Imidazole: A Versatile Molecule in Chemistry
Jun 6,2024
Introduction
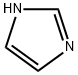
Imidazole is a significant compound in the field of chemistry, known for its wide range of applications and unique properties. As a five-membered aromatic heterocycle, imidazole's structure includes two nitrogen atoms at non-adjacent positions. This compound is fundamental in numerous biochemical processes and industrial applications. Its relevance spans from being a component in pharmaceuticals to playing a crucial role in catalytic processes.

Figure 1 Characteristics of IMIDAZOLE
Properties of Imidazole
Imidazole possesses distinct physical and chemical properties that make it an invaluable compound in various applications. It is a colorless to pale yellow crystalline solid with a characteristic odor. The molecular formula of imidazole is C₃H₄N₂, and it has a molar mass of 68.08 g/mol. One of its key features is its relatively high melting point of 89-91°C, which reflects its stable crystalline structure.
The compound is highly soluble in water, ethanol, and other polar solvents due to its ability to form hydrogen bonds. This solubility is attributed to the presence of nitrogen atoms, which can act as hydrogen bond donors and acceptors. Imidazole also exhibits amphoteric behavior, meaning it can function as both an acid and a base. This property is particularly important in biochemical systems, where imidazole residues in histidine play critical roles in enzyme catalysis and proton transfer mechanisms.
Major Components of Imidazole
Imidazole itself is a simple molecule, but its derivatives and substituted imidazoles are of great interest in both research and industry. The basic structure consists of a five-membered ring with two non-adjacent nitrogen atoms. Modifications to this ring structure can result in a wide variety of compounds with different properties and applications.
For example, benzimidazole, which has a fused benzene ring, is a crucial component in many pharmaceuticals, including antihelmintic drugs. Substituted imidazoles like 2-methylimidazole and 4(5)-methylimidazole are used in the manufacture of resins and other materials. Furthermore, imidazolium salts, which are ionic liquids, have gained attention for their role in green chemistry due to their low volatility and ability to dissolve a wide range of compounds.
Applications of Imidazole
The applications of imidazole are vast and varied, making it a compound of immense industrial and biochemical importance.
Pharmaceuticals
One of the most significant applications of imidazole is in the pharmaceutical industry. Imidazole derivatives are found in various drugs, including antifungal agents like clotrimazole and ketoconazole. These compounds work by inhibiting the synthesis of ergosterol, an essential component of fungal cell membranes. Additionally, imidazole-based drugs are used in the treatment of infections, cancer, and other diseases due to their ability to interfere with biological pathways.
Catalysis
In the realm of catalysis, imidazole and its derivatives serve as vital components. They are used as catalysts in polymerization reactions and as ligands in coordination chemistry. Imidazole-based compounds can stabilize transition states and intermediates, thereby accelerating chemical reactions. For instance, in the field of organic synthesis, imidazole is often used to catalyze the acylation of alcohols and amines.
Materials Science
Imidazole's role extends to materials science, where it is utilized in the production of resins and polymers. Imidazole derivatives act as curing agents for epoxy resins, which are widely used in coatings, adhesives, and composite materials. The stability and mechanical properties of these materials are significantly enhanced by the incorporation of imidazole-based curing agents.
Biochemistry
In biochemistry, imidazole is a critical component of histidine, an amino acid that is a building block of proteins. Histidine residues in enzymes are often involved in catalytic functions and metal ion binding. Moreover, imidazole is used in affinity chromatography for the purification of histidine-tagged proteins, leveraging its ability to bind to metal ions immobilized on chromatography media.
Storage and Handling of Imidazole
Proper storage and handling of imidazole are essential to maintain its stability and ensure safety. Imidazole should be stored in a cool, dry place away from sources of moisture and incompatible substances such as strong acids and oxidizing agents. The compound should be kept in tightly sealed containers to prevent the absorption of moisture from the air, which could affect its quality and reactivity.
When handling imidazole, appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves, goggles, and lab coats should be worn to avoid direct contact with the skin and eyes. In case of spillage, the area should be ventilated, and the spill should be cleaned up promptly using inert absorbent materials. Imidazole waste should be disposed of by local regulations and guidelines to minimize environmental impact.
![]() References
References
[1]Shalini, Kumari, Pramod Kumar Sharma, and Nitin Kumar. "Imidazole and its biological activities: A review."Der Chemica Sinica1.3 (2010): 36-47.
[2]Grimmett, M. R. "Advances in imidazole chemistry."Advances in Heterocyclic Chemistry12 (1970): 103-183.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- General Description of Imidazole Feb 11, 2022
Imidazole is a planar, five-membered, unsaturated, 6π electron ring system, comprised of three carbon atoms and two nitrogen atoms at 1,3-positions with two olefinic bonds.
- Evolutionary convergence in the biosyntheses of the imidazole Nov 5, 2019
The imidazole group is an ubiquitous chemical motif present in several key types of biomolecules. It is a structural moiety of purines, and plays a central role in biological catalysis as part of the side-chain of histidine, the amino acid
4-Hydroxybenzaldehyde (4-HBA) is a prominent organic compound widely recognized for its diverse applications in the chemical industry.....
Jun 6,2024APIRecent studies highlight melamine's neurotoxic effects, inducing apoptosis, disrupting metabolism, and impacting neuronal function, posing cognitive risks.....
Jun 6,2024APIImidazole
288-32-4You may like
- What is albendazole used for?
Jul 10, 2024
- X-PHOS: Properties and Applications as Catalyst
Jul 10, 2024
- Phenacetin: A Comprehensive Overview for Chemistry Professionals
Jul 10, 2024
- Imidazole
-

- $6000.00 / 1000kg
- 2024-07-10
- CAS:288-32-4
- Min. Order: 1000kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 500 tons
- Imidazole
-

- $6000.00 / 1000kg
- 2024-07-10
- CAS:288-32-4
- Min. Order: 1000kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 500 tons
- Imidazole
-

- $6.00 / 1kg
- 2024-07-10
- CAS:288-32-4
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: More than 99%
- Supply Ability: 2000KG/Month