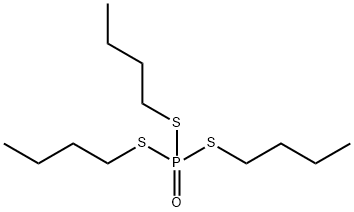
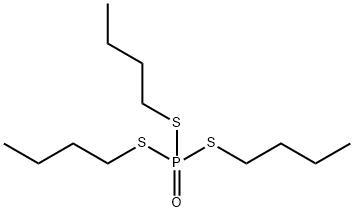
Toxicity of DEF
Jan 14,2022
DEF(1,2,4-Tributylphosphorotrithioate)is a cholinesterase-inhibiting organophosphorus pesticide compound used as a cotton defoliant that was registered in 1960.DEF is a colorless to pale-yellow transparent liquid with a skunk-like odor.It is completely miscible with n-hexane, dichloromethane, toluene, and 2-propanol and has an octanol–water partition coefficient of 3.31×105 at 25°C. DEF toxicity is primarily attributed to inhibition of various esterases, including acetylcholinesterase (AChE), butyrylcholinesterase (BuChE), neuropathic target esterase (NTE), and carboxylesterase, resulting in increased accumulation of endogenous acetylcholine (ACh) in cholinergic nerve terminals and related effector organs.
Use
DEF is an organophosphate chemical used as a cotton defoliant to facilitate mechanical harvesting. Recommended application rate is ~1–2.5 pints per acre per year applied as a diluted spray. Two products containing DEF as their active ingredient include DEF 6, manufactured by Bayer Corporation, and Folex 6 DC, manufactured by Amvac Chemical Co. Used for pest control in industrial agriculture (tends to be more toxic agents), organophosphates of low to intermediate toxicity are used to control ectoparasites on farm and companion animals and humans (head lice), and for home and garden pest control.
Environmental Fate
DEF is relatively stable in aqueous solutions (pH 5 and 7) up to 32 days but slightly degraded at pH 9 with a half-life of 124 days. The hydrolytic breakdown product of DEF is known as desbutylthio tribufos. DEF is stable up to 30 days in sandy loam soil exposed to natural sunlight, but degrades in aqueous solution upon exposure to natural sunlight for 30 days, with an estimated half-life of 44 days. The estimated soil adsorption coefficient (Kd) for DEF ranges from 60.6 for sandy loam soil to 106 for clay loam. The estimated soil adsorption constant (Koc) for DEF ranges from 4870 for silt loam to 12 684 for sand. DEF is highly persistent in soil with biodegradation half-lives of 745 and 389 days in sandy loam soil under aerobic and anaerobic conditions.
Based on water solubility, high soil adsorption, hydrolysis, and aerobic soil metabolism data, DEF is not identified as a potential groundwater contaminant. However, DEF is likely to become airborne following aerial application or ground spraying. Also, while DEF itself is not significantly volatile, its degradation product, n-butyl mercaptan (nBM), is volatile and accounts for a skunk-like odor near areas where DEF has been applied. DEF is also formed via release of the defoliant merphos, which undergoes rapid oxidation under environmental conditions to tribufos. DEF has a vapor pressure of 5.3×10-6 mm Hg at 25°C, suggesting its occurrence in both vapor and particulate phases in ambient atmosphere. Vaporphase DEF degrades by interacting with photochemically produced hydroxyl radicals; half-life for this reaction in air is estimated to be 5 h. Particulate-phase DEF gets removed from atmosphere by wet and dry deposition.
Mechanism of Toxicity
DEF is a relatively weak inhibitor of AChE. The compound is hydrolyzed to a large extent in the intestine to nBM, which is responsible for the late acute effects of DEF. The putative molecular target in neural tissue for initiation of delayed neuropathy is neurotoxic esterase or NTE. Metabolism proceeds by hydrolysis followed by methylation and successive oxidation of butylmercaptan, yielding the main metabolite (3-hydroxy)-butylmethylsulfone.
Several studies indicate that rodents metabolize and excrete delayed neurotoxic organophosphorus esters with great efficiency, whereas the adult chicken seems to have difficulty carrying out these processes. The feline (cat model) is intermediate between rodents and chickens. No human case of O-ethyl-O-nitrophenyl phenylphosphonothioate-induced delayed neurotoxicity has been reported despite the fact that it has been in use for over a quarter of a century. Some investigators propose that the cat may be a better model to extrapolate neurotoxicity results to humans.
Analysis of
the metabolism and residue levels of the defoliant S,S,Stributylphosphorotrithioate
in a goat model revealed that
majority of the metabolites were excreted in the urine,
although quantifiable amounts were recorded in the other
tissues (e.g., liver, kidney, muscle), milk, and feces. Major
metabolite was found to be 3-hydroxybutylmethyl sulfone,
and the two minor components in the urine were S,S-dibutyl
phosphorodithioate and S-butyl phosphorothioate.
- Related articles
- Related Qustion
DEET was first developed and patented by the US Army in 1946. It was approved for general public use by the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) in 1957 and was reregistered in 1998. It has been estimated that more than 1.8 million kg (....
Jan 14,2022Chemical pesticides ?Eugenol (C10H12O2) (CAS No:?97-53-0) is a volatile phenolic constituent of clove essential oil obtained from Eugenia caryophyllata buds and leaves.....
Jan 14,2022APIYou may like
1,2,4-Tributylphosphorotrithioate manufacturers
- 1,2,4-Tributylphosphorotrithioate
-

- $7.00 / 1KG
- 2020-03-16
- CAS:78-48-8
- Min. Order: 1KG
- Purity: 99%
- Supply Ability: 100kg