The synthesis method of Quinofumelin
Feb 18,2024
Description
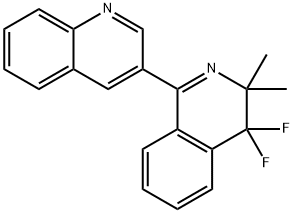
Quinofumelin, 3-(4,4-difluoro-3,3-dimethyl-3,4-dihydroisoquinolin-1-yl)quinoline, a novel fungicide developed by Mitsui Chemicals Agro, Inc., shows potent fungicidal activity against a broad range of ascomycete fungi, including P. oryzae. Mitsui and Bayer Crop Science have signed a global license agreement for developing and commercializing this active ingredient[1].
quinofumelin is a novel fungicide with a distinct chemical structure including 3-(isoquinolin-1-yl) quinoline, demonstrating fungicidal activity against a variety of fungi, shows potent activity against mold diseases in the fruit and vegetable segment, but also against rice blast. quinofumelin showed a high selectivity for fungal DHODH over human DHODH. Quinofumelin failed to inhibit the mycelial growth of the ΔN-HsDHODH gene insertion mutants, which further confirmed the strong fungal selectivity of quinofumelin. Highly fungal selective quinofumelin with a novel mode of action is expected to provide more effective options for managing plant diseases[2].
Synthesis method
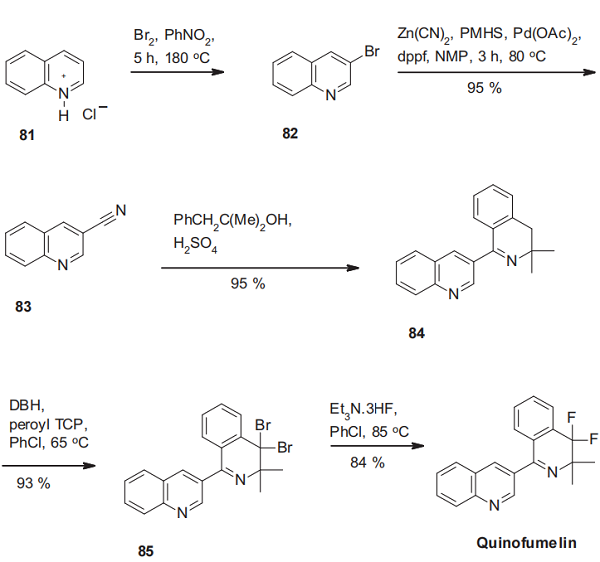
The synthesis of quinofumelin starts with the regioselective bromination of quinolinium chloride(81). The resulting 3- bromoquioline (82) is then transformed into the corresponding nitrile via a palladium-catalyzed cross-coupling reaction using zinc cyanide. The construction of the dihydroisoquinoline scaffold of quinofumelin is then achieved by a sulfuric acid-mediated Ritter reaction of 3-quinolinecarbonitrile (83) with 2-methyl-1-phenylpropan-2-ol and subsequent Bischler-Napieralski cyclization, delivering the dihydroisoquinolinylquinoline derivative 84. Finally, radical benzylic dibromination with 1,3-dibromo-5,5-dimethylhydantoin (DBH) using di-(4-tert-butylcyclohexyl)peroxydicarbonate (peroyl TCP) as initiator, followed by double halogen exchange leads to quinofumelin[3].
References
[1] Norikazu Higashimura. “The target site of the novel fungicide quinofumelin, Pyricularia oryzae class II dihydroorotate dehydrogenase.” Journal of Pesticide Science 47 4 (2022): 190–196.
[2] Norikazu Higashimura, Shinichi Banba, Akira Hamada. “Novel fungicide quinofumelin shows selectivity for fungal dihydroorotate dehydrogenase over the corresponding human enzyme.” Journal of Pesticide Science 48 1 (2023): 17–21.
[3] Stephane Jeanmart . “Synthetic approaches to the 2015–2018 new agrochemicals.” Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 39 (2021): Article 116162.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
Supplementation with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate monohydrate can synthesize neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, maintaining a healthy nervous system.....
Nov 4,2025Biochemical EngineeringSilver typically has a +1 charge when involved in an ionic bond. Although silver can form both +1 and +2 cations, the +2 is so rare that we usually name Ag + as silver ion, not silver(I) ion.....
Feb 18,2024Inorganic chemistry