Synthesis and Bioactivity of RU-58841
Oct 21,2022
General description
The non-steroidal antiandrogens, RU 58841 and RU 56187 are amongst the most active of a new series of N-substituted aryl hydantoins or thiohydantoins. Their pharmacokinetics and principal metabolic profiles have been evaluated in rat plasma after intravenous administration of a 10 mg/kg dose. The pharmacological profile of RU 58841 which displays a potent local antiandrogenic activity without systemic effects can be related to its very low propensity to form the N-desalkyl metabolite. The synergistic effects of RU58841 and minoxidil topical solution (2% and 5%) have also been reported in stumptailed macaques. The effect of combined treatment was most remarkable early on, but by 1 year no significant benefit of combined treatment was apparent relative to either treatment alone.
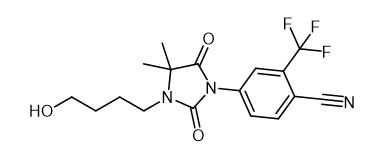
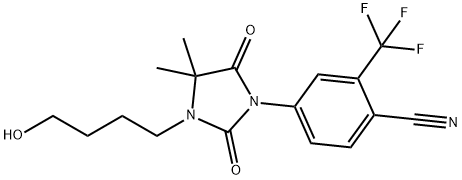
Fig. 1 The structure of RU 58841.
Synthetic routes

Fig. 2 The synthetic method 1 of RU 58841.
Dissolve 4-(4,4-dimethyl-2,5-dioxoimidazolidin-1-yl)-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzonitrile (1.00 g, 3.37 mmol) in dry DMF (25 mL). Wash NaH 60% suspension in mineral oil (280 mg, 7.00 mmol) twice in a sealed flask with dry n-hexane (5 mL) using a syringe. Add the solution of 4-(4,4-dimethyl-2,5-dioxoimidazolidin-1-yl)-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzonitrile in DMF to the flask containing the NaH by pressure equalizing funnel. Stir the two for 15 min until bubbles of H2 gas ceases. Add 4-bromobutyl acetate (680 mg, 3.49 mmol) by syringe through the addition funnel and wash with a second 25 mL portion of dry DMF. Stir the mixture and heat at 50°C for 2 h. Add a pellet of NaOH (200 mg), and deionized water (45 mL). Remove the DMF and water by evaporation to obtain 4-[3-(4-hydroxybutyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2,5- dioxoimidazolidin-1-yl]-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzonitrile. 1H NMR (300 MHz, 20 mg: 0.4 mL CDCl3): δ 1.52 (6H, s, CH3),δ 1.64 (2H, m, CH2-3),δ 1.82 (2H, m, CH2-2),δ 2.12 (1H, s, OH),δ 3.39 (2H, t, CH2-1, J 6),δ 3.68 (2H, t, CH2-4, J 6),δ 7.89 (d, ArH5, J 8),δ 7.98 (dd, ArH6, J 2, J 8),δ 8.13 (d, ArH2, J 2). 13C NMR (75 MHz, 20 mg: 0.4 mL CDCl3): δ 23.7 (s, CH3x2),δ 26.4 (s, al-C-2),δ 30.0 (s, al-C-3),δ 40.4 (s, al-C-1),δ 62.2 (s, hyd-C-5),δ 62.3 (s, al-C-4), δ 108.4 (s, C-4'),δ 115.3 (s, CN),δ 122.3 (q, CF3,J 136),δ 123.3 (q, C-2',J 5),δ 128.2 (s, C-6'),δ 133.8 (q, C-3',J17),δ 135.6 (s, C-5'), δ 136.8 (s, C-1'),δ 153.2 (s, hyd-C-2),δ 174.9 (s, hyd-C-4). IR (cm-1): 3392 (OH), 3133, 2944, 2876, 2234 (CN), 1774, 1719 (C=O), 1612 (C=O), 1505, 1438, 1413, 1377, 1312, 1179 & 1133 (C-F), 1051, 894, 837, 763, 675, 555. Elemental Analysis: C, H, N: calcd for C17H18N3O3F3: 55.28, 4.91, 11.38. Found: 55.19, 4.84, 11.28. HRMS GC-(EI) TOF-: calcd for C17H18N3O3F3 (M): 369.1300, observed:369.1294 [1].

Fig. 3 The synthetic method 2 of RU 58841.
This product was mixed in 5 ml of methanol and 1.5 ml of 2 N hydrochloric acid, and the mixture was stirred for 40 minutes at ambient temperature. The mixture was poured into 30 ml water and extracted with methylene chloride. The organic phase was washed with water, dried and the solvent was evaporated. After chromatography of the residue on silica (eluent methylene chloride-acetone (9-1), the fractions were obtained, and after crystallization from isopropyl ether. 4-(4,4-dimethyl-2 ,5-dioxo 3-(4-hydroxybutyl)-1-imidazolidinyl)-2-(trifluoromethyl) benzonitrile, 307 mg of the expected product wasobtained. das bei 102°C-103°C melts. analysis: C17H18F3N3O3; molecular mass= 369,35. calculated: C 55,28%, H 4,91%, F 15,43%, N 11,38%; found: C 55,2%, H 4,9%, F 15,3%, N 11,1%. IR-spectrum (CHCl3): 3628 cm-1 (OH); 2236 cm-1 (C=N); 1778-1724 cm-1 (C=O); 1615-1575-1505 cm-1 (aromatics) [2].
Bioactivity
As antiandrogen
The percutaneous absorption and the cutaneous distribution of a new antiandrogen, RU 58841, 0.5% in liposomes or in solution were compared after topical application. In vitro percutaneous absorption experiments were performed on human dermatomed skin with Franz diffusion cells. In vivo cutaneous distribution after application on the skin of hairless rat was studied with the method previously described by Schaefer and Stuttgen. The in vitro experiments showed that liposomes considerably reduce the RU 58841 percutaneous absorption compared to solution. After in vivo application, drug content of skin surface, stratum corneum, epidermis and dermis were measured, it demonstrated a slower permeation of the drug and a longer duration in the epidermis and dermis for the liposomes compared with the solution. The distribution profile of solution presented an RU 58841 concentration gradient decreasing from the surface to the deeper layers while an RU 58841 concentration increase between 30 and 150 mu m in depth was observed with liposomes showing an accumulation in the sebaceous structures. In conclusion, there is a trend towards a more favourable topical application of liposomes for local effects. They reduce percutaneous absorption, increase accumulation and retention of the drug in the dermis and produce a targeting in the sebaceous structures [3].
Acne and androgenetic alopecia are linked to androgen effects and therefore should improve following topical application of antiandrogens. Munster et al. present a new antiandrogen prodrug, RU 58841-myristate (RUM) for topical therapy. Almost devoid of affinity to the androgen receptor, as derived from investigations in the mouse fibroblast cell line 29+/GR+, RUM is rapidly metabolised to the potent antiandrogen RU 58841 by cultured human foreskin fibroblasts and keratinocytes, male occipital scalp skin dermal papilla cells, and by cells of the sebaceous gland cell line SZ95. In order to improve a specific targeting of the hair follicle, RUM was loaded on solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN), which are already known to support dermal targeting effects. Physically stable RUM loaded SLN were produced by hot homogenization. Penetration/permeation studies carried out using the Franz diffusion cell proved only negligible permeation of reconstructed epidermis and excised porcine skin within 6 h, implying a more topical action of the drug. Targeting to the hair follicle using SLN was visualised by fluorescence microscopy, following the application of Nile Red labelled SLN to human scalp skin. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) allowed to detect intact silver labelled SLN in porcine hair follicles of preparations applied to the skin for 24 h. RUM loaded SLN should be considered for topical antiandrogen therapy of acne and androgenetic alopecia [4].
The significance of the sebaceous gland pathway in the cutaneous permeation of an antiandrogen, 4-[3-(4-hydroxybutyl)-4,4-dimethyl-2,5-dioxo- 1-imidazolidinyl]-2-(trifluoromethyl)benzon (RU 58841), was studied with normal hairless rat skin and an induced scar hairless rat skin without sebaceous glands. RU 58841 was dissolved in an alcoholic solution and e
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
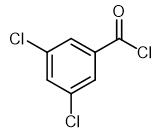
3,5-Dichlorobenzoyl chloride is an important organic and pharmaceutical intermediate.....
Oct 20,2022Organic Synthesis IntermediateBaicalein has many pharmacological activities such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic, antibacterial, antiviral, and antitumor.....
Oct 21,2022Biochemical Engineering