Meglumine: Properties and Pharmaceutical Applications
Jun 13,2024
General Description
Meglumine, a derivative of N-methylglucamine, is valued in pharmaceutical formulations for its water solubility and stability. Its basic nature allows it to form salts with various acids, enhancing compatibility with different formulations. In recent studies, meglumine has been utilized in innovative drug delivery systems for skin application. By forming hexagonal liquid crystals and lamellar polymeric networks with fatty acids, meglumine plays a crucial role in ensuring effective drug delivery through the skin. These systems exhibit good mechanical properties, biocompatibility, and bioadhesive characteristics, making meglumine a key ingredient in the development of advanced dermatological therapies.

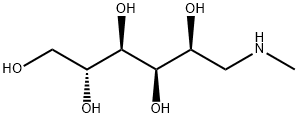
Figure 1. Meglumine
Properties
Meglumine, derived from sorbitol and classified as a derivative of N-methylglucamine, exhibits distinctive chemical and physical properties. Primarily known for its solubility in water, Meglumine manifests as a white crystalline powder with a sweet taste, facilitating its incorporation into various pharmaceutical formulations. Its water solubility renders it invaluable in pharmaceutical applications requiring water-soluble compounds. Moreover, Meglumine's basic nature, attributed to the presence of an amino group, enables it to readily form salts with diverse acids, a feature leveraged in its versatile applications. This property enhances its compatibility with a wide range of pharmaceutical formulations. Additionally, Meglumine demonstrates relative stability in its physical properties, contributing to its utility and reliability in pharmaceutical manufacturing processes. Overall, Meglumine's unique combination of solubility, stability, and chemical reactivity underscores its importance as an ultimate ingredient in pharmaceutical formulations. 1
Pharmaceutical Applications
Meglumine is a versatile compound increasingly used in pharmaceutical applications, particularly as a component of drug delivery systems designed for topical use on the skin. Recent studies, such as the one described in the provided text, highlight the innovative use of meglumine-based supra-amphiphiles that self-assemble in water to form structures capable of delivering drugs effectively through the skin. One key application of meglumine in this context is its role in forming hexagonal liquid crystals and lamellar polymeric networks when combined with fatty acids like oleic acid and stearic acid. These structures are crucial as they determine the system's efficacy in drug delivery. The meglumine-oleic acid (MEG-OA) combination, for instance, forms hexagonal liquid crystals at a 30-70 wt% water content. This formation is likely due to the specific curvature and increased water solubility provided by meglumine, which helps in maintaining an effective delivery matrix at varying water levels. Furthermore, meglumine is instrumental in the self-assembly of meglumine-stearic acid (MEG-SA) into a lamellar polymeric network, which is notable for its stability across a broad range of water contents (10-80 wt%). This stability can be attributed to the hydrophobic interactions between the fatty acid chains and the hydrogen bonds between meglumine molecules and water, which reduce the mobility of MEG-SA in water, thus maintaining the structure of the delivery system. The mechanical properties and biocompatibility of these meglumine-based systems are also significant, as both contribute to their suitability as skin drug delivery systems. The research shows that these systems possess appropriate mechanical characteristics and are compatible with biological tissues, making them potential candidates for encapsulating and delivering therapeutic molecules directly through the skin. Additionally, a notable finding from the research is the correlation between the amount of unfrozen bound water in these meglumine-based systems and their bioadhesive properties. This suggests that meglumine’s ability to interact with water not only affects the structural integrity and delivery capabilities of the drug delivery system but also enhances its bioadhesion, which is crucial for effective drug administration and sustained release on the skin. Overall, meglumine's role in these drug delivery systems is pivotal. It not only facilitates the structuring and stabilization of the delivery matrix but also enhances the system’s biocompatibility and bioadhesion, making it a valuable component in the development of advanced dermatological therapies. 2
Reference
1. Meglumine. National Center for Biotechnology Information. 2024; PubChem Compound Summary for CID 8567.
2. de Souza ALR, Fonseca M, Ferreira LMB, et al. Meglumine-based supra-amphiphile self-assembled in water as a skin drug delivery system: Influence of unfrozen bound water in the system bioadhesiveness. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2019; 184: 110523.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
Supplementation with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate monohydrate can synthesize neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, maintaining a healthy nervous system.....
Nov 4,2025Biochemical EngineeringL-Cystine, a sulfur-containing amino acid, crucial for protein folding, synthesis of taurine, sulfate, and glutathione, essential for metabolism, immunity, and cellular functions.....
Jun 13,2024APIMeglumine
6284-40-8You may like
- N-methylglucamine
-

- $1.00 / 500g
- 2025-12-20
- CAS:6284-40-8
- Min. Order: 300g
- Purity: 99.8%
- Supply Ability: 20 TONS
- Meglumine
-

- 2025-12-20
- CAS:6284-40-8
- Min. Order:
- Purity: 0.99
- Supply Ability:
- Meglumine
-

- $0.00 / 25kg
- 2025-12-19
- CAS:6284-40-8
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%min
- Supply Ability: 500kgs