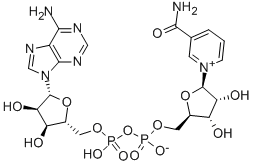
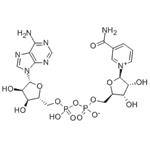
Oxidation and reduction of β-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+)
Jun 7,2024
β-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is an electron carrier as it carries electrons from hydride from one region of the cell to another. NADH, on the other hand, is a coenzyme that acts as a regenerative electron donor during catabolism. NAD can be found in two forms, NAD+ and NADH, known as redox pairs.
Oxidation and reduction are terms that describe the gain or loss of electrons by a molecule. Reduction is when a molecule gains electrons, such as when NAD+ gains electrons from a hydride to become NADH. In this case, we say that NAD+ is reduced to NADH. When NAD+ converts into NADH, it gains two things: firstly a charged hydrogen molecule (H+) and secondly two electrons. Since electrons are negatively charged, the positively charged NAD+ and H+, plus the two electrons, effectively cancel each other out and neutralise the resulting NADH molecule.
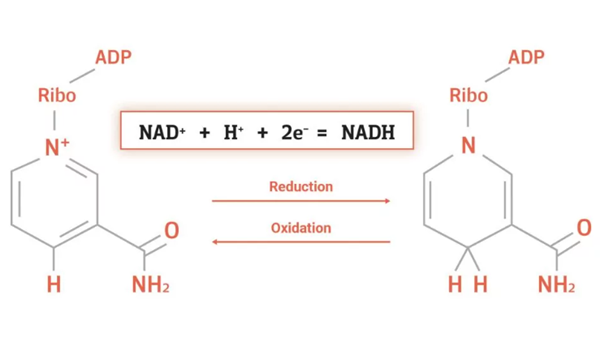
Oxidation is when a molecule loses electrons, e.g. NADH loses its hydride to become NAD+. In this example, we say that NADH is oxidised to NAD+. This process is by no means permanent and can happen over and over again in the same molecule. This means that NAD+ can constantly gain and lose electrons, thus emphasising its status as an electron carrier.
The NAD+/NADH interconversion can be used to generate large amounts of energy ATP required by the body, which is more common during cellular respiratory processes (glycolysis, the Krebs cycle and the electron transport chain). In glycolysis and the Krebs cycle, NADH molecules are generated from NAD+. Meanwhile, in the electron transport chain, all NADH molecules are subsequently split to form NAD+, producing both H+ and several electrons. H+ is used to drive a "pump" in the inner mitochondrial membrane, generating large amounts of energy in the form of ATP.After circulating through the pump, H+ combines with electrons and oxygen molecules to form water. All three stages of respiration produce ATP, but the greatest ATP production occurs in the electron transport chain.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- Side effects of NAD+ oral or injectable therapy Apr 17, 2024
NAD+ is present in every cell in the body, and is essential for the production of cellular energy and the maintenance of cellular health.
- NAD+:Introduction;Biosynthesis;Metabolism in aging and disease Nov 16, 2023
NAD+ metabolism has been linked to a variety of age-related diseases, mainly tumours, metabolic diseases, neurodegenerative diseases, and aging.
- β-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide: Biosynthesis, physiological function and application Apr 17, 2023
β-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide is a cofactor and plays a major role in metabolism, involved in redox reactions, carrying electrons from one reaction to another.
Supplementation with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate monohydrate can synthesize neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, maintaining a healthy nervous system.....
Nov 4,2025Biochemical EngineeringGlycidyl Methacrylate (GMA) is a clear, colourless liquid with a strong ester and fruity odour.....
Jun 7,2024Organic ChemistryYou may like
β-Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide manufacturers
- beta-Diphosphopyridine nucleotide
-
- 2025-11-08
- CAS:53-84-9
- Min. Order:
- Purity: 0.99
- Supply Ability:
- NAD+
-

- $41.00 / 500mg
- 2025-11-08
- CAS:53-84-9
- Min. Order:
- Purity: 99.09%
- Supply Ability: 10g
- β-Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide(NAD+)
-

- $0.00 / 1kg
- 2025-11-07
- CAS:53-84-9
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 100kg