The Versatile World of Ethyl Benzoate: Insights and Innovations in Chemistry
May 23,2024
Introduction
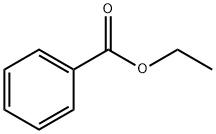
In the realm of organic chemistry, esters have always played a pivotal role due to their versatile applications across various industries such as pharmaceuticals, food, and cosmetics. Ethyl benzoate, a simple yet significant ester, exemplifies this versatility. Known chemically as C9H10O2, this aromatic ester, a derivative of benzoic acid, holds profound implications in the synthesis of fine chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and even in food flavoring, serving as a key ingredient that enhances both the quality and effectiveness of products. This article aims to provide a detailed examination of the synthesis, components, uses, and storage of ethyl benzoate, shedding light on its integral role in advancing chemical and industrial applications.

Figure 1 Characteristics of Ethyl benzoate
Synthesis of Ethyl Benzoate
The synthesis of ethyl benzoate is primarily conducted through the esterification of benzoic acid. This process involves the reaction of benzoic acid with ethanol in the presence of a strong acid catalyst such as sulfuric acid. The reaction follows the Fischer esterification mechanism, which is reversible. The key to maximizing the yield of ethyl benzoate involves shifting the equilibrium by removing water from the reaction mixture, either through the use of a Dean-Stark apparatus or by employing excess ethanol. Innovations in catalysis and process intensification continue to enhance the efficiency and environmental sustainability of this synthesis pathway.
Main Components
Ethyl benzoate, while a singular chemical compound, is characterized by its molecular constituents – an ethyl group (C2H5) attached to a benzoate group. The aromatic nature of the benzoate group contributes to the compound's solubility and reactivity characteristics, which are pivotal in its varied applications. This ester is typically clear, with a slightly oily texture and a sweet, floral aroma reminiscent of wintergreen or almonds.
Applications of Ethyl Benzoate
The applications of ethyl benzoate are remarkably diverse, reaching across multiple industries from pharmaceuticals to the food and beauty sectors. In pharmacology, ethyl benzoate is particularly valued as a flavoring agent to mask the taste of various medications, making them more palatable for consumers. This extends its utility to oral medicines, where taste can significantly influence patient compliance. In the realm of perfumery and cosmetics, ethyl benzoate's pleasant, slightly sweet scent reminiscent of almonds makes it a favored ingredient in perfumes and scented beauty products, enhancing the olfactory appeal of creams and lotions. Furthermore, its solvent properties are crucial in the synthesis of a broad array of organic compounds. This functionality makes ethyl benzoate indispensable in both research laboratories and large-scale industrial settings, where it aids in the production and refinement of complex chemical formulations. Its role is also expanding in the area of food flavorings, where it contributes to the aroma profiles of various edible products, demonstrating its versatile nature and the breadth of its applications in modern industry.
Storage and Handling
The storage of ethyl benzoate requires careful consideration to maintain its integrity and prevent degradation. It should be kept in a cool, well-ventilated area away from direct sunlight and heat sources. The ester should be stored in a tightly sealed and moisture-resistant container to prevent hydrolysis and the loss of aroma. Additionally, handling ethyl benzoate requires appropriate safety measures, including the use of gloves and eye protection to prevent irritation that can be caused by direct contact.
Conclusion
Ethyl benzoate serves as a cornerstone in the synthesis of a myriad of chemical products, showcasing its broad spectrum of utility in commercial and industrial applications. Its role in enhancing flavors, fragrances, and even pharmaceutical products underscores its importance in the chemical industry. As chemical processes evolve and demand for sustainable and efficient production increases, ethyl benzoate remains a topic of interest among chemical professionals, continually inspiring innovations in synthesis and application strategies. Through this deeper understanding, professionals are better equipped to optimize its use and contribute to advancements in their respective fields.
![]() References
References
[1]Attalah, Khalid M., et al. "Ethyl benzoate bearing pyrrolizine/indolizine moieties: Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of anti-inflammatory and cytotoxic activities."Bioorganic chemistry94 (2020): 103371.
[2]Yuan, Chao, Zhifang Lu, and Zhengyu **. "Characterization of an inclusion complex of ethyl benzoate with hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin."Food chemistry152 (2014): 140-145.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
Supplementation with pyridoxal 5'-phosphate monohydrate can synthesize neurotransmitters such as dopamine and serotonin, maintaining a healthy nervous system.....
Nov 4,2025Biochemical EngineeringDapagliflozin, has emerged as a pivotal player in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus.....
Nov 20,2024APIEthyl benzoate
93-89-0You may like
- Ethyl benzoate
-

- $1.00 / 1g
- 2025-12-19
- CAS:93-89-0
- Min. Order: 1g
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 1000kg
- Ethyl benzoate
-

- $0.00 / 200Kg/Drum
- 2025-12-18
- CAS:93-89-0
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 500mt/year
- Ethyl benzoate
-

- $45.00 / 1kg
- 2025-12-11
- CAS:93-89-0
- Min. Order: 1kg
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 100 mt