Exploring the Chemical Dynamics and Applications of 2-Ethyl Anthraquinone
Jul 1,2024
Introduction
In the realm of industrial chemistry, certain compounds serve as critical catalysts and intermediates, playing pivotal roles in various chemical synthesis processes. One such compound is 2-Ethyl Anthraquinone, a derivative of anthraquinone that is notable for its extensive application in the commercial production of hydrogen peroxide.

Figure 1 Characteristics of 2-Ethyl Anthraquinone
Chemical Properties
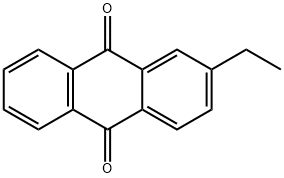
2-Ethyl Anthraquinone, with the chemical formula C_16H_12O_2, is characterized by its solid state at room temperature and its pale yellow crystalline appearance. The compound exhibits a melting point of approximately 108-111 °C and possesses relatively low solubility in water but high solubility in organic solvents such as chloroform, benzene, and toluene. Its molecular structure, featuring an anthraquinone core with an ethyl group attached at the 2-position, contributes to its stability and reactivity, making it a valuable component in various chemical reactions.
Main Constituents
The molecular composition of 2-Ethyl Anthraquinone primarily involves a base structure of anthraquinone, which consists of three benzene rings forming an extended aromatic system. The addition of the ethyl group at the second position significantly alters its chemical behavior, enhancing its reductive capabilities. This structural modification not only boosts its effectiveness as a reducing agent but also influences its physical properties, such as melting and boiling points. Additionally, this ethyl substitution impacts the electronic properties of the molecule, altering electron density and distribution across the aromatic system, which can affect its reactivity with other chemical species.
The positioning of the ethyl group is strategic, enhancing the compound’s solubility in organic solvents, which is crucial for its use in various industrial processes. This solubility factor plays a significant role in the practical applications of 2-Ethyl Anthraquinone, particularly in processes where the compound needs to be dissolved as part of chemical synthesis or extraction procedures. The altered solubility and improved reactivity make 2-Ethyl Anthraquinone a versatile and valuable component in the synthesis of complex chemical structures, broadening its utility beyond simple industrial applications to more specialized chemical processes.
Applications
The primary application of 2-Ethyl Anthraquinone is in the synthesis of hydrogen peroxide, a process that leverages its unique chemistry for industrial-scale production. In the anthraquinone method, 2-ethyl Anthraquinone is hydrogenated to form 2-ethylanthrahydroquinone, which subsequently reacts with oxygen. This reaction not only regenerates the original anthraquinone but also produces hydrogen peroxide. The cyclic nature of this process is highly valued for its efficiency and the exceptional purity of the hydrogen peroxide obtained, which is crucial for applications requiring high-grade materials, such as in the food processing and medical industries.
Beyond its pivotal role in hydrogen peroxide synthesis, 2-ethyl Anthraquinone serves as a crucial intermediate in the dye industry. Its robust chemical structure facilitates the synthesis of a wide array of color compounds. Through targeted functionalization, it contributes to the production of various dyes and pigments used in textiles, inks, and coatings, enhancing the versatility and depth of color offerings in these sectors.
Furthermore, the potential of 2-Ethyl Anthraquinone extends into the pharmaceutical sector, where it is being explored for synthesizing novel therapeutic compounds. Researchers are particularly interested in its capability to contribute to the development of new drugs that could offer improved efficacy and reduced side effects for treating a range of diseases. This exploration signifies a growing interest in multifunctional chemical agents that can provide a base for the innovation of next-generation medicinal products.
Storage Guidelines
Proper storage of 2-Ethyl Anthraquinone is crucial to maintain its chemical integrity and ensure safety. The compound should be stored in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and moisture. Storage containers must be tightly sealed to prevent contamination and exposure to air, which could lead to undesirable reactions. It is also recommended that 2-ethyl Anthraquinone be stored away from oxidizing agents and acids to prevent any hazardous interactions.
![]() References
References
[1]Yuan E, Wu C, Hou X, et al. Synergistic effects of second metals on performance of (Co, Ag, Cu)-doped Pd/Al2O3 catalysts for 2-ethyl-anthraquinone hydrogenation[J]. Journal of catalysis, 2017, 347: 79-88.
[2]Ma Q, Wang N, Liu G, et al. Enhanced performance of Pd nanoparticles on SBA-15 grafted with alkyltrialkoxysilane in 2-ethyl-anthraquinone hydrogenation[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2019, 279: 245-251.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
2-Ethylanthraquinone
84-51-5You may like
2-Ethylanthraquinone manufacturers
- 2-Ethyl Anthraquinone / Ethylanthraquinone
-

- $6.00 / 1kg
- 2024-08-26
- CAS:84-51-5
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 2000KG/Month
- 2-Ethyl anthraquinone
-

- $0.00 / 25Kg/Bag
- 2024-08-26
- CAS:84-51-5
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 1000mt/year
- 2-Ethyl anthraquinone
-

- $5.60 / 1KG
- 2024-08-20
- CAS:84-51-5
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 5000kg