Efficacy and effects of folic acid supplements on the human body
Jan 12,2024
Introduction of Folic acid
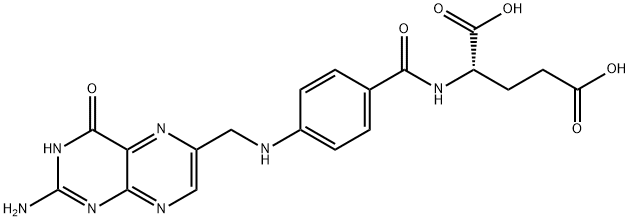
Folic acid is the active form of vitamin B9 and occurs naturally in many foods. Folic acid helps the body make healthy red blood cells and is vital during periods of rapid growth, such as pregnancy and foetal development. It is used to treat vitamin B9 deficiency and prevent pregnancy complications. It is also added to foods and sold as a supplement in the form of folic acid; this form is actually better absorbed than food sources - 85 per cent and 50 per cent, respectively. Folic acid helps form DNA and RNA and is involved in protein metabolism. It plays a key role in the breakdown of homocysteine, an amino acid that, if present in large amounts, can have harmful effects on the body.

Folic acid Supplements and Health
Folic Acid to Prevent Neural Tube Defects
Studies have found a link between too little folic acid and birth defects of the spine (spina bifida) and brain (anencephaly). Two large trials that randomly assigned women to take either folic acid or a placebo showed that too little folic acid increased a woman's chances of having a baby with spina bifida or anencephaly, and that consuming enough folic acid greatly reduced the incidence of these birth defects. Before and during pregnancy, women are encouraged to take folic acid supplements in addition to their food intake.
The upper tolerable limit for folic acid is 1000 micrograms per day; however, this level was established to avoid masking vitamin B12 deficiency and is not based on the bioavailability and metabolism of folic acid. Studies have shown that women of childbearing age do not get enough folate from food alone, even if they consume fortified foods. However, almost all women taking folic acid supplements exceeded the upper limit of folic acid intake. The upper tolerable limit of 1,000 micrograms set by folic acid supplementation recommendations and policymakers deserves careful review because of the potential adverse effects of exceeding the upper tolerable limit of folic acid absorption and metabolism, as well as the subsequent impact on the health of women of childbearing age.
Folic acid prevents or reduces cardiovascular disease
Studies have shown that elevated homocysteine levels contribute to the artery-clogging process of atherosclerosis, and that folic acid and vitamin B12 play a key role in converting homocysteine to methionine. Without adequate amounts of folate, vitamin B6 and vitamin B12, this conversion process becomes inefficient and homocysteine levels are elevated. On the other hand, homocysteine levels decrease with increasing intake of folic acid, vitamin B6 and vitamin B12.
Surveys have shown a lower risk of cardiovascular disease, stroke, and hypertension in people with higher dietary intake of folic acid, those who use multivitamin supplements, or those with higher serum folate levels. However, linking higher homocysteine levels and lower folate levels to heart disease risk does not necessarily mean that lowering homocysteine by taking folic acid and other B vitamins will reduce risk.
Surveys have shown a lower risk of cardiovascular disease, stroke, and hypertension in people with higher dietary intake of folic acid, those who use multivitamin supplements, or those with higher serum folate levels. However, linking higher homocysteine levels and lower folate levels to heart disease risk does not necessarily mean that lowering homocysteine by taking folic acid and other B vitamins will reduce risk. However, several large randomised trials of B vitamin supplements for lowering homocysteine levels and preventing heart disease and stroke failed to find a benefit. The study found that taking high doses of all three B vitamins lowered homocysteine levels but did not lead to a reduction in coronary heart disease events. An analysis of several studies showed that folic acid supplements reduced the risk of stroke in people who had not yet had a stroke, but did not reduce the risk of a second stroke in people who had already had one.
A meta-analysis of 26 randomized controlled trials found that folic acid supplementation was not associated with a decreased risk of cardiovascular disease, heart disease, or deaths from these conditions, but it was linked with a decreasing trend in risk of strokes. A meta-analysis of 30 randomized controlled trials found a 10% lower risk of stroke and 4% lower risk of overall cardiovascular diseases with folic acid supplementation. There was no significant effect on heart disease alone. However, the greatest benefit was seen for people with lower blood levels of folate and without a history of cardiovascular diseases. The supplements also appeared to most benefit those whose homocysteine levels had the greatest drop.
References:
[1] JIN J. Folic Acid to Prevent Neural Tube Defects.[J]. Jama-Journal of the American Medical Association, 2023. DOI:10.1001/jama.2023.14061.
[2] CAROLYN LEDOWSKY. Women Taking a Folic Acid Supplement in Countries with Mandatory Food Fortification Programs May Be Exceeding the Upper Tolerable Limit of Folic Acid: A Systematic Review.[J]. Nutrients, 2022. DOI:10.3390/nu14132715.
[3] MATTHEW QUINN. Global heterogeneity in folic acid fortification policies and implications for prevention of neural tube defects and stroke: a systematic review.[J]. EClinicalMedicine, 2023. DOI:10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.102366.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Folate synthesis Jul 25, 2024
The synthetic form of folate is folic acid. It's in an essential component of prenatal vitamins and is in many fortified foods such as cereals and pastas.
- Aplications and Side effects of Folic acid Oct 12, 2019
Folic acid is a type of B vitamin that is normally found in foods such as dried beans, peas, lentils, oranges, whole-wheat products, liver, asparagus, beets, broccoli, brussels sprouts, and spinach. Folic acid helps your body produce and ma
Supplementation with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate monohydrate can synthesize neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, maintaining a healthy nervous system.....
Nov 4,2025Biochemical EngineeringPolypropylene (PP), or polypropene, is a thermoplastic polymer used in various applications. It is produced via chain-growth polymerization from the monomer propylene.....
Jan 12,2024Organic ChemistryFolic acid
59-30-3You may like
- Folic acid
-

- 2025-12-20
- CAS:59-30-3
- Min. Order:
- Purity: 0.99
- Supply Ability:
- Folic acid
-

- $0.00 / 20kg
- 2025-12-19
- CAS:59-30-3
- Min. Order: 20kg
- Purity: 96%-102%
- Supply Ability: 1000 KGS
- folic acid
-

- $5.00/ KG
- 2025-12-19
- CAS:59-30-3
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99% hplc
- Supply Ability: 500TONS