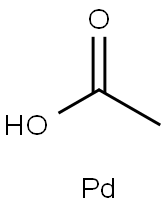
Palladium Diacetate: A Versatile Catalyst in Modern Chemistry
Oct 23,2024
Introduction
Palladium is a ubiquitous metal for the formation of carbon-carbon bonds in organic synthesis through transformations which are frequently catalyzed by practically every Pd-containing source. The nature of the real catalyst, which might be quite different from that of the precursor, is, however, a recurring subject of debate. The distinction between homogeneous catalysis by molecular species and “heterogeneous” catalysis by soluble metal nanoparticles is especially relevant in carbon-carbon coupling reactions, which are often performed under conditions favorable for the formation of Pd0 nanoparticles from molecular precursors.
However, key experiments on Heck, Suzuki, Sonogashira, and other coupling reactions support currently that the true catalyst in these reactions consists of monomeric or dimeric palladium complexes(palladium diacetate); the Pd nanoparticles added as precursors or formed in the catalytic medium are therefore mere reservoirs of palladium from which the metal atoms are leached by oxidative addition of the arylating agent.1

Figure 1 Characteristics of Palladium diacetate
Experiments
The simplest catalyst palladium diacetate [Pd(OAc)2] may be the most efficient of the Pd catalysts compared here for the Stille reaction in water. However, this conclusion must be qualified when the viability of catalyst reuse is considered in this analysis. 4-Iodoacetophenone was selected for testing recyclability because all the catalysts afforded good yields at 80 °C with this substrate and the products could be extracted from the aqueous solution with diethyl ether once the reaction had finished. The aqueous solution was then recharged with a new load of reactants, and a new reaction cycle was started.
Larger differences between the reactivity of palladium acetate and DENs were found in the case of the less water-soluble substrates. Thus, activated 4-iodoacetophenone reacted almost quantitatively in the presence of palladium acetate at 40 °C whereas the temperature had to be raised to 80 °C when using Pd DENs or PdII-dendrimer complexes to achieve yields close to 70%. A similar trend was observed in the case of 3-iodopyridine or inactivated 4-io-doanisole, for which DENs were of little use and palladium acetate afforded moderate yields only at 80 °C. It can therefore be concluded that the general order of activity of the compared (pre)catalysts is palladium diacetate > Pd DENs > dendrimer-palladium(II) complexes.1
Conclusion
The above experiments shed some light on the nature of the catalytic process and, especially, on the role of the dendritic templates. On the basis of the results published in the literature, we assume the existence of a dynamic equilibrium between the Pd nanoparticles and molecular palladium species during the catalytic process. The molecular species are most likely responsible for the observed activity and, in this sense, the comparison made in this work with molecular precursors such as palladium diacetate is relevant.
The leaching of palladium atoms from DENs is possibly produced after addition of ArI to the nanoparticle surface. A fraction of palladium(II) might then migrate from the dendritic interior to the solution, which explains the loss of palladium and the size increase of DENs observed during the recycling experiments. PdII species leached from the nanoparticle surface should, however, remain predominantly coordinated to the dendrimer during the catalytic process to explain the recurrent selectivity differences observed in the presence and absence of dendrimer. It is foreseeable that this initial reduction is accompanied by partial decoordination of Pd from the dendrimer, thus explaining the loss of activity and palladium content after the first (and only after the first) catalytic cycle.
In conclusion, palladium diacetate affords excellent yields in the Stille reaction in an aqueous medium with some substrates and that this simple catalyst performs somewhat better than dendrimer-encapsulated palladium nanoparticles, whose excellent reported activities are apparently limited to water-soluble substrates. From a practical point of view, however, it is important to highlight that DENs can easily be recovered by liquid-liquid extraction and reused in several catalytic runs. The presence of the dendrimer suppresses the homocoupling side reaction, which is also important from a conceptual point of view because it implies that the catalysis occurs under the influence of the dendrimer.1
References:
[1] MARíA BERNECHEA. Dendrimer-Encapsulated Pd Nanoparticles versus Palladium Acetate as Catalytic Precursors in the Stille Reaction in Water[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2009, 48 10: 4268-4591. DOI:10.1021/ic9002753.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- What is Palladium (II) Acetate? Apr 22, 2021
Palladium(II) acetate is a chemical compound of palladium described by the formula [Pd(O2CCH3)2]n, abbreviated [Pd(OAc)2]n. It is more reactive than the analogous platinum compound.
- Pd(OAc)2/Xantphos Catalyst System Feb 22, 2021
A recent report by Eastgate and Blackmond on a Pd/Xantphos-catalyzed C?H arylation reaction suggested that under their reaction conditions, the active ligand was not Xantphos or Xantphos bisphosphine oxide, but the bisphosphine monoxide for
Supplementation with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate monohydrate can synthesize neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, maintaining a healthy nervous system.....
Nov 4,2025Biochemical EngineeringPolyethylene-polypropylene glycol, known as Poloxamer 188, is a polydisperse mixture of triblock copolymers.....
Oct 29,2024APIPalladium (II) Acetate
3375-31-3You may like
Palladium (II) Acetate manufacturers
- Palladium (II) Acetate
-

- 2025-12-19
- CAS:3375-31-3
- Min. Order:
- Purity: 0.99
- Supply Ability:
- Palladium diacetate
-

- $0.00 / 100gram
- 2025-12-18
- CAS:3375-31-3
- Min. Order: 1gram
- Purity: ≥47%
- Supply Ability: 10mt/year
- Palladium (II) Acetate
-

- $10.00 / 1KG
- 2025-12-11
- CAS:3375-31-3
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 47.5%min
- Supply Ability: 6tons