Sunitinib in the Treatment of Thyroid Cancer
Feb 2,2024
General Description
Sunitinib is a multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor used in the treatment of various types of cancers. Its mechanisms of action include inhibiting PDGF-Rs, VEGFRs, and c-KIT, leading to tumor shrinkage and apoptosis. Preclinical studies suggest that Sunitinib has potential as a targeted therapy for certain types of thyroid cancer, particularly those with specific gene rearrangements. In clinical trials, Sunitinib demonstrated significant anti-tumor activity in patients with advanced thyroid cancer, including those with metastatic, RAI-refractory, and FDG-PET avid TC. Overall, Sunitinib is an important therapeutic option for patients with various types of cancers, especially those who have not responded to other treatments or have limited treatment options.

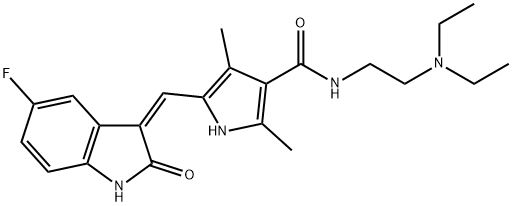
Figure 1. Sunitinib
A tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the treatment of various cancers
Sunitinib is an oral, multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) that is used in the treatment of various types of cancers. It has a low molecular weight and acts by inhibiting the activity of certain receptors involved in tumor growth and progression. One of the key mechanisms of action of sunitinib is the inhibition of platelet-derived growth factor receptors (PDGF-Rs) and vascular endothelial growth factor receptors (VEGFRs). By simultaneously inhibiting these receptors, sunitinib reduces tumor vascularization and induces apoptosis (cell death) in cancer cells, leading to tumor shrinkage. Sunitinib also targets other important receptors, such as c-KIT, which plays a role in gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST). Inhibition of c-KIT by sunitinib is particularly beneficial for patients with GIST who are resistant to other treatments. Clinical trials have shown that sunitinib is effective in treating imatinib-resistant GIST, with significantly longer time to tumor progression compared to a placebo. It has also been approved for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC), a type of kidney cancer that is usually resistant to chemotherapy or radiation. In RCC patients, sunitinib has demonstrated longer progression-free survival, improved quality of life, and higher tumor shrinkage rates compared to interferon-alpha therapy. Furthermore, sunitinib has been approved for the treatment of well-differentiated pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors and has shown effectiveness in other solid tumors, including metastatic breast, lung, and colorectal cancers. Overall, sunitinib is an important therapeutic option for patients with various types of cancers, especially those who have not responded to other treatments or have limited treatment options. 1
Sunitinib in Thyroid Cancer
Preclinical studies
Sunitinib is a drug that has undergone preclinical studies to evaluate its efficacy in various types of thyroid cancer. In vitro studies have been conducted to assess its effects on different cellular pathways and gene expressions. One study demonstrated that Sunitinib inhibited the phosphorylation of a synthetic substrate peptide, indicating its potential to inhibit cell growth. Another study showed that Sunitinib could inhibit the growth of cells with rearrangements in the RET/PTC1 gene, which is associated with thyroid cancer. Furthermore, Sunitinib was found to be effective in inhibiting the growth of cells with RET/PTC rearrangement but not BRAF mutated cells. This suggests that Sunitinib may specifically target cells with this particular gene rearrangement. In studies involving human cell lines obtained from anaplastic thyroid carcinomas (ATCs), Sunitinib showed limited effectiveness, indicating that it may not be efficacious in treating ATC. In vivo anecdotal studies have also been conducted. These studies involved patients with metastatic differentiated thyroid cancer (DTC) and medullary thyroid cancer (MTC). Sunitinib demonstrated sustained clinical responses in some patients with DTC, leading to tumor reduction. It also resulted in partial disease response in patients with progressive metastatic PTC or MTC. Additionally, there were reports of complete response and significant disease reduction in patients with ATC when treated with Sunitinib. Overall, preclinical studies suggest that Sunitinib has potential as a targeted therapy for certain types of thyroid cancer, particularly those with specific gene rearrangements. 2
Clinical studies
Clinical studies were conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of sunitinib in TC patients with aggressive disease. In one phase II study, sunitinib was administered at 50 mg/day to 37 DTC patients and 6 MTC patients, resulting in 13% achieving partial response (PR), 68% a stable disease (SD), and 10% had progressive disease (PD) in DTC patients. In MTC patients, 0% achieved PR, 83% a SD, and 17% had a PD. In another trial, sunitinib was administered at 37.5 mg daily to 18 patients with metastatic, RAI-refractory, and FDG-PET avid TC, resulting in a positive response rate in all patients with DTC histology. In a phase II trial, sunitinib was administered at 50 mg/day on a 4-week schedule to patients with locally advanced or metastatic TC, resulting in a confirmed PR for 2 patients, an unconfirmed PR for 3 patients, and SD for ≥12 weeks for 4 patients. In another phase II trial, sunitinib was administered at 37.5 mg/die continuously to patients with FDGPET-avid, iodine-refractory well-DTC and MTC, resulting in an ORR per RECIST of 31%. The results of these studies suggest that sunitinib exhibits significant anti-tumor activity in patients with advanced TC. 2
Reference
1. Deeks ED, Keating GM. Sunitinib. Drugs. 2006;66(17):2255-2268.
2. Ferrari SM, Centanni M, Virili C, et al. Sunitinib in the Treatment of Thyroid Cancer. Curr Med Chem. 2019;26(6):963-972.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
- An oral multiple tyrosine kinase receptor inhibitor: Sunitinib Oct 31, 2023
Sunitinib is an oral multiple tyrosine kinase receptor inhibitor. It is usually well tolerated but can cause fatigue, malaise, and rash.
Yes. The therapeutic fluoropyrimidines 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and 5-fluorocytosine (5-FC) have long been used to treat human cancer and severe invasive fungal infections, respectively.....
Dec 16,2024Biochemical EngineeringDabigatran Etexilate, a prodrug converted to dabigatran, selectively inhibits clot formation. RE-LY trial showed noninferiority/superiority to warfarin in preventing stroke/embolism.....
Feb 2,2024APISunitinib
557795-19-4You may like
- Sunitinib
-

- $0.00 / 10G/Bag
- 2025-04-08
- CAS:557795-19-4
- Min. Order: 1G/Bag
- Purity: 0.99
- Supply Ability: 100kg
- Sunitinib
-
- $1.00 / 1kg
- 2025-04-08
- CAS:557795-19-4
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 200
- Sunitinib
-

- $0.00 / 1g
- 2025-04-08
- CAS:557795-19-4
- Min. Order: 1g
- Purity: 99%min
- Supply Ability: 1000G