The reduction reactions of Phenylsilane
Jul 31,2024
Introduction
Phenylsilane (PhSiH3) is an organosilicon compound that is benzene, and hydrogen is replaced by a silyl group. It may be used as a reducing agent to partially reduce phosphine oxide groups in poly(4,4′-diphenylphenylphosphine oxide) (PAPO) to phosphine. It can also undergo photopolymerization with methyl methacrylate(MMA) to form poly(MMA) containing SiH groups. PhSiH3 may be a silicon source to synthesize crystalline Si nanowires via Au-nanocrystal-seeded supercritical fluid-liquid-solid (SFLS) synthesis.
Reduction reactions
Hydrosilylation reactions are commonly used to reduce carbonyl bonds in fine chemistry, catalyzed by transition metal complexes. The activation of phenylsilane was highly dependent on the physical properties of the solvent, such as the polarity, and the highest conversions were obtained in acetonitrile and propylene carbonate, with yields of 46 % and 97 %, respectively.
In addition to methyl aryl ketones, ethyl aryl ketones and fluoromethyl aryl ketones were readily reduced by phenylsilane in high yields and enantioselectivities when catalyzed by hCAII in whole cells. Various heterocyclic ketones, including 2- and 3-acetylpyridine, 3-acetylpyrazine, and 1-acetylfuran, were readily reduced in high yields and exceptionally high enantioselectivity[1].
Thee reduction of phosphine oxides by phenyl silane is considered less demanding and, therefore, more commonly useds. They offer considerable advantages over other reducing agents, such as nonaggressive behaviour, simple and mild reaction conditions, low toxicity, good functional group tolerance, relatively simple purification of products, and a predictable and highly enantioselective stereo-chemical outcome. For these advantages, they have been recently used as suitable reductants in the critical steps of catalytic Wittig, Appel, and Mit-sun bu, as well as in related reactions[2].
Uses
A copper-catalyzed protocol for reductive methylation of amines and imine with formic acid as a C1 source and phenylsilane as a reductant is reported, affording the corresponding methylamines in good to excellent yields under mild conditions[3].
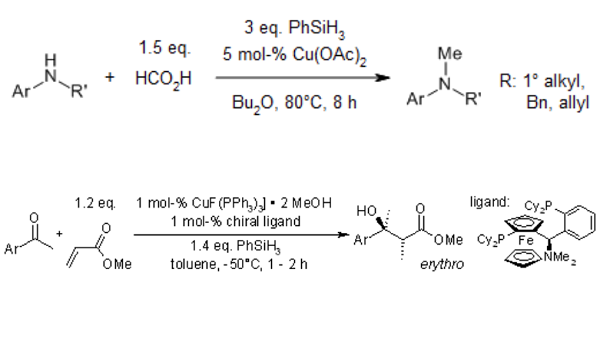
A new strategy for ketones' catalytic asymmetric aldol reaction was developed that relies on a chiral copper(I) complex-catalyzed domino reduction/aldol reaction sequence in the presence of phenylsilane[4].
References:
[1] PENGFEI JI. Abiotic reduction of ketones with silanes catalysed by carbonic anhydrase through an enzymatic zinc hydride[J]. Nature chemistry, 2021, 13 4. DOI:10.1038/s41557-020-00633-7.
[2] OLEG M. DEMCHUK K M P Radomir Jasiński. New Insights into the Mechanism of Reduction of Tertiary Phosphine Oxides by Means of Phenylsilane[J]. Heteroatom Chemistry, 2015, 26 6: i, 391-462. DOI:10.1002/hc.21279.
[3] CHANG QIAO. Copper(II)-Catalyzed Selective Reductive Methylation of Amines with Formic Acid: An Option for Indirect Utilization of CO2[J]. Organic Letters, 2017, 19 6: 1257-1496. DOI:10.1021/acs.orglett.7b00551.
[4] JULIA DESCHAMP. Highly Diastereo- and Enantioselective Copper-Catalyzed Domino Reduction/Aldol Reaction of Ketones with Methyl Acrylate.[J]. ChemInform, 2006, 37 24. DOI:10.1002/chin.200624084.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
Supplementation with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate monohydrate can synthesize neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, maintaining a healthy nervous system.....
Nov 4,2025Biochemical EngineeringNinhydrin and 1,8-diazafluoren-9-one (DFO) are the two primary reagents for visualizing the amino acids contained within a fingerprint residue.....
Jul 31,2024Organic reagentsPhenylsilane
694-53-1You may like
- phenylsilicon
-
- $1.00 / 500g
- 2025-12-16
- CAS:694-53-1
- Min. Order: 300g
- Purity: 99.8%
- Supply Ability: 20 TONS
- Phenylsilane
-
- $2000.00 / 20kg
- 2025-12-16
- CAS:694-53-1
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 1 tons
- Trifluoromethanesulfonic anhydride
-

- $10.00 / 1KG
- 2025-12-11
- CAS:358-23-6
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 100 mt






