021
Doxorubicin hydrochloride is an antitumor antibiotic agent that inhibits DNA topoisomerase II. DNA intercalator that inhibits nucleic acid synthesis and induces apoptosis. Reduces intracellular tau levels.
Sodium triacetoxyborohydride enables precise amine synthesis via selective reduction of imines and can be detected by GC method using 3,4-dihydroisoquinoline.....
Jul 4,2024APIFusarium oxysporum enables eco-friendly synthesis of strontium carbonate, vital in bioceramics for bone regeneration, showcasing microorganism potential in material production.....
Jul 4,2024APIDoxorubicin hydrochloride
25316-40-9You may like
Doxorubicin hydrochloride manufacturers
- Doxorubicin Hydrochloride
-

- $0.00 / 1Kg/Bag
- 2024-07-22
- CAS:25316-40-9
- Min. Order: 1Kg/Bag
- Purity: 99% up, High Density
- Supply Ability: 20 tons
- Doxorubicin hydrochloride
-

- $10.00 / 1kg
- 2024-07-10
- CAS:25316-40-9
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 10000 tons
- Doxorubici Hydrochloride
-

- $120.00 / 1kg
- 2024-05-29
- CAS:25316-40-9
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 20ton