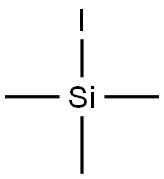Iodotrimethylsilane: Applications as Reactive Ligand and its Preparation Method
May 11,2024
General Description
Iodotrimethylsilane is a versatile chemical compound that acts as both a synthetic reagent and silylating agent. Its importance extends to surface etching and passivation of perovskite nanocrystals for LED applications, ensuring efficiency and stability.
Iodotrimethylsilane is prepared using eco-friendly methods, guaranteeing high purity and conversion rates. With its ability to enhance ligand interactions and surface passivation, Iodotrimethylsilane is a valuable asset in industrial and laboratory settings, driving advancements in the chemical industry. Its multifaceted utility highlights its potential to propel technological progress, offering innovation and efficacy across various applications.

Figure 1. Iodotrimethylsilane
Overview
Iodotrimethylsilane, also known as Trimethylsilyl iodide, is a chemical compound with the molecular formula C3H9ISi. It possesses a molecular weight of 200.0935 and a CAS number of 16029-98-4. This compound is a colorless to pale red flammable liquid with a boiling point of approximately 106°C and a density of 1.406 g/cm³. Its primary usage lies as a significant synthetic reagent and silylating agent, especially in the synthesis of cephalosporins such as ceftazidime. Iodotrimethylsilane is also renowned for its ability to introduce trimethylsilyl groups to alcohols, enhancing the volatility of the resulting silyl ethers, which can be beneficial in gas chromatography analysis. However, due to its corrosive nature and the generation of hydrogen iodide upon contact with moisture, it requires careful handling during transportation and storage. With proper care, Iodotrimethylsilane remains a valuable chemical intermediate in numerous industrial and laboratory applications. 1
Applications as Reactive Ligand
Iodotrimethylsilane serves as a reactive ligand in surface etching and passivation of perovskite nanocrystals (NCs), crucial for efficient pure-red to deep-red LEDs. Resurfacing NCs with conductive ligands addresses dynamic ligands-surface interaction, a fundamental issue in perovskite light-emitting diodes. Previous ligands had drawbacks like weak interactions or dependence on polar solvents. TMIS resolves these by offering good solubility in non-polar solvents and reacting with oleate ligands to produce HI for surface etching and passivation, facilitating strong-binding ligands on NCs. Red perovskite light-emitting diodes using Iodotrimethylsilane exhibit an external quantum efficiency (EQE) of ≈23%, 11.2-fold higher than controls, among the highest for CsPbI3 perovskite light-emitting diodes. This ligand strategy extends to CsPbBr3 systems, yielding EQE of ≈20% at various wavelengths from 640 to 664 nm. This marks the first use of a chemically reactive ligand strategy across different systems, proving effective for red perovskite light-emitting diodes across a range of emissions. Iodotrimethylsilane offers a promising avenue for enhancing the efficiency and stability of perovskite light-emitting diodes through improved ligand interactions and surface passivation. 2
Preparation Method
The method for preparing Iodotrimethylsilane involves several steps to achieve a high conversion rate of 99% and a purity exceeding 99%. Firstly, anhydrous lithium iodide is prepared by adding anhydrous sodium iodide to an organic solvent containing anhydrous lithium chloride, followed by filtration to obtain anhydrous lithium iodide. Secondly, this anhydrous lithium iodide is reacted with trimethylchlorosilane, catalyzed by a quaternary ammonium salt catalyst or without a catalyst, at a temperature range of 20-80°C for 8-10 hours. Toluene, cyclohexane, chloroform, dichloromethane, ethyl acetate, acetone, ethanol, or a mixture thereof can be used as the organic solvent. The method offers several advantages: it is simple, safe, and environmentally friendly, with mild reaction conditions. It avoids the use of hazardous chemicals like metallic potassium or sodium and eliminates the challenge of high-temperature iodination. Furthermore, it allows for the recycling of materials: the organic solvent can be reused, lithium chloride remains intact throughout the reaction, and trimethylchlorosilane vaporized during distillation can be reused in subsequent reactions. This recycling reduces production costs and minimizes waste generation. Overall, this method provides a straightforward and safe synthesis route for Iodotrimethylsilane, with high conversion rates and purity, while ensuring environmental sustainability. 3
Reference
1. Iodotrimethylsilane. National Center for Biotechnology Information. 2024; PubChem Compound Summary for CID 85247.
2. Zhao F, Duan HW, Li SN, et al. Iodotrimethylsilane as a Reactive Ligand for Surface Etching and Passivation of Perovskite Nanocrystals toward Efficient Pure-red to Deep-red LEDs. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2023; 62(46): e202311089.
3. Li CL, Wang QM, Zhai YL, Chu RQ. Method for preparing trimethyliodosilane. 2017; Patent Number: CN106928268.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Iodotrimethylsilane:an important silanization reagent Dec 22, 2023
Iodotrimethylsilane is an important silanization reagent with a wide range of applications in the chemical and pharmaceutical fields.
- Iodotrimethylsilane: properties and applications in organic synthesis Sep 8, 2023
Iodotrimethylsilane is a versatile compound used in organic synthesis for introducing iodine atoms and forming carbon-carbon bonds. It also cleaves bonds, dealkylates ethers, and modifies nucleosides.
- Iodotrimethylsilane : A Mild and Efficient Reagent for the Reduction of Azides to Amines Nov 20, 2019
In the last two decades an explosive growth has been witnessed in the use of organo-silicon reagents in organic synthesis. Iodotrimethylsilane with remarkable reactivity as a hard-soft reagent has been known for a wide spectrum of synthetic
Cetearyl alcohol, derived from plants, serves as a versatile ingredient in skincare, providing moisturizing, emulsifying, and stabilizing benefits.....
May 11,2024APIRecent synthesis advancements of 4-Chloro-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine enhance kinase inhibitor development, offering high yields and accessibility for researchers.....
May 11,2024APIIodotrimethylsilane
16029-98-4You may like
Iodotrimethylsilane manufacturers
- Iodotrimethylsilane
-

- $0.00 / 1kg
- 2024-06-14
- CAS:16029-98-4
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 0.99
- Supply Ability: 50000kg
- Iodotrimethylsilane
-

- $30.00 / 1kg
- 2024-06-03
- CAS:16029-98-4
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 100 tons
- Iodotrimethylsilane
-

- $10.00 / 1kg
- 2024-04-24
- CAS:16029-98-4
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99.6%
- Supply Ability: 100000